In an era, when IT infrastructure is considered as the backbone of the business, networks have emerged as the heart of the IT infrastructure. Earlier, the role of networks was limited to communication and data transfer, but owing to the digital revolution, their need is more than ever. Not only physical devices and components, but virtual components and endpoints are also included in the modern networks. Present day networks are more complex and difficult to manage than earlier ones.
Earlier, network administrators used to manually perform almost every function of the network mapping. However, over time, complexities of connected devices and increasing popularity of emerging technologies forced businesses to look out for new and efficient alternatives. Then emerged modern network mapping software solutions that are designed to deliver enhanced network mapping, monitoring, and management capabilities. Besides documenting and mapping network topologies, these capabilities are great to proactively detect inefficiencies, security gaps, and performance bottlenecks.
In 2025, more and more businesses are planning to invest in a robust network mapping software that is the need of the hour.
This blog is an attempt to familiarize readers with the concept of network mapping in 2025 and why businesses should focus on it. Additionally, it also attempted to answer questions like;
- What is network mapping?
- What are the differences between traditional network mapping and modern AI-based network mapping?
- What does network mapping look like in hybrid, virtual, and in-house setups?
- What are the benefits of investing in AI-based network mapping software?
- Why network mapping should matter in 2025?
- When misused or exploited, can networking mapping tools also present security risks?
What is Network Mapping?
Network mapping is the process of discovering and visualizing the connected devices, their interconnections and transport layers, giving a better and a clear view of the network topology. Network maps include network diagrams, flow charts, device inventories, etc., which are required to concisely demonstrate the network architecture. It is among the most effective ways to identify physical and logical connectivity within real and virtual networks.
Benefits of Network Mapping
In 2025, network mapping is becoming one of the most focused network aspects to achieve better visibility and control over the network. It comes with extensive benefits such as network visualizations, rapid diagnosis of network issues, network security, task automation, and many more. Owing to the benefits, the global network mapping software market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.3% in the upcoming years.
Visualize and map entire network infrastructure
At present, sudden increases or decreases in wireless devices, access points, servers, and other cloud-based components have become common to accommodate organizational needs. In such scenarios, manually mapping and visualizing the wireless infrastructure could be time consuming. However, IT teams can use network mapping tools that can quickly map and visualize the entire network infrastructure and build dynamic wireless maps of all connected access points and SSIDs. Not only quick mapping, but these solutions can also show the relationship between wireless and wired networks for better flexibility and understanding.
Rapid diagnosis of network issues
IT teams can rely on network mapping software solutions that can clearly and visually represent the network topology for a comprehensive view of network connections, traffic flow, device status, etc. Through this comprehensive view, IT administrators can properly assess the current network state to identify the root causes of network issues. Apart from all these, network mapping tools also offer automated alerts that send automated alerts with contextual information to the users whenever an issue is there. For instance, if a random access point goes offline, network maps can quickly reveal the affected node and connection. IT teams can also use this information to isolate and fix the issues without disrupting the entire network.
Better network security
Implementing network mapping software can help businesses enforce better network security and control. These software solutions are useful in understanding the way different devices interact with each other, setting up baselines, classifying devices into security zones, detecting device behavior, identifying unknown devices and cyberthreats associated with endpoint vulnerabilities, etc. Advanced insights to spot unusual device behavior and connections that could potentially result in security breach are also offered by network mapping software. Network security costs can also be optimized with enhanced security features of network mapping tools. For instance, whenever a certain endpoint uses more data than expected, IT teams can take a look at the network map to identify the device and remedy it before it can be exploited by hackers, ensuring timely protection.
Better resource utilization
Another major benefit of network mapping solutions is better resource utilization. Network mapping tools can identify underutilized devices or bandwidth bottlenecks and automatically make relevant modifications to balance the overall network consumption. For instance, if a device is using a huge amount of network data or bandwidth while other devices are idle, then the mapping software can automatically make load-balancing adjustments to distribute the network efficiently.
Improved network control and visibility
Network mapping tools offer a complete overview of all connected network devices along with real time insights with better visibility. They can determine the current state of network infrastructure, know which devices exist in the network, which ones can cause outages and issues, etc. Multi-level network discovery functionalities are also offered by these software solutions to map every component, whether WiFi access points, IoT devices, clients, etc., ensuring complete visibility in real-time. As per Cisco’s Global Networking Trend report, 75% organizations are planning to implement tools that offer end-to-end visibility. This makes visibility as one of the major driving factors behind the increased implementation of network mapping solutions.
