We've seen an enormous surge in the use of various technologies to support organizations' learning and training initiatives in the past few years. The pandemic has compelled schools and organizations worldwide to engage in digital learning experiences using e-learning software to continue to teach their learners without having to meet them in person.
Even outside of this forced change, schools and students were rapidly making use of the educational opportunities that the internet and technology provided. In 2018, i.e., even before the pandemic hit, around 34% of college students reported taking at least one online course while pursuing their degree.
Thus, as schools and corporations consider ways to integrate various forms of digital learning into their curriculum and training programs, they may come across terms like ‘blended learning’ and ‘flexible learning.’ Even though these two terms sound similar, they use different teaching methodologies.
What is the difference between Blended Learning and Flexible Learning?
Blended learning integrates the best of both worlds - traditional classroom learning as well as high-tech online learning. Whereas flexible learning refers to a teaching style in which learners have control over how, what, when, and where they learn; and focuses more on online and distance learning methods.
School administrators and corporate organizations should consider the differences between the two systems to choose the one that best suits their requirements and the learning experience they wish to offer.
So, let’s dive right into the definitions, key differences, and application scenarios for blended learning and flexible learning approaches.
What is Blended Learning?
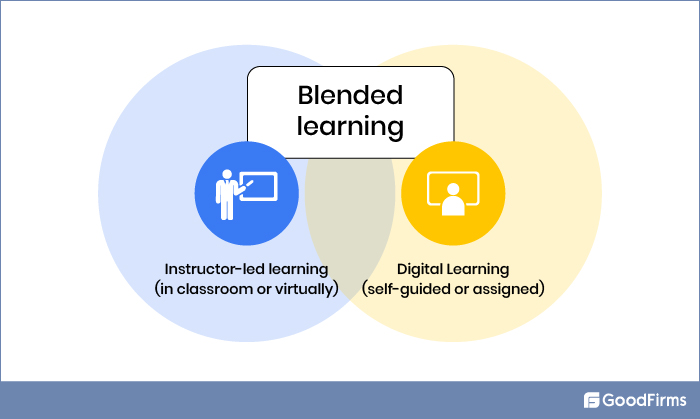
Blended learning integrates the best of both worlds of learning management systems - traditional classroom learning as well as high-tech online learning. You can appeal to all types of learners by using all bases - those who learn best in a classroom environment involving face-to-face interaction with a guide/instructor and self-motivated individuals who learn best from partially autonomous, computer-based learning. The instructor-led training can be in-person or online, through a live virtual classroom or two-way videos.
Blended learning is also known as “flipped classroom,” “hybrid learning,” or “mixed learning.” Unlike full-fledged e-learning, the online learning section of the training doesn’t take the place of face-to-face learning with a teacher. Instead, teachers use technology to improve the learning experience and deepen understanding of specific topics. Instructors may, for example, send out a link to a video and ask learners to watch it at home, then discuss doubts in class.

(Source)
Blended learning represents a significant change in teaching approaches. It has the ability to improve student outcomes in ways that traditional teaching cannot. Blended teaching models enable each aspect of learning to be taught using the most suitable medium for a particular topic.
This method of learning, which has been extensively researched and implemented in K-12 and university education, is also an excellent option for enhancing corporate training, particularly when it comes to upskilling employees for the rapidly changing digital economy.
Below are some of the features of the blended learning approach:
Features of Blended Learning
- Blended learning takes every kind of learner into consideration - whether they prefer classroom training, online classes, or a mixture of both.
- As it uses both offline and online techniques, the latest learning trends and modalities can be included by instructors in the curriculum.
- Blended learning is an interactive, fun, and engaging approach to learning.
- Learners can acquire knowledge from a variety of content types, practice what they’ve learned, and interact with teachers and other team members at any time on any device.
- The focus of blended learning is on improving learning outcomes with the use of an efficient learning management system.
- The ability to modify the learning approach and maintain a balance between online and on-site learning enables students as well as employees to attain the best results.
- As online teaching becomes a part of the process, the communication between learners, instructors, and team members is improved.
After having an understanding of what blended learning is and how it works, let’s take a step ahead and have a look at the types of blended learning models that are in use right now.
