IoT technology is at the forefront of innovation. Paired with 5G technology, it’s transforming homes, cities, and even healthcare, making everything smarter and more connected. The IoT devices create a network that facilitates seamless communication and data sharing.
While IoT is a blessing, it can also cause severe security and privacy issues. Since these devices collect personal and sensitive data, it can result in severe consequences if they fall into the wrong hands. What makes matters worse is IoT developers spend less time securing these devices and more time on the functionality end. Blockchain in IoT technology offers a solution to this challenge by innovatively improving IoT security.
Consult top Blockchain development companies on Goodfirms to help you implement blockchain solutions to enhance IoT security, ensuring data protection against cyber attacks.
Understanding the Intersection of Blockchain in IoT Security
When IoT devices communicate with each other, traditional security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and authentication protocols are not good enough, especially when the scale and complexity of IoT networks are continually evolving. When compromised shared data makes its way into critical IoT devices, it may put the entire network at risk. That’s why there’s more focus on encryption protocols and cryptographic hash functions to ensure data isn’t tampered with.
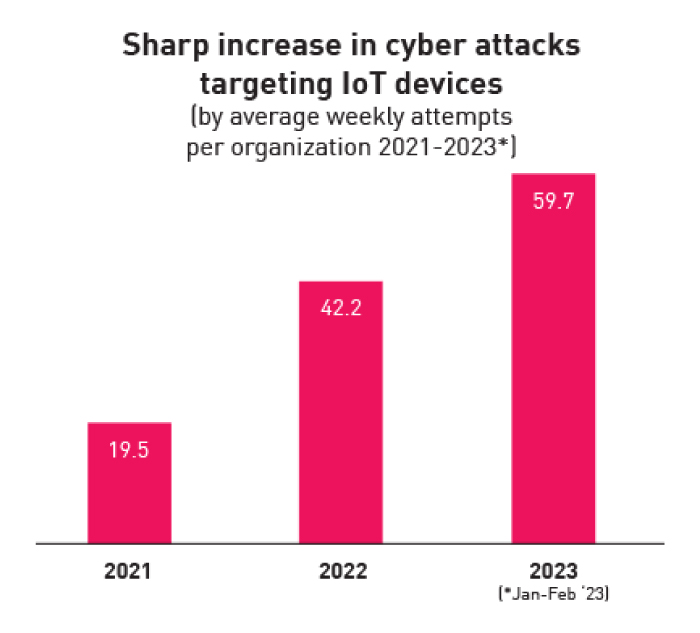
Check Point Research reports an alarming uptick in cyberattacks targeting IoT Devices.
Highlights:
- The first two months of 2023 saw a 41% surge in weekly attacks targetting IoT devices per organization compared to 2022.
- Every week, 54% of organizations face cyber attacks targeting IoT devices.
- IoT devices in European organizations face major attacks, followed by APAC and Latin America-based organizations.
IoT devices are known for their data privacy issues, which means hackers can steal sensitive data. The only way out is to adopt data encryption techniques.
IoT devices are also prone to attacks due to weak or nonexistent authentication practices. To address this issue, businesses must implement multifactor authentication, secure password policies, and ensure access control to secure networks.
That’s where Blockchain comes in - it tackles these technology challenges and fills those gaps.
Role Of Blockchain In IoT Security
Blockchain's decentralized nature records transactions in several computers, reducing the chances of a single point of failure. This feature makes blockchain a valuable tool for boosting IoT security.
Another great feature of blockchain is its immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed, creating a reliable record that cannot be played. Plus, blockchain's transparency means all participants can see the data, which builds trust among all devices and users.
Smart Contracts automate transactions between devices. When pre-defined conditions are met, these automated contracts execute on their own, ensuring secure operations within the IoT ecosystem.
