Blockchain, which is also known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), makes the record of any digital asset transparent and unalterable. The technology uses a decentralized network and cryptographic hashing. It is considered a revolutionary technology as it reduces security risks and brings transparency in a scalable manner. It was first brought into the limelight with a cryptocurrency called Bitcoin, but it can be applied in diverse domains.
Blockchain technology is used in supply chain management, healthcare, data management, and law enforcement.
In other words, blockchain technology is here to stay and will increasingly be adopted by several organizations across the globe. Blockchain technology has taken security and transparency in operations to an unprecedented level. As a result, businesses are hiring top blockchain development companies in the UK to utilize the technology to increase productivity and improve customer service.
However, there are some misconceptions regarding the technology and its uses. This blog will discuss the 7 most common mistakes made while using Blockchain technology.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
There are three important concepts for proof-of-work blockchains: blocks, nodes, and miners.
Block: Every chain consists of several blocks, each with three basic elements, which include Data in the block, nonce, and hash. Nonce, "number used only once," is randomly generated when a block is created. A Hash is a number permanently attached to the nonce.
Nonce generates the cryptographic hash when the first block of a chain is created. Data in the block is considered signed and remains tied to the nonce and hash unless it is mined. A miner creates new blocks on the Blockchain via a process called mining. As every block has its unique nonce and hash and references the previous block's hash in the chain, it is challenging to mine a block, especially on large chains.
Miners use specialized software to solve the complex mathematical problem of finding a nonce that generates an accepted hash. The nonce is 32 bits, and the hash is 256, so approximately 4 billion nonce-hash combinations must be mined before the correct one is found. When this happens, miners are said to have seen the "golden nonce," and their block is added to the chain.
Changing previous blocks requires re-mining the blocks with the change and the earlier ones. This makes it extremely difficult to manipulate blockchain technology since finding a "golden nonce" requires enormous time and computing power.
A blockchain is decentralized, as no computer or organization owns the chain. It is a distributed ledger through the nodes connected to the chain. The nodes can be any electronic device that maintains copies of the chain and keeps the network functioning. Every node has its copy of the chain, and the network has to algorithmically approve any newly mined block for the chain to be updated. Each participant is allotted a unique alphanumeric identification number showing their transactions. Thus, combining public information with a system of checks and balances creates trust and security.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
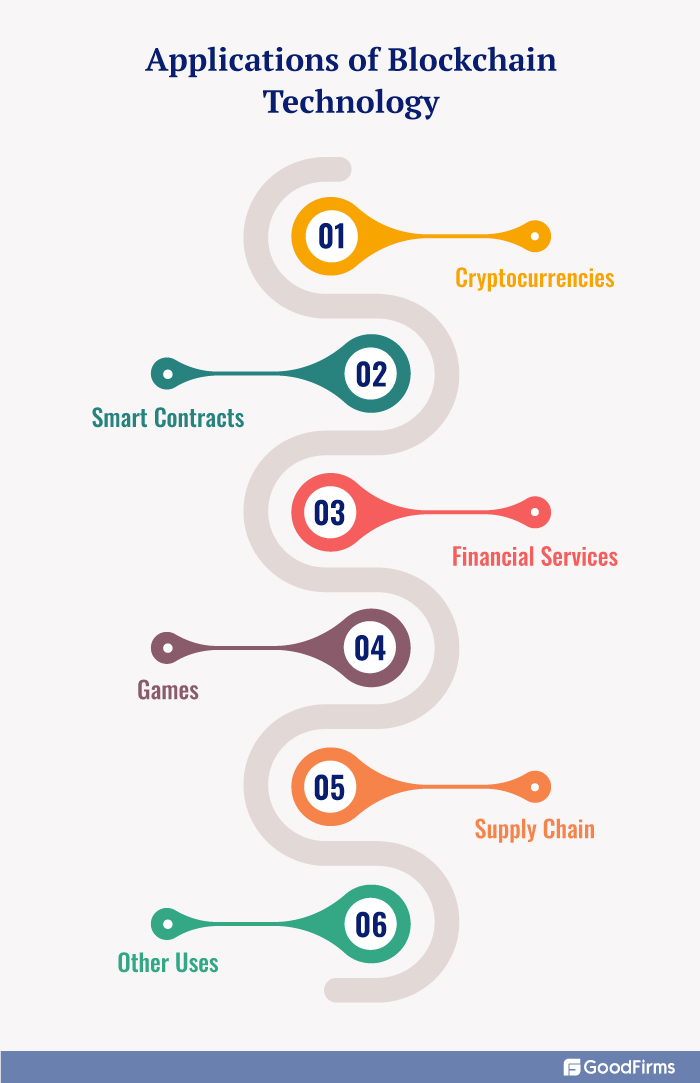
- Cryptocurrencies: The Bitcoin network and the Ethereum network are both based on the Blockchain
- Smart Contracts: These are proposed contracts that get partially or fully executed when certain conditions are met.
