Accuracy is of paramount importance in making business choices. Flawless manufacturing productivity and exceptional customer service require accurate and up-to-date inventory information. Faulty processes, voluminous transactions in inventory, wrong data entries, misplacement of inventory, and insider theft are a few of the many reasons responsible for the mismatch between inventory records and the actual stock in hand. While it is essential to rectify these inaccuracies, it is also crucial to keep businesses running smoothly. In short, businesses need to audit inventory with minimum disruptions to daily operations.
It can be achieved through the cycle counting method of inventory verification. It is a popular sampling technique that regularly counts small amounts of stocks in a specified time without disturbing the overall stock operations. The cycle count process fixes the discrepancies between inventory records and the stock units on the shelves. This article will provide you with the critical information and essential aspects you need to know about the cycle counting process.
What is Cycle Counting?
Cycle count is an incremental method of counting inventory to keep a tab on inventory levels more accurately. It works by physically counting a small portion of an inventory throughout the year with an objective to count each stock unit at least once. Generally, it is performed by trained 'warehouse counters' who keep counting stocks without disturbing daily operations. The counters create a system to easily transit inventory through the warehouse maze even when counting is under process.
Why Is Cycle Counting Essential To Maintain Inventory Accuracy?
For product-based businesses, accurate inventory count is essential to reconcile physical stock with recorded inventory quantities. To achieve the inventory accuracy, the physical inventory count should match the official inventory records. Although, companies cannot completely nullify all inventory errors but can improve the error eradication rate significantly with the cycle counting process.
How does it work?
For audit purposes, businesses have to match the cost of inventory on books with the value of inventory in the warehouse, while for operational purposes, they need to match the count of inventory on books with actual units held in the warehouse.
There are two methods to achieve this.
- Physical count of the entire inventory (once annually)
- Cycle Counting (continuous throughout the year)
Physical counting of entire inventory (Annual Inventory Count)
A physical verification or physical counting of the entire stock is a comprehensive exercise requiring a trained workforce, vast resources, and complete pause on operations. The operations in a warehouse facility are stopped to count all items at one time. Therefore, a physical inventory count is not always feasible. Moreover, any glitch at the end or unsolved inaccuracies can lead to a futile counting exercise (without solving the actual pain points).
Cycle Counting
Cycle counting mitigates the issues of the entire physical counting method. Cycle counting adopts a unique strategy of counting only samples or selected inventory on an ongoing basis. It counts the most fluid stocks on a priority basis. The cycle count procedure is less disruptive to daily operations. You need not halt the entire warehouse operation, and only the part of the warehouse where the cycle count is being executed has to be put on hold. Even if the entire inventory count process is faulty, it gets detected in the sample count.
Why Is Cycle Counting Better Than The Physical Counting Of Entire Stocks?
While smaller warehouses, retailers, small store owners, and distributors can conduct a physical count of the entire inventory after business hours or by limiting business hours for a few days, large-scale businesses with a huge inventory pile, offering 24/7 services, have to use the most optimum method for their inventory audit.
Fortunately, cycle counting provides the right solution . Another difference between annual inventory count and cycle counts is that the former method is used for projecting the financial value of inventory on a given day of the year, whereas the latter is a method to maintain the IRA (Inventory Record Accuracy) high rate throughout the year. According to a study by the RFID Journal (2025), companies adopting RFID-enabled cycle counting improved their inventory accuracy from an industry average of ~65% to over 93%, while also reducing stockouts and overstocking issues.