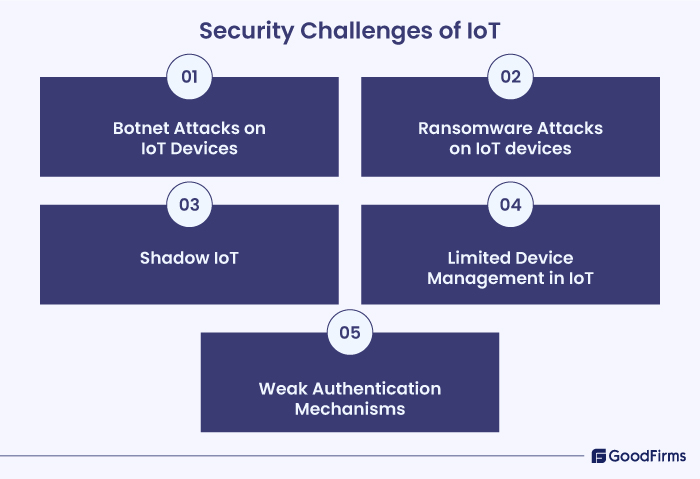
5 Major IoT Security Problems and How Blockchain Addresses Them
Here, we present 5 top IoT security issues and how blockchain mitigates them.
#1. Botnet Attacks in IOT Devices
A botnet is a group of privately held devices called “bots” connected to the Internet that hackers control remotely using a command and control (C&C) server.
The C&C server gives bots instructions to carry out an array of malicious actions like:
- Sending spam messages
- Launching DDoS attacks
- Stealing sensitive data like passwords or credit card numbers
- Mine cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Monero by using the processing power of infected devices
- Click fraud ads to improve the revenue of shady sites
- Purchase tickets more quickly than humans so that they can resell them at a higher price
The worst part? These bots can spread across different networks, infecting more devices.
A botnet is a group of privately held devices called “bots” connected to the Internet that hackers control remotely using a command and control (C&C) server.
Key Highlights about IoT botnets:
Vulnerability: IoT devices are often attacked as they have weak security features such as default passwords, obsolete software, and poorly maintained network settings.
Malware: "Botnet malware" infects multiple devices utilizing a command and control (C&C) server.
Common attacks: The most prevalent use of IoT botnets is launching DDoS attacks, in which a large number of infected devices overwhelm a target server with traffic, making it unavailable.
Popular example: The "Mirai" is a popular example of a botnet that targets IoT devices and the damage such networks can cause.
4-Step Blockchain Strategy to Secure IoT Devices from Botnet Attacks
Decentralized Security: Decentralized security is a huge benefit for blockchain. Since there’s no single point of failure, like centralized C&C servers, it’s much harder for hackers to take control of systems. Devices connect securely through a decentralized network, which makes forming botnets difficult.
Immutable Device Identity: Blockchain gives each device a unique, hack-proof identifier. This helps track and verify every action that an IoT device takes, which prevents compromised devices from integrating with botnets.
Autonomous Device Communication: IoT devices use smart contracts to share data securely without needing central control, reducing the risks of botnet attacks. Instead of relying on centralized servers, botnets follow the rules the blockchain sets, making them harder to form.
Distributed Ledger for Malware Updates: Leveraging Blockchain, IoT shares malware signatures or threat detection rules across all devices. This decentralized approach ensures all devices get the latest malware data, making it hard for hackers to tamper with the data. In traditional centralized systems, a single point gets attacked, while in this method, all devices stay updated and secure, offering an additional layer of protection.
#2. Ransomware Attacks in IOT Devices
Ransomware in IoT refers to situations where hackers control your smart devices, such as fridges, thermostats, or security cameras, and then demand that you pay some cash to get the access back. The hackers lock you out or make the device stop working until you hand over some money.
Key Highlights about Ransomware in IoT
Vulnerabilities: Hackers can deploy ransomware by exploiting IoT devices with weak passwords, outdated software, or insecure networks.
IoT Devices Lack Processing Power: IoT devices are lightweight and energy-efficient, so they lack enough processing power. This makes it difficult to execute strong security protocols like encryption and authentication for IoT devices like smart home appliances, wearables, and industrial controllers, making them vulnerable to ransomware attacks.