Network performance optimization
Through network mapping tools, IT administrators can gain critical insights into different aspects of the connected devices, ranging from performance and health to usage patterns and device load. This helps network administrators identify poorly performing endpoints and weak spots to proactively optimize network performance. According to a state of network operations report, around 55% businesses are prioritizing increasing network performance. For instance, if a device is experiencing low latency and network speed, network mapping solutions can analyze the data flow and identify which devices can function in the same manner even after reducing the bandwidth. Through this, more bandwidth can be re-allotted to the devices that require extra speed for better functioning.
Customizable network mapping
Besides other functions, many comprehensive network mapping tools can also let users customize their network maps. Users can add background images, labels, icons, etc., as per their business needs. Apart from visual customizations, businesses can also color code devices, add different views, manual device entries, etc. For instance, businesses that require different views for different departments can configure the network mapping software as per their requirements. Through this, each department will get the network view as per the configurations, ensuring different teams can only see relevant aspects of the network.
Task automation
At present, around 40.6% businesses are struggling with shortage of skilled staff in managing network operations. This problem can be resolved through task automation capabilities. Automated network mapping software comes with robust features like automated network discovery, network topology change tracking, network diagram export, compliance reporting, analytics, WiFi scanning, intelligent alerts, etc., that are best to streamline network management, maintain complex server room networks, map mixed networks, optimize WiFi coverage, assess network security, and perform many more related tasks. For instance, an organization with thousands of connected devices needs to efficiently manage their IT network. But manually connecting, monitoring, mapping, management, etc., of the network is time consuming. In such a scenario, automated network mapping tools can be used to automate monotonous and complex functions to ensure maximum productivity, efficiency, and performance.
Efficient planning and forecasting
Modern network mapping solutions also offer powerful data visualizations, analytics, and reporting features that offer detailed insights into each and every aspect of the network. Through these features, IT administrators can efficiently plan and forecast network infrastructure needs.
Network Mapping Then and Now
From simple and manual to highly intelligent automation capabilities, network mapping has gone through a tremendous transformation, entirely changing the way modern IT infrastructure is managed.
|
Basis |
Network Mapping Then |
Network Mapping Now |
|
Scalability |
Limited scalability due to manual process |
Highly scalable due to AI-driven and cloud-integrated platforms |
|
Complexity |
Higher |
Lower due to modern features |
|
Security |
Weak and limited security measures |
Highly advanced security features to safeguard networks and data |
|
Performance Optimization |
Manual optimization |
Highly automated performance optimization through advanced insights |
|
Automation |
Basic automation capabilities |
Advanced automation with self healing, automated troubleshooting, etc. |
|
Transparency |
Lack of transparency |
Real time network discovery, mapping, and management |
|
Alerts and notifications |
Simple logs and emails having limited information |
Real time, automated alerts through multiple delivery modes |
|
Customization |
Rigid, limited templates and customization |
Extensive customization capabilities from layouts to real-time adjustments |
|
Integration |
Poor integration capabilities with common incompatibility issues |
Seamless integration with cloud as well as in-house components |
|
Real-time updates |
Periodic scans that too manual |
Real-time data sync |
|
Reporting |
Static logs and basic charts were used for reporting |
Advanced analytics and automated reporting |
|
Visualization |
Simple 2D diagrams with without interactivity |
Interactive 3D visualizations with a wide range of templates, effects, and easy to use interface. |
In its earlier phase, network mapping was all about manually updating the topology maps, diagrams, spreadsheets, etc., to document the network infrastructure. Traditional network mapping methods presented challenges in terms of scalability, transparency, network optimization, security, etc., making the overall process more complex and time consuming. The network maps generated through this method get outdated even before they are fully completed due to continuous changes caused by the addition/removal of devices. However, in the past, most of the network infrastructure was on-premise; therefore, manual network mapping was not a serious concern. However, as the technology progressed, traditional network mapping tools became redundant over time. Issues associated with configuration mismatches, security threats, scalability, lack of transparency, etc., led to significant gaps, causing inefficiencies and more challenges for the IT administrators.