(IRA) Inventory Record Accuracy and Tolerance Goals
Once you have conducted cycle counting and have derived significant conclusions regarding error causes, you can calculate the accuracy rate for inventory. You should consider a realistic number in mind for your inventory error tolerance. It is possible that the physical count and the inventory records do not match precisely for every item, and there will be a reasonable tolerance. The formula for counting accuracy is:
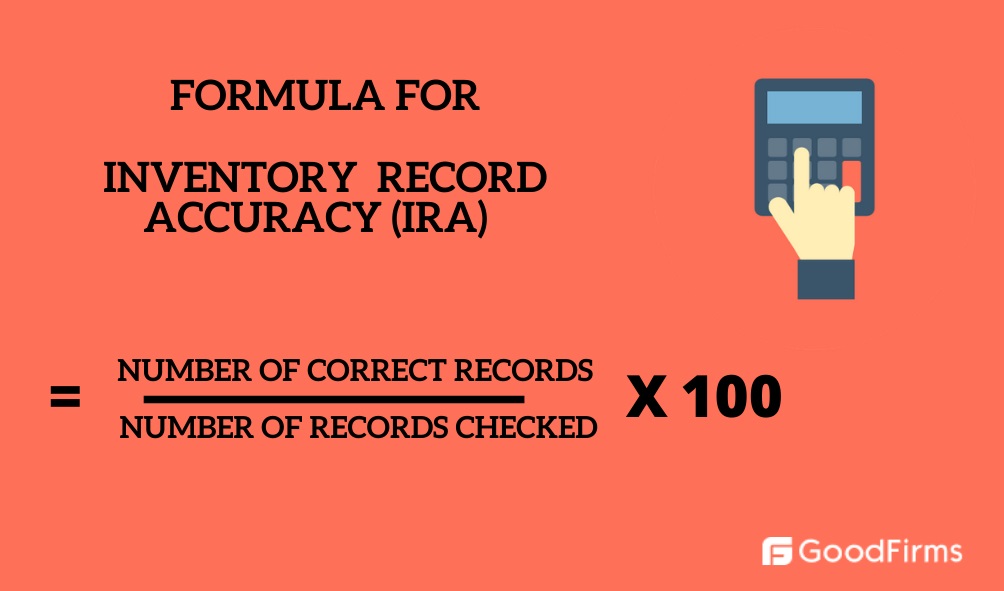
What Should Cycle Count Achieve For Your Inventory Management Goals?
Cycle Count process should:
- Identify the causes of inventory errors and discrepancies.
- Pay priority attention to a higher value and high mobility products.
- Achieve accuracy in the process with timely corrections of inventory miscounts
- Keep the stock levels appropriate.
- Increase workforce capacities, improve product flows, and increase inventory management efficiency.
- Periodically check different sections of inventory throughout the year and keep inventory records accurate for meeting regulatory compliance and financial audit
- Replace the comprehensive end of the year annual physical countwith smaller counts on a continuous basis.
- Alleviate the need for a complete shutdown of operations
- Ensure the inventory figures reported on the balance sheet are accurate.
- Enable data-driven decision-making by integrating cycle counting results with inventory management software and ERP systems.
- Support demand forecasting and supply chain planning by providing more accurate, real-time inventory visibility.
- Reduce losses from shrinkage, theft, or misplacement through frequent checks and faster anomaly detection.
- Facilitate smoother adoption of automation technologies (e.g., RFID, IoT sensors, drones) for more efficient warehouse operations.
- Enhance customer satisfaction by minimizing stockouts and ensuring product availability.