Impact beyond data encryption: Traditional ransomware simply encrypts data on a computer, while IoT ransomware can cause real-world issues like power outages, halting factory production, or malfunctioning medical equipment.

Ransomware in IoT refers to situations where hackers control your smart devices and demand that you pay some cash to get the access back.
Examples of IoT Ransomware Attacks:
Smart home ransomware: The user is locked out of his smart home when the hacker encrypts the control systems and demands money from the owner to regain access to heating, lighting, and security features.
Smart TV ransomware: Malicious actors can lock the TV screen and unlock it only when they are paid the demanded amount.
Smart thermostat ransomware: Hackers take control of the smart thermostat and set extreme temperatures, forcing the user to pay to restore normal temperature.
Connected car ransomware: Locking features like door access or navigation, exhorting money to regain functionality.
Industrial ransomware: Derailing the manufacturing process by taking over connected machinery, leading to production stoppages and financial losses.
3-Step Blockchain Strategy to Secure IoT Devices from Ransomware Attacks
Immutable Data Storage: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures tight data security. In other words, ransomware attacks cannot alter or encrypt the critical device data. In case an attack happens, blockchain could still maintain a secure, unchangeable backup of configurations and data. This ensures the data is not lost and can be retrieved without ransom payment, reducing the impact of ransomware attacks.
Decentralized Control of IoT Devices: Given blockchain’s decentralized feature, IoT devices are no longer controlled by a central entity that malicious actors can easily hack into and demand a ransom. Commands come only from multiple verified sources, ensuring only trusted entities manage devices.
Smart Contracts for Automated Recovery: Smart contracts are pre-equipped to execute predefined actions in the event of a ransomware attack. If a smart contract detects a rare behavior, it can restore the device data or functionality without requiring human action, preventing downtime.
#3. Shadow IoT
When unauthorized IoT devices connect to a network, it’s called Shadow IoT. This can include anything from employees’ devices to IoT sensors installed without following the standard security protocols. The big issue is that these devices bypass standard security measures, leaving the network open to attacks.
Key Points about Shadow IoT
Unauthorized devices: The IT department does not monitor these devices, which allows attackers to easily enter the network and steal data.
Security Issues: Shadow IoT devices lack strong passwords, encryption, and continual software updates, making them easy attack targets.
Data breaches: Shadow IoT devices inadvertently leak sensitive data, such as personal information or business secrets.
Botnet creation: Shadow IoT devices can create large botnets to launch malicious DDoS attacks.

3-Step Blockchain Strategy to Secure Network from Shadow IoT
Automatic Detection of Unauthorized Devices: Blockchain keeps a verified list of all authorized devices on a network. So, when an unauthorized device (shadow IoT) attempts to enter the network, the blockchain system detects and flags it using smart contracts, blocking access to unauthorized devices.
Audit Trail of Device Activity: Every translation and interaction recorded in Blockchain is irreversible, which helps maintain an audit trail for every device. This helps network administrators track when a shadow IoT device tries to enter the network.
Secure Device Authentication: Blockchain enforces strict cryptographic authentication for IoT devices. Shadow devices without proper cryptographic keys are denied network access, reducing the risk of breaches introduced by shadow devices.
#4. Limited Device Management in IoT
Limited device management in IoT refers to a situation whereby the capacity to monitor, update, and control connected devices is limited due to factors such as low processing power on the device, weak network connectivity, or lack of dynamic management platform features, which makes managing a large number of IoT devices within a system difficult.
Key Highlights of Limited Device Management in IoT:
Management Platform Limitations:
Basic Configuration: Only with basic features devices fail to make changes as per requirements.
Poor scalability: As the number of IoT devices increases, managing each device becomes time-consuming and inefficient, resulting in provisioning, configuration, and monitoring issues. In provisioning, in the absence of scalable tools, not every device can be perfectly set up, as there can be inconsistencies and delays. Configuration management can be complicated as the same configuration has to be repeated for an extensive network of IoT devices. However, with limited device management, the repetitions won’t be free of vulnerabilities, performance issues, and downtime.