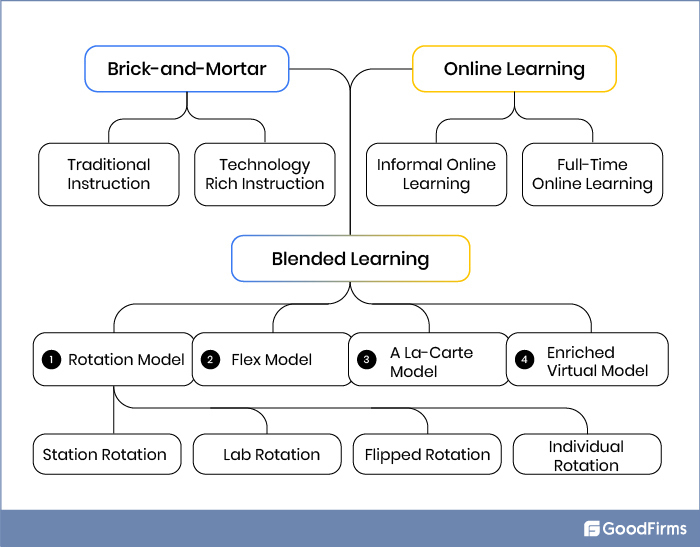
Types of Blended Learning Models
There are 4 types of blended learning models that offer varied approaches to trainers to establish an advanced and customized learning environment for learners.
Let’s go through the details about these blended learning models.
#1 Rotation Model
This concept is also used in traditional learning; however, in a blended learning situation, online education using e-learning software plays an important role in the rotation mix. According to this concept, learners in the same group rotate between several tasks and exercises, one of which is online learning.
The rotation model can be implemented in 4 different ways:
a. Station Rotation
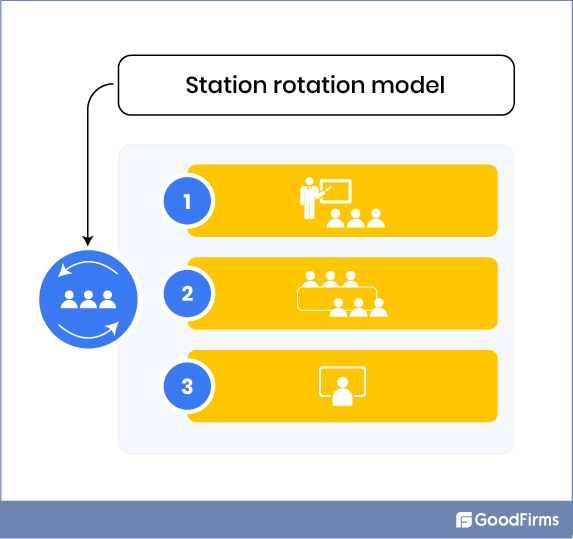
As the term applies, learners must rotate between activities, allocating equal time to each task of the training program and obtaining knowledge in the most practical and progressive manner. Here, learners are divided into groups, and different tasks are assigned to them in the form of stations.
For instance, three groups of learners are created. Group A begins at station 1, learning a new subject online through articles, videos, lectures, presentations, and other methods. Group B is at station 2, where they have to learn through online practical examples and case studies.
While Group C starts at station 3, where they will learn via in-person discussions and lectures. All these groups of learners rotate through the 3 stations.
b. Lab Rotation
In lab rotation, learners move between face-to-face sessions and computer labs for online training, similar to how they rotate between various tasks in the Station rotation technique.
c. Flipped Rotation
“Online learning and offline application” is the motto of the flipped rotation model. The aspects of lectures and practical homework are reversed in a flipped classroom model. Learners prepare for class sessions by studying new material at their home, and class time is spent on active learning and implementing newly acquired knowledge.
Discussions, case studies, and project work are used to accomplish this. The instructor’s job is to lead the learners by answering their questions and assisting them in applying course topics. The course content can be shared best through a learning management system or emails.
d. Individual Rotation
This strategy involves dealing with every learner individually instead of handling the entire group in the same manner. Individuals rotate between online and offline activities in a way that is most efficient in enhancing their individual learning outcomes based on their profiles because everyone comes from different backgrounds and has unique strengths and limitations.
#2 Flex Model

In the flex learning model, learners are in command, and they learn primarily through online platforms, with trainers on hand to assist them whenever required. Learners feel empowered and responsible because they have the option to choose how they want to learn and the comfort of being able to learn at their own pace.