Benefits Of The Cycle Counting Process For Inventory
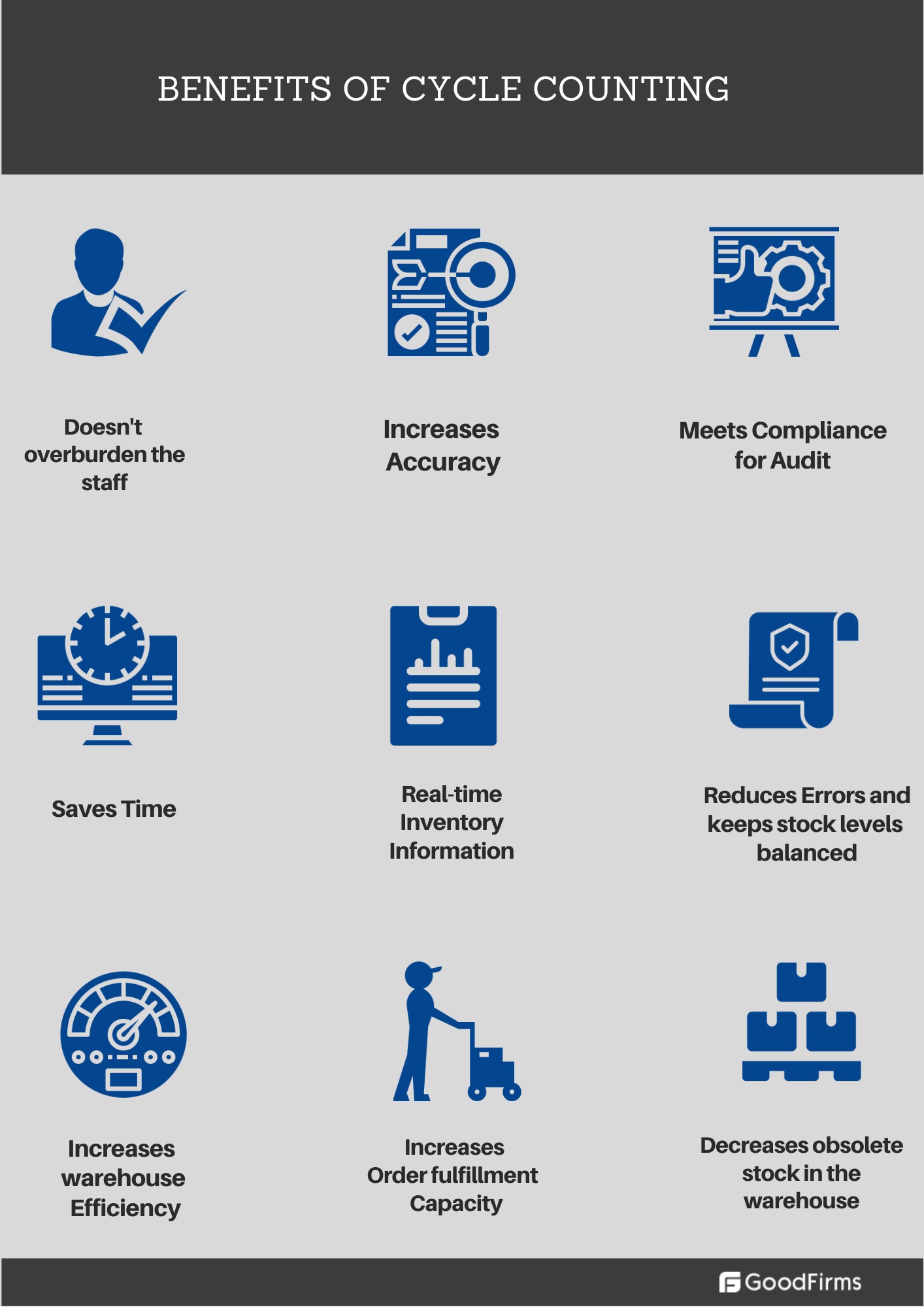
- Inventory is a large and valuable number on the balance sheets of companies. Physical inspection of inventory is therefore essential for maintaining reliable financial records. Cycle counting keeps the number accurate, and therefore, investor trust remains intact.
- Cycle counting is shorter in duration, and therefore, it doesn't overburden the staff as at the end of the year physical inventory count.
- Accurate inventory data is essential to maintain the manufacturing levels balanced. Cycle counting keeps manufacturing and sales operations smooth and without interruptions. Your sales department, retailers, distributors, stores, etc. don’t have to face the stock-out issue.
- Missing stocks can cause warehouse chaos and mismanagement. It is a waste of time to look for missing items. It's a quick process for error detection and reporting of inventory count. Cycle counting gives faster insight into breakdowns in shipping, complex inventory transactions, and process issues.
- Any order fulfillment requires a sufficient number of physical stock in the warehouse. If record books and physical items mismatch, then it may halt the order fulfillment process. Cycle counting improves your ability to fulfill orders. Cycle counting allows smaller batches of products and therefore causes no backlog of orders.
- A strong distribution strategy, multi-location management, and supplier management depend on how robust the inventory management is.Cycle counting acts as a guide for stocking and distribution decisions.
- It mitigates excess inventory carrying costs and decreases the amount of obsolete stock in the warehouse.