The rise of cloud platforms and IoT devices also added more complexities to the network mapping. As a result, IT teams started looking for better network mapping options to ensure efficient, secure, and adaptable network infrastructure. This resulted in the rise of modern network mapping tools that offer dynamic visualizations, multi layered network management, real time discovery, advanced insights, agility, security, AI anomaly detection, data driven performance optimization, robust automation, and many more features to quickly map modern IT networks with ease. Through network mapping tools, network observability can also be improved which is crucial for better end to end visibility. 39% businesses believe that observability provides better end to end visibility. Thus, by leveraging modern mapping tools, businesses can ensure complete visibility and control over their network infrastructure.
Network Mapping In A Hybrid, Virtual, And In-House Setup
Here’s a step-by-step guide for network mapping in a hybrid, virtual, and in-house setup:
1. Understand the network components:
In-house Infrastructure
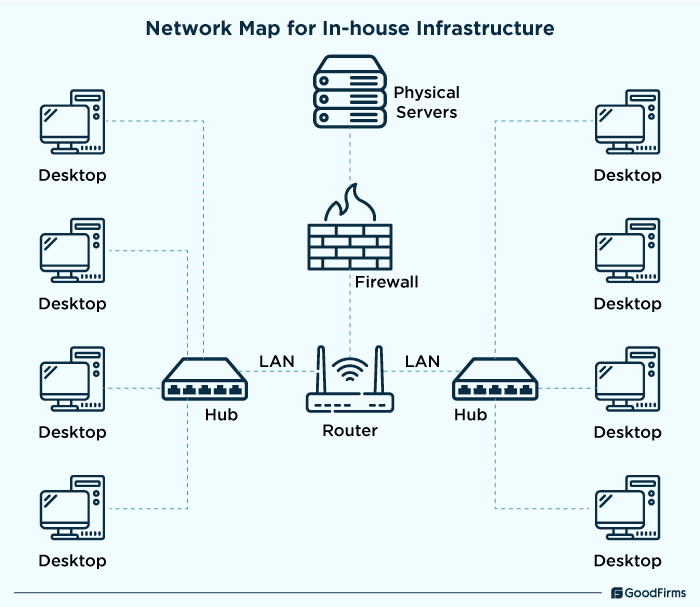
In-house network infrastructure or on-premise network includes various network components, and devices that work together to maintain a high-performing, efficient, and secure network. The following are a list of components in an on-premise set-up;
- Physical Servers (Web, DB, Application)
Physical servers act as the backbone of in-house network setups. For instance, web servers help process HTTP/HTTPS requests from users; databases help store and manage the structure data for fast data retrieval, and application servers are responsible for providing resources and computational power to execute operations smoothly for users.
- Switches, Routers, Firewalls, and other network hardware
Network hardware components like switches, routers, firewalls, etc., are also required to handle data packet forwarding, segment networks, prevent intrusion, distribute traffic, and perform many more functions with ease.
- Local Area Networks (LANs) connecting internal devices
A local area network connects all internal devices for communication, data transmission, and resource sharing. Wired connections, wireless access points, virtual LANs, etc., are some major LAN components to ensure seamless connectivity between different devices.
Virtual Infrastructure
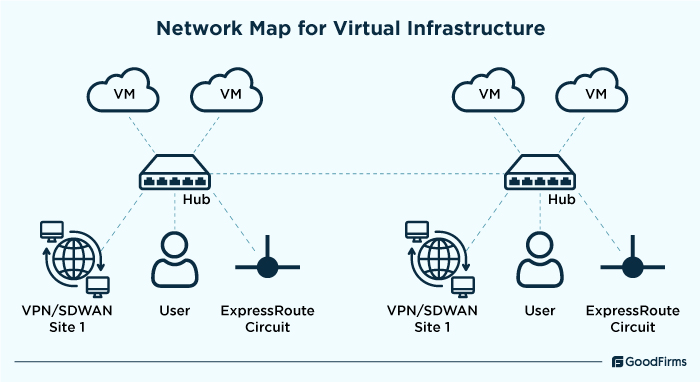
Virtual infrastructure refers to the collection of software defined components that works using shared hardware. These include virtual machines, containers, VLANs, etc., as follows;
- Virtual Machines (VMs), containers, hypervisors
Software-based emulation of physical computers that run and act like standalone systems are called virtual machines. These virtual machines operate using hypervisors that allow multiple VMs to run on a single computer system. Containers are the portable environment in which an application and its interdependencies are packed together.
- Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) and software-defined networks (SDNs)
VLANs and SDNs are also pivotal components of a virtual infrastructure for centralized control, enhanced security, and network automation.
Hybrid Infrastructure
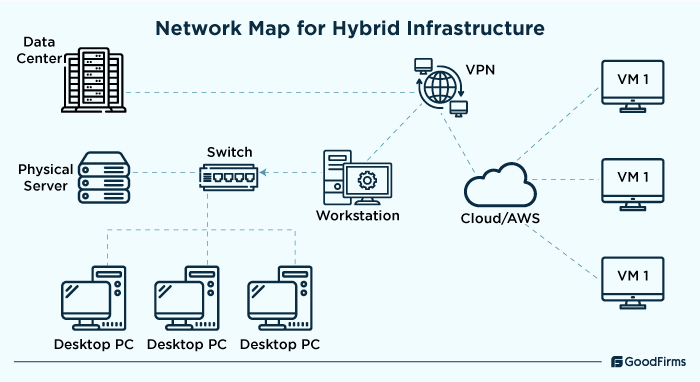
Hybrid Infrastructure is rapidly becoming popular among the businesses owing to the flexibility, scalability and performance it offers. According to network performance monitoring research, around 61% businesses are running hybrid infrastructure to streamline their operations.
- VPN or other connection between data center and AWS
This is a key component of hybrid network infrastructure which is mostly used to enforce encryption standards like AES-256 to ensure safe communication across the business systems and cloud infrastructure. It enables encrypted communication between on-premises data centers and cloud platforms like AWS.
- Physical and virtual systems
Physical systems refer to the traditional hardware-based infrastructure required to run applications that do not support cloud migration. These include on-premises servers, networking equipment, firewalls, etc. Virtual systems are the ones that can be smoothly operated and managed on cloud infrastructure. These include virtual machines and instances, containers, Kubernetes, load balancers, etc.
- Private Link or Peering between VPCs and internal systems
Private link is used in hybrid infrastructure to ensure low latency, secured communication, and access on-premise infrastructure from cloud platforms like AWS without exposing the traffic to the public internet.
2. Identify the connection points
Having a clear idea of all the connection points is required to properly map every relevant component and device. In addition, IT teams can also understand the way different types of devices communicate with each other, and how this relationship impacts the data flow and performance of the connected devices. Commonly used connection points include IP addresses, firewall systems, filtering equipment, routers, switches, and various other endpoints. Also consider focusing on data sources for network flows, application traffic, packet data, etc., to identify each and every connection points For hybrid infrastructure, IT teams should can identify the connection points by focusing on gateways, VPN connections, data flow between cloud and on-premises resources, routing cable connections. Similarly, for the virtual infrastructure, IT teams should identify virtual switches, routers, firewalls, etc. For the in-house infrastructure, IT teams should trace the cables and connections to physical routers, access points, and switches.
3. Document the devices and virtual instances
Documenting network devices and virtual instances helps maintain a comprehensive network record. It acts as a reference guide or roadmap to IT infrastructure that is used to gain detailed information into different network design, layout, operations, setup, maintenance, etc. The network devices and virtual instances documentation generally include a schematic representation of network topology, hardware and software inventory, physical network connections, IP address allocations, network servers, network recovery plans, etc. While documenting the devices and virtual instances for each infrastructure type, consider focusing on the manufacturer, serial number, model, location, hostname, IP address, access and permission management, operating systems, lifecycle management, and many more.
4. Define subnets and VLANs
Subnets are the smaller networks within a larger network. VLANs or virtual local area networks refer to the logical segmentation of a physical network that allows devices in different locations to communicate as if they are on the same physical network. IT administrators can reduce traffic congestion, improve security, enhance IP address management, optimize network performance, and do much more by defining the subnets and VLANs. When defining subnets, businesses should assess network requirements, determine subnet size, assign IP ranges, configure network devices, etc. Whereas for defining VLANs, businesses should focus on VLAN structure planning, VLAN IDs assignment, switch configurations, VLAN routing implementation, etc.