#3 A La Carte Model
The A La Carte model implies that learners can choose which courses they wish to take online and which they wish to take through face-to-face training sessions. In both cases, they have a trainer to assist them with their learning, which can also be an online trainer.
This learning model is similar to the flex model as it enables learners to pick how they want to learn in order to achieve the best results.
#4 Enriched Virtual Model
Learners in this blended learning approach follow a trainer-provided timetable that includes both virtual and face-to-face training. Unlike a virtual-only learning model, which does not require classroom training, this model requires students to attend on-site training sessions when asked.
They can, however, receive most learning materials and engage in tasks virtually. A learning management system is the best approach to enable learners to guide their own training while also keeping an eye on them when they watch videos and eventually participate in classroom discussions.
At a glance, a blended learning strategy appears to be more adaptable and versatile than a single-method approach. In addition to its flexibility, below are some reasons why blended learning is the right choice for upskilling employees in the rapidly expanding digital economy.
Benefits of Blended Learning in Corporate Training
- Unmatched flexibility: A blended learning program makes more sense for firms when they need to train more than one employee in their preferred learning style. Online self-paced videos, live instructor-led classes, and hands-on practice by engaging in applied learning projects can satisfy all kinds of learners.
- Cuts costs and increases ROI: When compared to other modalities of learning, a blended learning strategy can dramatically reduce the cost of upskilling personnel as it requires fewer instructors. It can also improve ROI by lowering costs of instructor fees, travel expenses, and training material costs.
- Improves feedback: Blended learning is also a technique that allows for a lot of feedback. Employee retention can be measured through periodic online assessments, quizzes, and projects. In addition, an employee can contact the instructor for help with doubts.
- Provides employees more control: People are proven to learn better when they have control over their pace. This is crucial for corporate training as employees are not traditional students and may face major time restrictions in addition to balancing heavy workloads and personal life.
- Improves learning: Blended learning helps improve learning as it integrates e-learning methods. The combination of multimedia and instructional design used in e-learning creates a very rich learning environment that is also recurrent. And it is this repeatability that aids employee learning.
As time passes and circumstances necessitate new types of learning, blended learning is growing in popularity and utility. However, as the relevance of new educational technologies for blended learning grows, so do the challenges. Below are the most pressing challenges in implementing blended learning and how modern ed-tech can help overcome them.
Challenges of Blended Learning and How Technology Helps
- The right teaching technology: Organizations could end up spending a lot and face a huge efficiency crisis if they don’t evaluate which tools are best for them. The use of the wrong tools can bring an unnecessarily steep learning curve, which would lead learners and instructors to spend more time figuring out how to use them than actually learning. The solution to this is interactive flat panels that combine multiple functions into a single platform.
- Maintaining course and learners’ progress: In blended learning programs, there arises a situation where instructors underuse digital tracking tools due to less exposure to current technology which makes it difficult to track the learners’ progress on the course. Organizations can help level the playing field by giving learners more time to finish tasks and providing more tailored assistance. Good classroom management software allows you to record classes so that students can access them anytime they like, as well as provide access to online content from almost everywhere, be it school, home, or a local library.
- Participation and attendance: Remote learning, which forms half of blended learning, requires a lot of self-discipline. The key is to make blended learning so appealing that it overcomes any potential distractions. Smart tools, such as unified interactive flat panels can help you do this by gamifying classes. Experience points, achievements, explicit mission goals, and teamwork make the classes more fun and interactive.
- Maintaining the effectiveness of programs: Since it is not the norm, people often question the efficacy of blended learning programs. A curriculum that clearly explains not only what learners will learn but also how they’ll learn becomes easier to plan and share with the help of effective ed-tech tools.
Corporate example: When Ticketmaster realized their customer service was weak, they implemented a blended learning strategy that mixed self-paced e-learning with a real-world practice that could be seen and graded for immediate feedback.
Now that you have a clear idea of the Blended learning approach, let’s move to the second part of the blog and understand the Flexible learning approach.
What is Flexible Learning?
Flexible learning refers to a teaching style in which learners have control over how, what, when, and where they learn. Flexible learning environments take into account how physical space is used, how learners are paired while learning, and how time is utilized during training. With enough space, learners could be assigned designated breakout areas where they can collaborate and work.