- Improves audit readiness by maintaining accurate, real-time records that meet regulatory and compliance requirements.
- Supports digital transformation initiatives by integrating with RFID, IoT, and AI-powered inventory management tools.
- Enhances sustainability by lowering waste from overproduction and expired inventory.
- Provides better forecasting data, enabling smarter procurement and supply chain planning.
Types of cycle counting methods
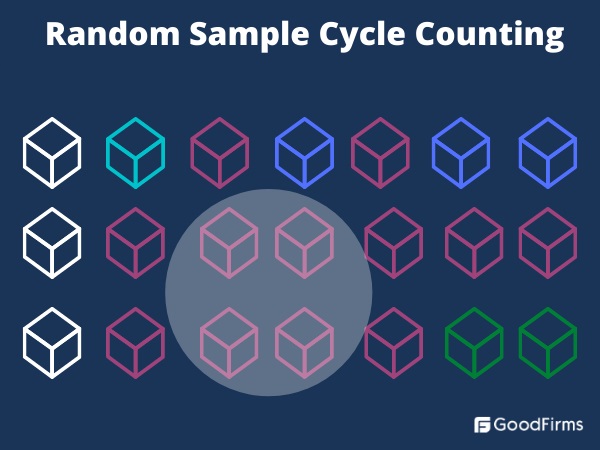
1. Random sample cycle counting
When there are multiple items in a warehouse in vast quantities, certain stock units and specific categories can be counted using a random sampling method. Random sample cycle counting is conducted every day for several days to cover all item categories over time.
Inventory managers can use two types of methods to do a random sample cycle count:
The first method is diminished population counting, where a certain number of items are counted randomly and then excluded from the next counting sessions. This process is carried out until samples from all items are counted at least once.
The second one is constant population counting, which involves counting the same items again frequently. However, as the selection of items is random, inventory managers may end up counting the same inventory multiple times, and some other stock may be entirely excluded from the counting process.
2. ABC cycle counting
ABC cycle counting is a popular cycle counting method where the stocks in the warehouse are categorized into 'A,' 'B,' and 'C' variants. This method is also known as Pareto Analysis. Pareto analysis is a process of organizing thoughts and delivering structured solutions. It is based on the principle that 80% of the impact is caused by 20% of the elements in a group. Therefore, more focus is required for the elements that cause maximum impact.
When applied to inventory counting, ABC is a kind of product category where A is the product that brings maximum revenue, and while B is moderately important products with steady but lower sales compared to A. And C are comparatively slow-selling products with lower margins and low-revenue. The ABC cycle counting process gives more importance to strategically important items and counts them more frequently than others. This classification is based on various other factors related to individual stock categories:
- Inventory turnover ratio for particular stocks
- Annual revenue from the stock category
- Frequency of sale
- User demand and Consumption
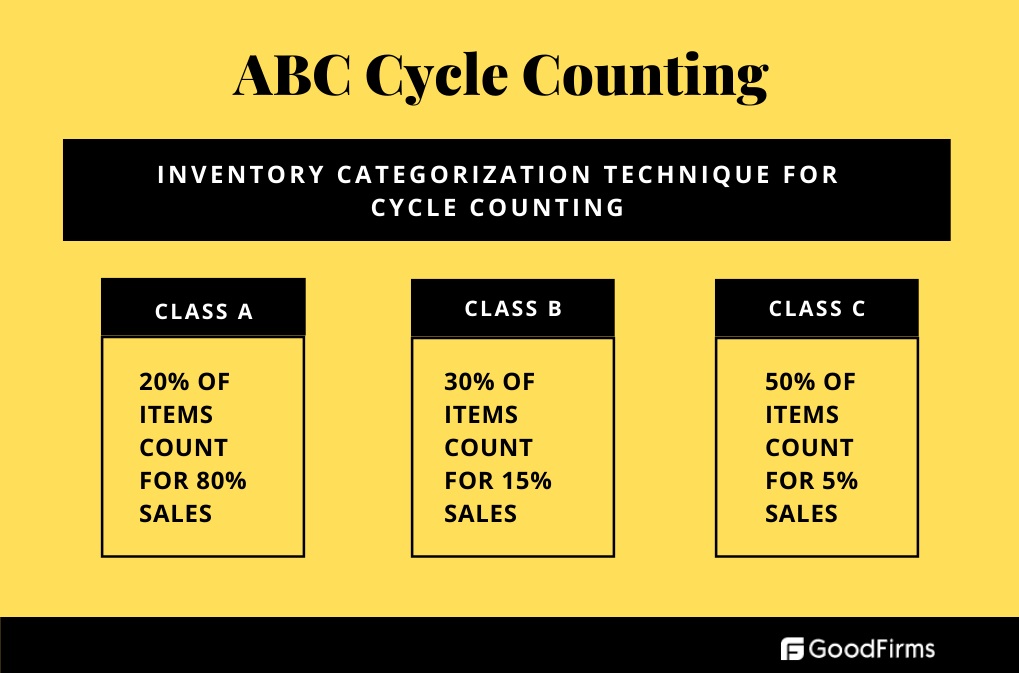