- Financial Services: Banks are interested in using distributed ledger technology to cooperate with companies.
- Games: Bitcoins and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are used in video games for monetization.
- Supply Chain: Blockchain technology is used in Supply Chain Management.
- Other Uses: It can be used in domain name services, peer-to-peer insurance, and distributed ledgers.
Top Countries in Blockchain Development
Canada
There are over 200 blockchain companies in Canada with over 1500 workers. Toronto and Vancouver are the two cities that have led the way in blockchain solutions. The majority of the firms are into cryptocurrency, fintech, or consulting.
Australia
With the blockchain industry constantly evolving, the Australian ecosystem is also making rapid strides. Australia is positioning itself to take full advantage of the economic benefits associated with blockchain technology. The government also supports this cause by investing in Blockchain technology in Australia.
India
Blockchain technology companies in India mainly operate in the banking and financial services sector. Many corporations are adopting blockchain technology to improve effectiveness and add value to their services. The government also increasingly uses blockchain technology for land records, healthcare, insurance, and other services.
Interesting Statistics on Blockchain Adoption
- Global spending on blockchain solutions was projected at USD 6.6 billion in 2021(Statista)
- Cross-border payments and settlements were the most significant use case in 2021(Statista)
- Bitcoins are the market leader in cryptocurrency in terms of price index & capitalization(Statista)
- In 2021, China was the largest owner of blockchain technology patents(Statista)
Mistakes Made While Using Blockchain Technology
There is no doubt about the increasing interest in blockchain technology and its applications. However, many blockchain projects do not see the light of day due to misconceptions regarding the technology and mistakes made by the developers. So, companies still experimenting with technology must watch out for these mistakes and take a proactive approach. This blog discusses seven common mistakes that should be avoided at all costs.
Mistake#1: Not Making the Most of Blockchain Protocols
The primary application of Blockchain in enterprises is decentralized ledger technology. However, the biggest mistake is ignoring other features of the Blockchain, like Smart Contracts, tokenization, and decentralized consensus, which are hardly used in projects. The most common reason for this is the confusion regarding protocols. Developers assume Blockchain is a comprehensive application that lets them develop solutions according to their requirements. However, it should be used as a protocol for integrating required functionalities into an application solution.
Organizations are not using all the features provided by Blockchain Technology, raising the question of whether they really need this technology. Before making the decision to use Blockchain technology, professionals should carefully study possible use cases of the technology in their organization. Clarity on the objective of the Blockchain Use Case helps in a seamless transition into projects that will use a wide range of Blockchain features.
The most common reason for limited awareness of blockchain functionalities for different use cases is a lack of protocol clarity. In fact, if enough people are aware of the proper protocol, the technology can be widely used in logistics and healthcare in various ways.
Mistake#2: Considering Blockchain Only as a Storage Mechanism
The application of Blockchain for secure information exchange and storing records leads to many wrong beliefs. CIOs get confused between Database Management Systems (DBMS) and Blockchain. The existing blockchain platforms cannot support complex data models or assure high throughput or low latency. They were built to provide an immutable, authoritative, and trusted record of events among a dynamic assortment of unrelated stakeholders. The technology is not scalable yet, as each node on the peer-to-peer network receives a copy of the distributed ledger after each update; as the chain grows, performance slows.
Blockchain does not focus on the complete "Create, read, update, delete" model. This is the central point of difference between Blockchain and DBMS. CIOs should not make the mistake of considering blockchain technology as a superior alternative to traditional database management solutions. It should be seen only as a "Write-Once, Append-Many electronic ledger, and a conventional DBMS may be a better option in many cases.