Flexible learning is multi-layered and multi-faceted. It is, in its broadest sense, a series of approaches to learning that vary in terms of time, place, pace, content, and mode. Its overall goal is to provide learners with more possibilities and options while also giving them more control over their learning through a range of learning modes.
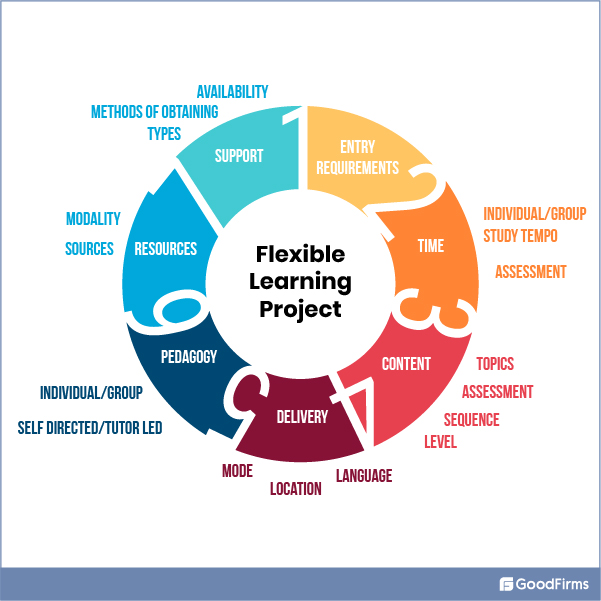
By providing the learners more control over the learning process, the instructor becomes the manager and facilitator of the process by creating or arranging access to appropriate materials. In this process, technology plays an important role. As a result, flexible learning is not a new educational model but rather a collection of prevailing, established, and emerging ways of learning and teaching that it welcomes, extends, and mixes.
This flexibility can be found in:
- In-person classroom training
- Distance learning
- Online learning
- Virtual learning
- Blended learning
- Resource-based learning
- Independent learning
This list is not exhaustive - flexibility can be found in a variety of other learning methods. It doesn’t imply that one strategy is superior to the other, but it might use any combination of them to advance the learning as required. In general, there are numerous approaches to make education more flexible and beneficial to students on-campus, off-campus, off-shore, and internationally.
Below are some of the features of the flexible learning approach:
Features of Flexible Learning
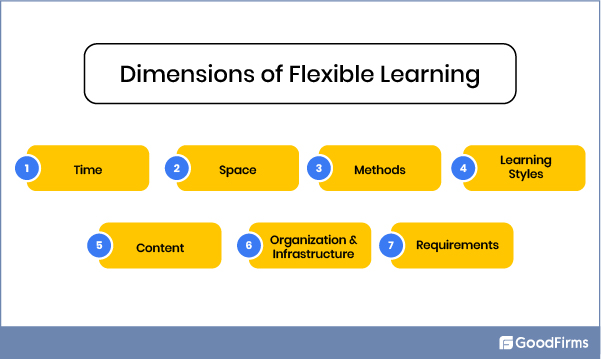
- Flexible access: Learners are admitted into courses without a need for traditional educational background and have the freedom to decide when to enter or exit a course.
- Flexible content: The course content is broken down into multiple modules which learners can refer to as they need.
- Flexible participation: Teachers and support staff are available for learners as per their requirements and convenience.
- Flexible teaching and learning methods: The teaching and delivery mode is determined by combining the subject’s requirements with the needs of the individual learner.
- Flexible resources: Online learning material is available for the learners, which they can refer to and learn according to their pace.
- Flexible assessment: Assessment is done based on the competency of learners rather than time spent on a course.