5. Classify network components by security zones
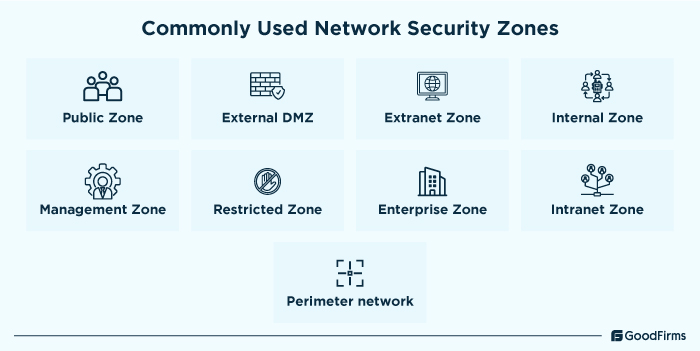
Once the connection points are identified, devices are documented, and subnets and VLANs are defined. The next step is to classify each of the network components by security zone. Each and every network component, ranging from network equipment and devices to VLANs and firewalls, can be classified into separate security zones as per their access and priority level. Commonly used network security zones include Public Zone, External DMZ, Extranet Zone, Internal Zone, Management Zone, Restricted Zone, etc. Businesses need to identify and categorize their network components to logically group them as per their security requirements. For in-house network infrastructure, the External DMZ and Perimeter network is used to filter internet traffic before entering the internal network, Extranet zone is used to provide controlled access to remote professionals, and Restricted and Management zones are used to ensure sensitive data and administrative controls stay protected. In virtual network infrastructure, Public and External DMZ are used to protect cloud-based applications while filtering malicious traffic, Extranet Zone is used to securely integrate Saas and external devices, and Management and Perimeter zones are used to ensure security enforcement through cloud firewalls, IAM, etc. For hybrid network infrastructure, Public zone is ideal to host scalable cloud-based applications, Internal and Enterprise zones are great for ensuring secure workflows between cloud and in-house systems, Perimeter network is used to integrate cloud-native security features with traditional firewalls, and Extranet zone can be used to enable controlled partner access.
6. Visualize data flowing through the network components
Network data visualization is of great importance to network administrators in understanding how data moves across different components which is critical to detect network problems, determine dependencies, track traffic and usage patterns, etc. For visualizing the data flowing through the network components, consider focusing on data flow sources, entry point mapping, defining data storage, categorizing network types, etc. Also, network mapping software with robust visualization abilities can also be implemented to efficiently visualize the data flowing through the network components.
7. Utilize the right tools for network mapping
Another important step is to select and utilize the right network mapping with robust capabilities to handle the relevant functions of hybrid, virtual, and in-house setup. Every type of infrastructure, whether hybrid, in-house or virtual, needs features like analytics, auto discovery, advanced alerting, compliance management, and seamless integration with existing apps to properly map the networks.
8. Monitor and maintain the network map
The final step is to continuously monitor and maintain the network maps. IT teams should continuously collect and analyze the traffic data on a regular basis from all available sources whether they are applications, services, or network devices. This data collection and analysis is used to gain a better overview of network behavior, which can further be used for adjusting network configurations, forecasting new trends and patterns, detecting potential security vulnerabilities, etc., with minimum hassle. Through continuous network map monitoring and maintenance, inspection of individual data packets, identification of potential security threats, and improvements in overall network performance becomes easy. Taking help from professional network monitoring services for the entire IT infrastructure could also help manage and monitor the network efficiently.
Benefits of Investing in an AI-based Network Mapping Software?
The network complexities are rapidly growing for which Artificial Intelligence could be one of the investments for businesses. Artificial Intelligence in network mapping not only helps eliminate complexities but also assists those businesses that are struggling with effective management of dynamic and distributed network environments. According to AI Native Networking Research, over 40% of the core IT spend of G2000 will be allocated to AI initiatives by the end of 2025. These tools come equipped with real-time insights, automated network discovery, predictive analytics, and various other capabilities to prevent typical issues associated with network visibility, manually carrying out tasks, analyzing traffic patterns, managing fragmented data, and ensuring efficient troubleshooting while also helping them to gain a unified view of the network architecture.