Mistake#3: Smart Contracts Can Currently Replace All Paper-based Legal Contracts
A smart Contract is a code that automatically executes legally relevant events and actions that are part of the agreement. The leading utility of Smart Contracts is to reduce the need for trusted intermediaries, prevent fraud, and reduce arbitration costs. They are commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and are fundamental building blocks of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications. Smart contracts are not necessarily agreements approved by law, with some countries being exceptions.
Smart contracts are the most powerful application of new blockchain technology. They add dynamic behavior to transactions and can be understood as stored procedures linked to specific transaction records.
However, it is not a stored procedure in a centralized system. Still, it is executed by all nodes in the peer-to-peer network, which causes challenges in scalability and manageability that have not been addressed yet. The technology will undergo significant changes, so CIOs should not pursue full adoption but first run small experiments.

Mistake #4: Believing that Blockchain Governance Issues Cannot be Solved
In a Private Blockchain, governance is handled by the Blockchain's owner. A supply chain consortium may have several members; the originating firm is generally in charge of onboarding, verifying financial information, and resolving disputes.
Blockchain governance issues are primarily significant on public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These issues are mostly technical in nature, and the lack of focus on resolving them demotivates companies from investing in Blockchain projects.
However, governance issues can be resolved when large companies in the blockchain ecosystem take the necessary initiatives to develop groups to establish governance models. The collective consensus among large enterprises can help improve the credibility of the governance models, resulting in the resolution of governance issues. These conflicts or governance issues can pose significant challenges to a project's success, even if the technology being used is secure and stable.
Mistake #5: Blockchain is Ready for Large-Scale Production
Blockchain can have a wide array of applications across several diverse industries. Many of the current products in the blockchain landscape overlap with similar features, and some complement each other. Start-ups with venture funding are developing several blockchain projects.
Open-source blockchain applications supported by communities without a single, centralized vendor are a significant source of blockchain technology projects. This assortment of various blockchain applications is confusing and a source of mistakes.
Another misconception is that blockchain technology is ready for production use, while the market is primarily composed of fragmented platform offerings, trying to differentiate themselves in various ways. Some platforms are built for confidentiality, some for tokenization or digital representation of goods or a currency, and some for universal transactions. However, most platforms are not good enough for large-scale production, which requires security, network management, and requisite systems.
Mistake #6: Inadequate Investment of Resources in Blockchain Projects
Enterprises make the mistake of allocating inadequate resources to Blockchain projects. This is because blockchain professionals have doubts regarding the areas where they must invest their resources. Lack of clarity about resources of knowledge, time, and money also creates bottlenecks. Professionals assume that blockchain projects focus on blockchain-specific programming skills.
However, blockchain-specific programming accounts for only 10% of the code scripted for blockchain solutions. In other words, blockchain professionals should have proficiency in comprehensive and general programming skill sets. Additionally, developers should thoroughly understand scripting software that can interact with the blockchain network.
Most blockchain professionals are currently looking at pseudo-experts and online resources, resulting in disastrous failures. Enterprises are also not acting to counter the lack of resources for blockchain technology applications. As a result, blockchain projects do not have the quality assurance that other technology projects have. Enterprises should also look for investors who can fund Blockchain projects and professionals who would like to contribute with their technical skills.
Mistake #7: Expecting Interoperability of Blockchain Platforms
Some businesses make the mistake of assuming blockchain technology's interoperability with other blockchain solutions. While this may be possible in some cases, interoperability is still a challenge when most platforms and their protocols are being designed and developed. CIOs should not select a blockchain platform with the notion that it will interoperate with next year's technology from a different vendor.
It will take at least 2-3 years before blockchain functionalities are fully exploited and more nuances of the technology are known. When that stage is reached, it will be possible to integrate different platforms to develop a distinct solution. However, the interoperability of Blockchain technology solutions platforms is currently very low.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology is far from reaching a stage where it has been substantially understood, and all its possible applications have been visualized. So, Blockchain companies should avoid making these seven mistakes for the time being. They should allot more resources to understand blockchain technology and its applications, which can help improve their productivity over time. As the need for digitization of records and decentralized networks increases, blockchain technology will be one of the concepts most looked at.
New features emerge daily on the Blockchain horizon, and organizations seek an innovative landscape. Interest in Blockchain technology and its various applications shows that we have just seen the tip of the iceberg. Technology leaders need to remove some bottlenecks and allocate resources adequately for each project.