Types of Flexible Learning Modes
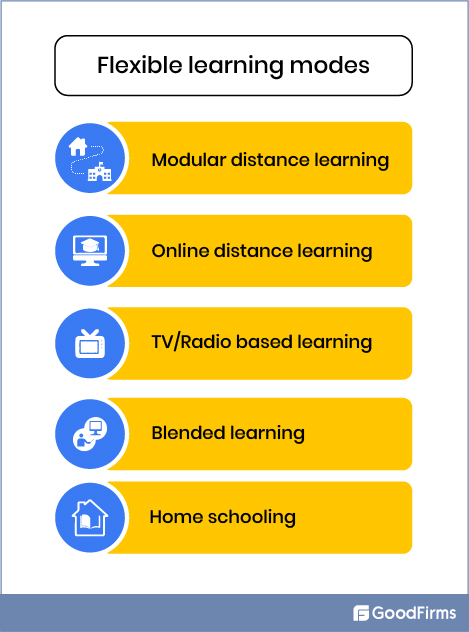
#1 Modular Distance Learning
In modular distance learning, learners can employ self-learning modules (SLMs) in physical form, which are delivered by schools/universities to their stakeholders’ homes. This enables learners who don’t have ready access to the internet to continue learning even without attending the learning premises.
#2 Online Distance Learning
In online distance learning, trainers are in charge of arranging synchronized sessions for learners with a steady internet connection using video conferencing channels. Students are required to commit time to complete and submit tasks using their assigned learning management system, just as they would in regular classes, but from the comfort of their homes.

Source: Goodfirms
#3 TV/Radio Based Learning
This refers to the transformation of self-learning modules (SLMs) into multimedia assets that can be broadcasted across television and radio networks. This learning model has the advantage of being more accessible to individuals who already have basic gadgets at home. Schools may also give supplementary learning resources in the form of CDs, USBs, and DVDs.
Learners can also contact their teachers for help through calls or text messages, and where authorized, teachers can also visit their homes on a periodic basis to clear their doubts.
#4 Blended Learning
As we saw earlier, blended learning is basically a combination of face-to-face and online learning. Students can complete most of their learning activities utilizing online platforms, but in-person discussions can take place during scheduled physical classes at school.
For instance, in-person training days, weekly assignments, and frequent peer-to-peer discussions through an online platform can be a part of a blended learning approach.
#5 Home Schooling
As an alternative to traditional schooling, parents working as educational facilitators for their children have been increasingly popular in recent years. Parents who choose this flexible learning method can work with a regular school to have their children’s knowledge credited using the school’s criteria in order to receive a certificate of completion. Modules, worksheets, activity sheets, and gadgets are examples of learning systems that will be employed.
Given the varied learning styles, flexible learning is an ideal approach to creating training programs for employees without incurring large financial expenses. Below given are some advantages of moving corporate learning to a flexible learning system.
Benefits of Flexible Learning in Corporate Training
- Best for remote-working employees: The main benefit of flexible learning is that learners are not tied to training in a particular city or region. This is best for employees working remotely as they can be trained as per their convenience. In such cases, online training software can be used to monitor the learning process and maintain a sync between the tutor and the learner.
- No disengagement from work: Training can be done at any time outside of work hours, which does not affect the outcomes of their work efforts.
- Automation and standardization: Training methods can be set up once and used over and over again without needing a huge number of professionals. It provides the opportunity to teach not just individual employees, but entire departments, divisions, and branches according to the same set of standards.
- Updated content and learning material: It is considerably easier to edit, correct, and update training materials while working with flexible learning methods. This simplifies and streamlines the entire procedure.
While flexible learning models are better than traditional training methods, there are still certain challenges to implementing remote learning techniques and technologies. Below are the most pressing challenges in implementing flexible learning and how they can be overcome.
Challenges of Flexible Learning and How Technology Helps In Overcoming Them
Meeting learners’ needs: Learners should be provided with all the materials as soon as they sign up for the course, i.e., books or video tutorials. Using e-learning tools, a curriculum and a course flow can be created, which helps the learners stay on track. Video conferencing software can be used to periodically conduct doubt-clearing sessions, bridge the physical gap, stay connected, and build their confidence.
Staying connected: Asynchronous communication causes many problems for instructors when it comes to remote learning. Having synchronous communication options can help alleviate the difficulties of not being able to interact face-to-face. This issue of distance can be solved by obtaining live feedback, whether through a web conference or audio lessons.
Correct assessment: The assessment of effort and artistry in online courses may be entirely subjective. Instructors can use rubrics to fine-tune an assignment’s objective and expectations. Rubrics can also be used to define standards for various levels of achievement and used as a scoring tool, with the standards being clear and explicit to the learners.
Peer review and delegation of tasks: Instructors may get overwhelmed by the workload in online classes. Increased peer collaboration and review relieve educators of the burden of reviewing and feedback. Long and complex assignments can be broken down into phases, with students submitting deliverables at different times.