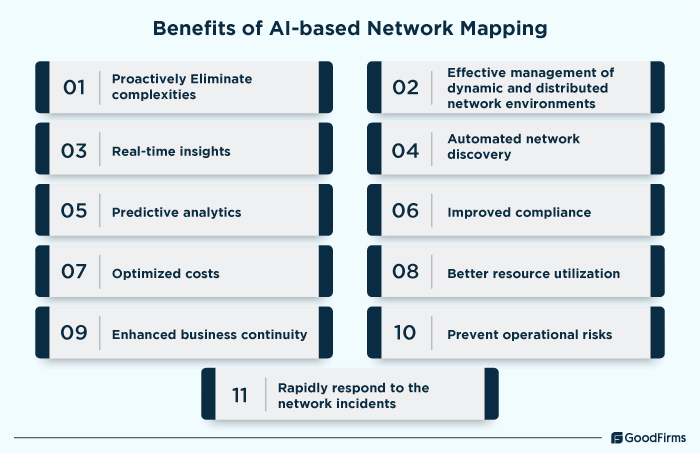
Besides these abilities, another major benefit of AI-based network mapping tools is that it can smoothly integrate with other existing artificial intelligence software, ITSM systems, network monitoring tools, etc. Robust security measures and functionalities are also offered by AI-based network mapping software solutions to effectively identify, assess, and mitigate any security vulnerability caused by the network inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Overall, investing in an AI-powered network mapping software brings numerous benefits to IT teams in terms of improved compliance, cost savings, better resource utilization, enhanced business continuity, optimized operational risks, etc.
Top Reasons Why Network Mapping Should Matter in 2025
Modern network mapping tools are among the most crucial resources for businesses in the digital age for efficiently managing network topologies and maps. Here are some of the top reasons why network mapping should matter in 2025 as follows;
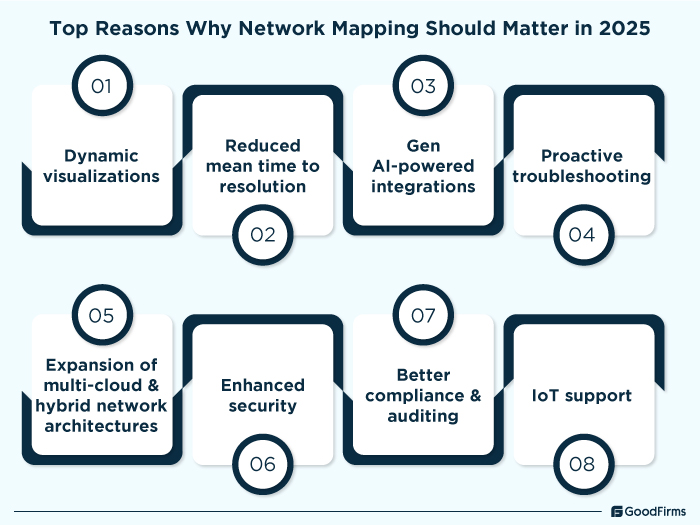
Dynamic visualizations
As networks are becoming complex over time, static data visualizations no longer serve their purpose. Instead modern network mapping tools offer dynamic visualizations that provide real-time interactive representation of the network infrastructure. These dynamic visualizations enable IT teams to monitor live traffic flow, identify device relationships, enhance security, and quickly adapt to infrastructure changes.
Reduced mean time to resolution
Through modern network mapping software, IT teams get the needed capabilities to swiftly detect and respond to any network issue. Whenever, any device behaves abnormally or finds a bottleneck reducing the network latency, these software solutions send the alert to the respective teams, ensuring enhanced visibility into the network infrastructure, minimized downtime, and maximized performance.
Gen AI-powered integrations
With the launch of DeepSeek open source AI, Gen-AI powered integrations can level up network mapping and monitoring functions in 2025. As the technology progresses, Gen AI-based network mapping would help network administrators proactively identify potential network failures, eliminate security threats, implement preemptive measures, etc., ensuring streamlined network mapping, monitoring, and management.
Proactive troubleshooting
Integration of AI and automation in network mapping is great to proactively manage and troubleshoot IT and network issues. Modern network mapping tools can predict failures and bottlenecks, automatically diagnose connectivity issues, provide instant and real-time insights into root causes, etc., through which they can quickly identify and resolve the issues without wasting any time.
Expansion of multi-cloud & hybrid network architectures
The multi-cloud networking market is expected to cross $6.02 billion in 2025 with a CAGR of 26.5%, indicating an increase in multi-cloud network architecture. To handle this immense growth and growing network complexities, Network mapping tools are among the worthy investments to ensure seamless integration, performance optimization, and efficient functioning of the IT network. Through these tools, businesses can quickly visualize, map, and manage complex interconnections across diverse environments.