Irregular Updates: Software or firmware updates are difficult as they have limited processing power, increasing security risks.
Minimal Monitoring: The collection of real-time data from devices is limited, which slows down proactive troubleshooting and performance.
Low Computing Capabilities: IoT devices have limited computing capabilities and low processing power, which makes updating and configuration changes in large data volumes and running complex management software difficult.
Increase Vulnerability to Attacks: Limited device management can delay the patching of security vulnerabilities on devices, increasing cyber threats.
4-Step Blockchain Strategy to Secure IoT Devices from Limited Device Management
Distributed Firmware Updates: Blockchain enables secure and decentralized software updates in IoT devices, ensuring that devices with low processing capabilities are updated from trustworthy resources without centralized intervention.
Distributed Device Monitoring: WithBlockchain, continual monitoring and logging of device activities helps troubleshoot performance issues and perform predictive maintenance even as the network scales.
Smart Contracts for Automated Management: Smart contracts automate the provisioning, configuration, and monitoring of IoT devices. For instance, a configuration change in one device is automatically replicated across all devices using a smart contract, eliminating human intervention and error-prone processes.
Blockchain as a Trust Layer: Blockchain functions as a trust layer wherein every device securely verifies and authenticates with every other device in the network, enhancing overall security and management.
#5. Weak Authentication Mechanisms
Some IoT devices use common passwords, simple PINs, and their like that attackers can easily crack. They also lack proper authentication mechanisms, making it easier for attackers to gain access to sensitive data and critical functions.
Key Points about Weak Authentication in IoT devices:
Default passwords: IoT devices generally come with pre-set predictable passwords that attackers can easily exploit without cracking complex encryption.
Insufficient password complexity: Simple passwords are allowed. Strong passwords that use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters are not enforced.
Lack of multi-factor authentication: Additional verification steps beyond password are not required, leaving devices vulnerable to attacks.
There is no proper device registration process, so there is no mechanism to verify and register new devices on a network, thereby allowing unauthorized devices to connect to a network.
Limited encryption capabilities: Weak or zero data encryption between devices, making information vulnerable to interception.
7-Step Blockchain Strategy to Secure IoT Devices from Weak Authentification
Decentralized Authentication: Blockchain assigns each IoT device a unique cryptographic identity. These identities are securely verified via smart contracts, reducing the need for easily guessable credentials.
Immutable Credential Management: Blockchain can enforce strong credentials through passwords and encryption keys and even track changes, ensuring accountability and using complex, hard-to-guess passwords.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) via Smart Contracts: Implement smart contracts that ensure multi-factor authentication for any IoT device trying to access sensitive data or vital functions and ensure that only credible entities gain access.
Secure Device Registration and Onboarding: Identity and ownership of the IoT devices are cryptographically verified before allowing network access. This ensures that any unregistered or unauthorized devices are automatically blocked.
End-to-End Encryption via Blockchain: End-to-end encryption through Blockchain enables the exchange of encrypted data between IoT devices while maintaining an immutable log of all interactions on a distributed ledger, which makes it difficult for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities in communication channels.
Automated Security Updates: IoT devices receive automatic updates and security patches through the blockchain network, reducing the risk of outdated, vulnerable authentication mechanisms.
Audit and Accountability: A distributed blockchain ledger keeps track of all authentication attempts, including successful and failed attempts, giving a clear audit trail for monitoring and mitigating security incidents.
Wrapping Up
Blockchain in IoT addresses key security challenges such as botnet attacks, ransomware, shadow IoT, limited device management, and weak authentication mechanisms. By decentralizing control, providing data immutability, and leveraging smart contracts, blockchain creates a hack-free infrastructure for IoT devices.
As IoT networks expand and become more interconnected, the security risks also grow. Blockchain’s ability to distribute trust, automate processes, and maintain transparency provides an essential foundation for safeguarding IoT networks. This blend of technologies can elevate IoT security, ensuring safer, more reliable, and resilient ecosystems that drive smarter homes, cities, and industries forward.