Corporate example: The computer giant CDW made the switch to a synchronous learning platform to enable both in-office and remote workers to use the same learning resources and tools. These e-tools were then integrated with hands-on experience so that learners could put their skills to test and improve their performance.
Flexible learning is quite a broad term, and Blended learning is one of its learning modes. As blended learning is a part of flexible learning, they possess a lot of common characteristics. However, there are some differences between both, and the learning experience that they offer is a major one.
Blended learning offers a more immersive learning experience, whereas flexible learning experiences are majorly one-directional. As per the 70/20/10 learning and development model, just 10% of learning takes place in a traditional classroom setting. The rest, 20% and 70%, come from interaction with peers and demanding assignments, respectively.
A major drawback of most of the flexible learning modes is that they are too far from learners' everyday lives. Although online learning tools can assist learners in memorizing theoretical concepts, they often lack context. And new information doesn’t really stick to learners’ minds without context.
Because of its interactive and engaging character, blended learning exposes learners to a variety of stimuli and motivates them to apply what they’ve learned in their daily work. That’s where 70% of the professional development takes place.
Blended learning, when combined with peer-to-peer interaction and conversations on a learning management system, truly sets learners up for success. And even though these developmental connections may only account for 20% of learning, it is that 20% that can make or break the learning experience.
To better understand the difference between blended learning and flexible learning, let’s have a look at their pros and cons.
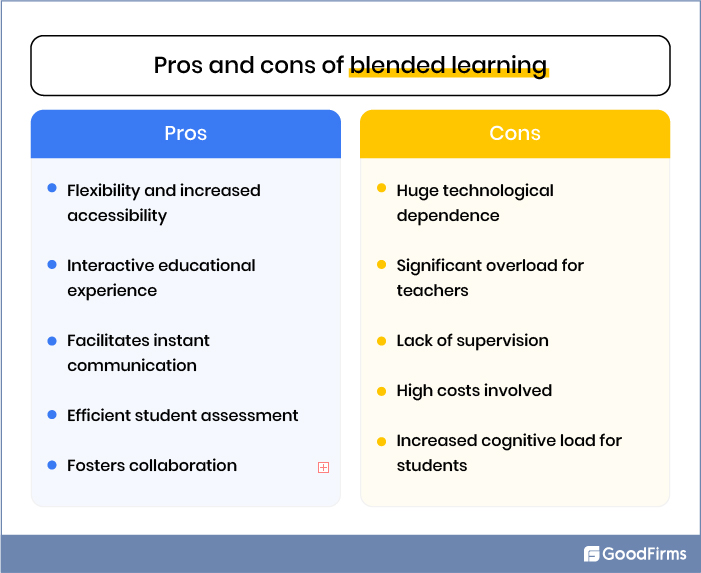

Thus, there are defined pros and cons to whether you implement blended learning or flexible learning within your organization or educational institute. To make better decisions about which approach would be better for your organization, let’s have a look at the prominent difference between both of them.