Enhanced security
Through network mapping, IT administrators can acquire a comprehensive view of all devices and data flows, making it easy to identify vulnerabilities, unauthorized access points, and unsecured endpoints.
Better compliance and auditing
At present, governments from all around the world are hugely focusing on compliances, making it mandatory to comply with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, NIST, ISO, etc. In such complex scenarios, businesses should opt for network mapping. It helps with comprehensive network documentation, automated policy enforcement, incident investigation, data governance, reporting, auditing, etc., ensuring all the standards are met proactively.
IoT support
The number of IoT devices in 2025 is anticipated to reach around 20.1 billion, making IoT support mandatory for network related functions. Network mapping can help IT teams automatically discover and catalog IoT endpoints, identify vulnerable IoT devices, provide real time insights into data flows, visualize device data, etc., ensuring connected IoT devices remain secure and functional without any issues.
When Misused Or Exploited, Can Networking Mapping Tools Also Present Security Risks?
Yes, network mapping tools can also present security risks when they are misused or exploited. Since they are used to identify and map entire network infrastructure, a small mismanagement issue can help hackers infect the entire system with malicious actors and threats as follows;
Ransomware
Often, ransomware attacks are among the most common cyber attacks that target unpatched systems to compromise a device. In addition, most small and medium sized businesses do not report such attacks as they occur, making them a huge threat to the business success and growth. These attacks allow hackers to encrypt sensitive data and render the overall operations inoperable which can lead to operational downtime, financial loss, reputational damage, etc.
DDoS Attacks
Network DDoS attacks are also widely being used by hackers to gain unauthorized access to business data. In such attacks, hackers flood the websites and networks with a huge amount of traffic. IoT devices and systems with poor security defenses are the most easy targets for such attacks. Through such attacks, legitimate users often experience accessibility issues and even businesses can experience an increase in downtime and service disruptions.
Insider Threats
According to a data breach investigation report, around 68% cyber attacks are caused by human elements. As most of the network security defenses are configured to prevent external threats, cyberattacks due to insider threats have become a major issue at present. Insider threats often lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, and poor employee satisfaction, causing issues in the long term too.
Data exfiltration
This is another critical cyber risk caused by mismanagement and exploitation of network mapping software. In these attacks, hackers leverage vulnerabilities like improper network configurations, unpatched systems, and poor access control to gain unrestricted access into the network. After accessing the infrastructure, they can easily locate and compromise sensitive data associated with customer records, intellectual property, financial information, etc.
Best practices to mitigate such risks:
To mitigate the above discussed cybersecurity risks, businesses should follow the following best practices;
- IT teams should use diverse backups, updated antivirus systems, patch management, etc., security features to proactively detect network weaknesses.
- Implementing reliable network mapping software having unusual traffic activity detection capabilities can combat and eliminate complex network-based DDoD attacks.
- Network mapping solutions that offer automated testing, A/B testing, security audits, automated scripts, and various other security features can help simulate real-world cyber attacks and ensure adherence to compliance.
- Providing proper training and development sessions to employees could also facilitate optimal implementation and utilization of network mapping tools.
- Ensure end-to-end encryption of network maps and IT infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access.
- Having proper network monitoring systems in place with real-time network management and monitoring capabilities.
- Leveraging a secured remote management and monitoring software with role-based access control features for securely executing remote work functions.
Conclusion
In 2025, when the number of hybrid, virtual, and in-house network infrastructure are constantly evolving at a rapid pace, businesses need to have comprehensive visibility and control over their network connectivity and components. Modern network mapping tools are the most reliable and efficient options to achieve this enhanced visibility which also facilitates proactive security, intelligent automation, and flawless operations for your entire IT and network infrastructure. Whether to map and manage physical servers, virtual machines, or multi-cloud connections, a well-developed network map is helpful for businesses in many ways. Modern network mapping solutions come integrated with emerging technologies like AI, ML, IoT, etc., to enhance operational efficiency, strengthen network security, ensure regulatory compliances, etc. Interestingly, startups and small businesses can use free and open source network mapping software to gain unparalleled network uptime.




.jpg)