There is no fixed number for counting items in the three categories. However, a typical process has a frequency of six counts for item category 'A,' two counts for category 'B,' and one count for category 'C.' While ABC analysis is useful in managing inventory management's financial aspect by focusing on high-worth goods, it can lead to delay in shipments of items in the class 'C.'
Example of ABC cycle counting:
Suppose a company has established the ABC category for its inventory which is:
A items = 20, 000 unit,
B items = 75,000 unit,
C items = 1,20,000
Total Items=2,15,000
Calculate the number of counts required per day:
The company’s policy is to count A items every month (25 working days), B items every quarter (75 working days), and C items every six months (150 working days).
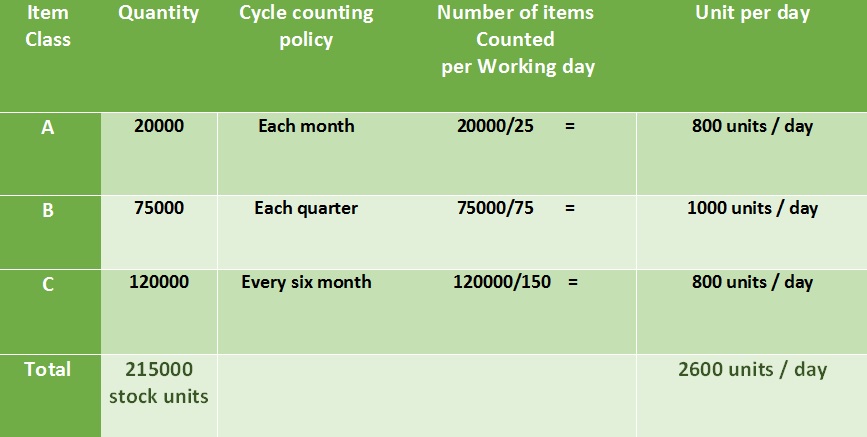
By adopting cycle counting and ABC analysis, the organization will have to count only 2600 items per day rather than undertaking the yearly count of 2,15,000 items in one go.

Other Methods:
Location-based cycle counting
Location-based cycle counting focuses on a selected area to count the inventory. It treats all items equally. This method divides the warehouse into sections, and inventory in every location is counted for a regular interval. One drawback of the location-based cycle counting is if the item has been moved, it will not get registered. Another drawback of this cycle counting method is that the financial value of items is not given any importance while conducting location-based cycle counting.
Opportunity based cycle counting
The opportunity based cycle counting reserves the counting process only for key events. Cycle counting is scheduled whenever a significant activity happens in the organization. For example, when a company receives large orders, reorders, order cancellations, stocks falling below the necessary scale, etc.
Hybrid Method
The hybrid method uses two or more methods for cycle counting. This approach utilizes the pros of multiple methods and eliminates the drawbacks of individual methods to achieve the maximum possible efficiency in cycle counting.
Transaction based cycle counting
The transaction-based cycle counting method relies on counting the stocks after a fixed number of transactions with that particular category.
Process control cycle counting
The process control cycle counting method considers only the items that are easy to count. Process control cycle counting is practically a faster and feasible option that requires less time and effort to count.