Top 7 Differences Between Blended Learning and Flexible Learning
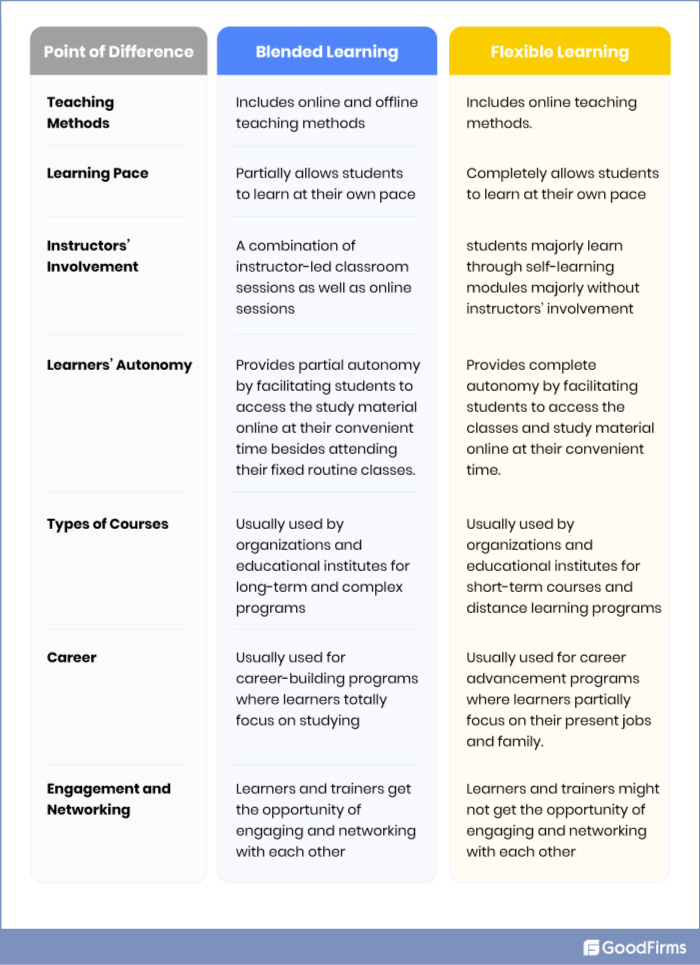
After going through the difference between blended learning and flexible learning at a glance, let’s understand them in detail -
#1 Teaching Methods
Blended learning takes into account both offline and online teaching methods. There’s always an instructor present in all the blended learning models. Learners are required to attend on-site training sessions periodically. Whereas in flexible learning, a majority of teaching takes place through online methods, with very limited or no face-to-face interaction.
#2 Learning Pace
Blended learning enables learners to study a portion of the course online and learn according to their convenience. The ‘flipped classroom’ model allows learners to begin with the knowledge they gained through online course content and then supplement it with instructor-led training in classrooms. Whereas in flexible learning, learners have complete control over how, what, when, and where they learn.
#3 Involvement of Instructors
Blended learning is a combination of instructor-led classroom sessions as well as online sessions. In all the models of blended learning, students have a trainer to assist them with their learning, which can also be an online trainer. Whereas in flexible learning, students majorly learn through self-learning modules, without the need to attend the learning premises.
#4 Learner’s Autonomy
In a blended learning model, students can engage in the online portion of the course and review class materials from anywhere and anytime they have access to the internet. This allows them to learn wherever they want while giving them a sense of autonomy and control over their learning process. In flexible learning modes, learners have complete autonomy rather than partial control, which enables them to effectively balance their learning and external obligations.
#5 Variety of Programs And Courses
Blended learning models are generally adopted by schools and universities for higher-level degree courses, i.e., long-time and complex programs, where conducting classroom sessions is necessary to impart the required knowledge. Whereas through flexible learning, learners can opt for a variety of short-term skill-building courses. Full-fledged degree programs are also available through distance learning.
#6 Career Building and Advancement
Blended learning courses are all about career-building programs that prepare students for their careers. In comparison, flexible learning courses are largely about career advancement that learners can take while they are working, between jobs, or taking time to raise a family.
#7 Networking and Engagement
Networking and interaction between learners and trainers effectively take place in a blended learning environment. As partial training occurs in classrooms, learners get an opportunity to engage with trainers as well as other team members. Flexible learning models lack the social aspect of learning in a class. Some courses allow learners to interact with teachers and other students online; however, it’s not quite the same as meeting them in person.
Finally, let’s have a look in which situations blended learning and flexible learning would be the right choice.
When is Blended Learning the Right Choice?
Blended learning is better suited to longer-term, more complex organizational learning courses, such as leadership training, where learners must be able to apply what they’ve learned to their work frequently and receive enough support from the learning community.
When is Flexible Learning the Right Choice?
Short-term tactical courses with practical how-to videos, interactive exercises, and training sessions that enable students to freely ask their doubts and participate in the learning experience are most suited for flexible learning.
Wrapping Up
Technology has become an increasingly significant aspect of our daily lives, including how classrooms are organized and how students learn. Online learning picked up its pace more due to Covid and the trend has the potential to continue due to the flexibility it offers to both corporate learners and educators. Developing digital learning possibilities can help tap into this potential and find new ways to engage learners. Carefully examine how these various technologies might fit in with your objectives and the advantages they offer.
Whether you choose a blended learning model or a flexible learning system for providing training, this curated list of Learning Management Systems (LMS) on Goodfirms will help you find out the best software that helps provide effective learning experiences to your students.