Automated cycle counting
The automated count cycle method works by scanning a barcode on the products. A barcode scanner reads the barcode information, and the data is synchronized in real-time by the central computer system. A barcode scanner, connected mobile or computer devices, barcode labels on items, inventory software, and barcode printers are used for this process.
Modern Cycle Counting Process:
The modern cycle counting process has evolved with the integration of AI and ERP systems to automate ABC classification. AI algorithms continuously analyze sales velocity, profitability, and demand patterns to dynamically categorize items into A, B, or C classes. High-priority items (Category A) are counted more frequently, while slower-moving items (B and C) are counted less often, though their classification can automatically change as demand fluctuates. This dynamic approach ensures high inventory accuracy, optimized labor allocation, and efficient stock management. Integration with RFID and IoT sensors allows real-time updates of stock movements, reducing manual errors and improving inventory record.
Reasons for errors in inventory count records:
- Location-related errors:
- Poorly marked location, missing location mark, placing items in the wrong spot, no location coding, etc. cause inventory count blunders.
- Errors in stock keeping labels: Unclear, misprinted, and duplicate labels may confuse, and the inventory can be misplaced.
- Employee errors: Wrong input of data, stock theft, undocumented item sale or purchase, poor handwriting, distractions such as overuse of social media, mobile phones, etc. are also significant reasons for inventory-related errors.
- Technical errors: Software glitches, device malfunction, faulty scanners, etc. can cause significant inventory errors.
- Process errors: Shipping errors, delayed dispatch, complex processes, unclear SOPs, poor workflows, over-ordering, etc.
- Storage related errors: Poor space, insufficient storage capacity, storage full, etc.
- Automation gaps: Even with warehouse management systems (WMS), errors can occur if automation tools RFID, IoT sensors, or AI-driven platforms are not properly calibrated or maintained.
- Cybersecurity risks: Inventory systems increasingly face cyberattacks and data breaches, which can alter or corrupt inventory records.
- Integration challenges: Businesses using multiple systems ERP, e-commerce, and logistics platforms may often face synchronization errors, leading to mismatched data across channels.
How does cycle count your inventory effectively?
For effective cycle counting, a well-planned approach and checklist should be kept handy. Below guidelines and practices can help you in standardizing your cycle counting process:
Guidelines:
- Collect historical inventory data and previous error records for better insights into probable discrepancy zones
- Distribute the counting related tasks to each staff member with proper guidelines and counting equipment
- Establish protocols, make schedules, make SOP for accurate tracking and management reporting.
- Get prior inputs, feedback, and suggestions from auditors and be clear about auditing requirements.
- Update and audit your digital records before the cycle count.
- Set up a system to track the key metrics.
- Prepare the warehouse for cycle count by stopping order picking and stock movement in the area chosen for inventory count.
- Create a count sheet and add all items and their categories to the sheet.
- Perform cycle counting first on high-value, high-volume goods using the methods discussed in the article. Choose the appropriate cycle counting model based on your requirements
- For goods that cannot be physically counted, consider weighing them on standard scales. (for example nails)
- Leverage automation tools such as RFID, drones, and AI-powered scanners to speed up cycle counting and reduce manual errors.
- Integrate cycle counting directly with ERP/WMS systems for real-time updates and better synchronization across supply chain channels.
- Use predictive analytics to identify high-risk areas for discrepancies and schedule cycle counts more strategically.
- Apply mobile apps or handheld devices with barcode/RFID scanning to digitize the counting process and eliminate paperwork.
Best Practices:
- Cycle counting should be a part of the daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly operations of your business.
- The location designated for cycle counting should not see the addition or removal of stocks until the process is completed.
- Inventory accuracy can be increased by increasing the cycle count frequency. Therefore, aim to count inventory as many times as you can.
- You should not add or modify the digital inventory records during the cycle count process.
- Focus on counting only one category at a time.
- Select a specified time for cycle count, inform the people in the warehouse before the scheduled count to ensure their normal operations and workflow doesn't get disturbed.
- Consider seasonality of products, peak times, and events that cause a surge in demand in mind before conducting the inventory count process.
- Eliminate the source of errors to alleviate the discrepancies of similar types in the future.
- Ensure that you define and document your cycle counting process thoroughly using a reliable inventory record system for it.
- Adopt mobile apps, handheld RFID scanners, or AI-powered tools to digitize the counting process and minimize manual errors.
- Use predictive analytics to schedule cycle counts for high-risk items or locations where discrepancies are most likely.
- Incorporate cycle counting into compliance and audit frameworks to meet regulatory and financial reporting requirements.
- Leverage automation technologies such as drones and IoT-enabled smart shelves to improve counting efficiency in large warehouses.
List of items/staff required for performing cycle counting:
Retailers, large manufacturers, and eCommerce businesses who need to count inventory without closing their facilities or stores can partially count the merchandise continuously using the cycle count process. However, they need certain items and trained staff to do this activity efficiently. Below is the checklist:
1. Staff
A well-oriented staff that knows how to count inventory and enter it digitally is required for accurate inventory counting. You can also hire professionals and experts known as ‘counters’ to do this job.
2. Stock-list
A complete list of selected stocks for cycle counting should be kept handy.
3. Counting tools and material
Arrange the tools required for cycle counting in advance. You will need a pen, paper, digital devices, barcode scanners, cameras, stockroom maps, or RFID handheld readers etc.
4. Inventory counting system
The inventory counting system is required to manage, organize, and streamline the entire cycle counting process.
5. Automation Tools
Businesses can also include RFID tags, IoT-enabled smart shelves, and drones in warehouses to automate parts of the cycle counting process.
6. Mobile Applications
Businesses can integrate mobile apps with ERP/WMS allowing staff to input data in real time, eliminating paperwork and reducing errors.
7. AI & Analytics Support
Businesses save both time and resources, can adopt AI-powered analytics tools to predict high-risk areas for discrepancies and recommend cycle count priorities.
Importance of Warehouse layout and Organized inventory keeping for Cycle Counting:
While all the above practices and tactics can make you an expert in cycle counting, poor warehouse management can fail your cycle count process terribly. If your warehouse is a mess and your inventory is poorly located then cycle counting can become a stressful exercise.
See the below example of two companies A and B:

While Company A had its inventory organized and therefore the time taken for counting one SKU is just one min, Company B takes 3 mins to count the same as their inventory is found unorganized and at multiple locations.
This shows how important it is to keep the warehouse layout and inventory organized for efficient cycle counting and saving workforce hours. Cycle counting can be made hassle-free if you have a well-structured warehouse and an organized inventory management system.
Inventory Management System and Cycle counting
The procedures and methods of cycle counting inventory can yield better results with inventory management tools and automated processes. Warehouse management systems offer advanced capabilities for intelligent cycle counting. Human errors can be eliminated by implementing inventory management software with multifaceted capabilities for computation and reporting. Inventory cycle count is not an independent function, and multiple variables play together in achieving cycle count optimization. The software also helps by sending automatic prompts for counting specific items.
Inventory systems and digital solutions help in streamlining other processes such as stock locating, order allocation, replenishment, electronic identification system, shipping, product serialization, and many more. An inventory management system can also be very helpful in determining ABC product categories automatically. The AI-powered WMS now uses predictive analytics to detect anomalies and schedule cycle counts proactively before discrepancies escalate. Businesses are also increasingly implementing IoT-enabled smart shelves and drones in large warehouses to automate cycle counts and reduce reliance on manual staff.
Inventory management systems are essential in specific industries where inventory cannot be touched. For example, in the medical and chemical industries, the inventory management system integrates with counting devices and Radiofrequency devices to update inventory count without physically touching the inventory.

Conclusion
Inventory management software takes care of all variables of cycle count, such as the scope of the count, count frequency, item location, item categorization, etc. To know more about inventory management software's pricing and detailed features read our Buyer's guide for Inventory Management system. With the integration of technologies such as inventory management software, you can conduct complex inventory processes such as cycle counting efficiently and achieve inventory accuracy goals easily.








