In the era of online shopping, every website - from a large eCommerce store to a small niche e-retailer - is vulnerable to several types of cyber security threats. Some of these threats are accidental, some intentional, while others occur due to human error. However, without proper eCommerce site security measures, each threat can result in the loss of sensitive customer data, disruption to the normal course of business, fraud, financial scams, and reputational harm.
Because of the pandemic, internet traffic spiked up considerably last year, the amount of money spent online also increased substantially. This situation opened new doors for cybercriminals. The eCommerce transaction entails multiple entities at different stages, generating various vulnerability and attack points for fraudsters. While the buyer side fraud consists of chargebacks, fake buyer accounts, fraudulent claims, promotion/coupon abuse, the merchant side frauds involve selling counterfeit and non-fulfillment. And so, eCommerce developers must use essential security tools and techniques to protect online stores from cyber threats and hackers.
Goodfirms surveyed 138 business owners worldwide to know how companies can set up a robust cyber security framework.
How Many Organizations Have Experienced Cyber Threats?
The eCommerce industry comprises an abundance of customers' data and digital transactions, making itself the magnet for cybercriminals. Omnichannel retailers saw a 50% rise in fraud across their digital networks in 2020 compared to 2019.
The recent unlucky victim of a ransomware breach is the software vendor, Kaseya. Around 1,500 companies got affected by this supply chain ransomware attack. It is considered one of the most severe attacks, with hackers demanding $70 million in cryptocurrency to restore all the affected businesses' data.
Goodfirms research also reveals that 60.9% of the surveyed business owners have experienced cyber threats at least once.
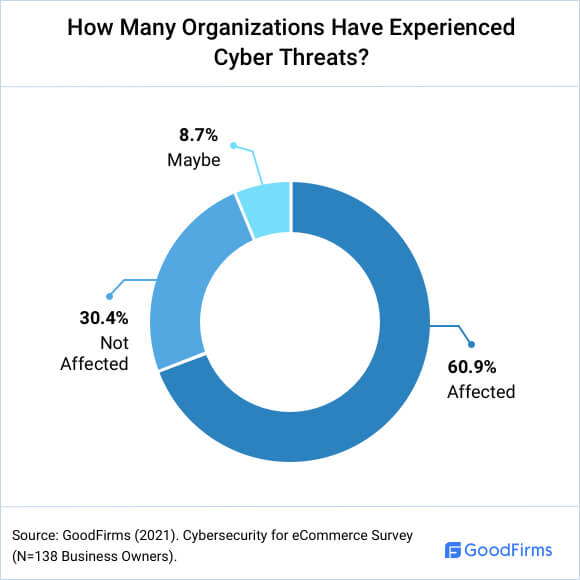
With hackers becoming more organized, innovative, and technologically advanced, eCommerce website security must be a top priority for any organization.
What is eCommerce Security?
Security of eCommerce consists of protocols and guidelines to ensure safe transactions of products and services over the internet.
Today's customers do not hesitate to go to another website at the slightest hint of unsecured transactions or data breaches. Businesses that want to acquire new customers and retain the old ones must follow certain eCommerce security basics, such as -
- Authenticity (of user and data source),
- Confidentiality (no interception during the transmission),
- Privacy,
- Integrity (information intact during its transmission)
What Are The Top Security Threats To eCommerce Websites?
E-businesses need to understand various cyber terminologies and threats and be extra vigilant to fend off the attacks. Here are the top security threats.
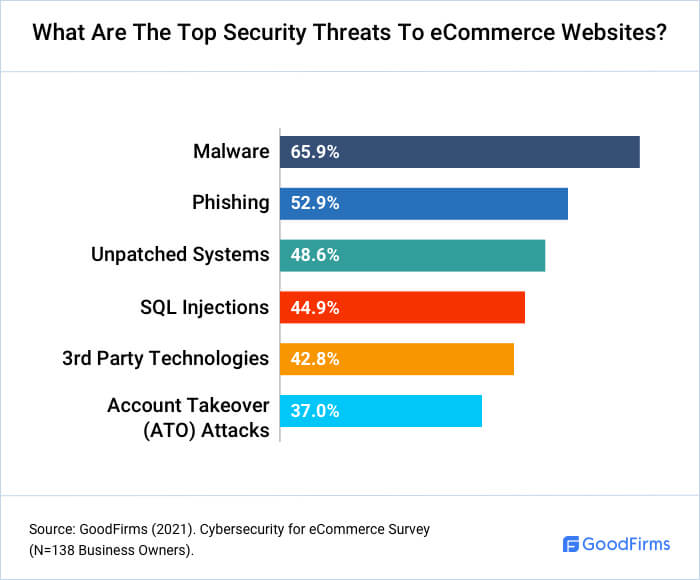
1) Malware
Retailers lose tens of millions in revenue every year because of digital malware. Consumers unknowingly download malware through free software bundles, bad extensions, and a free, unsecured Wi-Fi network, resulting in plenty of pop-ups, competitor product recommendations, banner ads, and other distractions.
Trojan Horse
Gigi J.K., CEO of Virtina, considers Trojan Horse, which makes up 51.45% of all malware, as one of the prime threats to eCommerce sites. He says, "Trojan Horse is a type of malware used by hackers planning access to the user's system. This malware is disguised as a useful software that can be downloaded online but it is designed to damage, interrupt the functions, steal data and harm your data or network."
Targeted Ransomware Attacks
Shiv Gupta, CEO of Incrementors, staunchly believes that a single ransomware attack can hugely damage small and midsize businesses, serving to steep costs linked with downtime and rescue. He says, "Ransomware's success is chiefly owed to the relative purity with which a storm can reach ravaging effects. Ransomware kits are dirt cheap and easily accessible on the dark web. Ransomware agents have devised inventive ways to spread faster, dodge endpoint security codes and launch successful strikes on targeted companies and individuals."
2) Malicious Bots
A malicious bot is malware designed to take control over an affected computer and perform automated tasks such as stealing information. Here are some of the types of bad boats.
- Bots for Inventory Control - Hackers program automated bots to add sought-after or limited edition products to fake user accounts to take items out of circulation. And so, the legitimate customers cannot find the products in the inventory and cannot purchase them. Merchants are left with a large inventory and low sales. Often some valuable items are sold at inflated prices in the black market or on third-party sites.
- Botnets for DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) - Mostly, bots are used nowadays to flood a targeted resource with requests, queries, or packets. Such an attack makes a network or resource unavailable for users, resulting in the interruption or temporary suspension of services.
- Bots for Brute Force Attacks - Attackers use scripts and applications as tools to try out various password combinations to bypass authentication processes. Nowadays, bots do the job of systematically attacking websites by trying the lists of credentials obtained from the dark web or security breaches.
3) Phishing
Phishing hackers generally rely on impersonation and take advantage of the distributed, virtual nature of eCommerce. Online retailers deal with multiple independent entities like fulfillment centers, payment card processors, call centers, etc. Employees at one end of an entity might not be sure whether the email asking for particular information is from the authenticated source in the eCommerce chain.
Customers also have to bear the brunt of this threat. "Phishing occurs when hackers pose as the legitimate owners of a company and present fake copies of website pages or emails in order to fool users into believing their legitimacy in order to steal their banking information or sensitive account details," says Michael Knight, Co-founder and Head of Marketing at Incorporation Insight.
He says, "Most phishing emails contain content that informs users that something is wrong with their account or sends out lucrative offers to users. All in the hopes of having users click a link where malicious software is immediately downloaded into their device or to obtain sensitive user information and bank accounts."
4) Unpatched Systems
Knowledge of the software updates and having resources and strategies to keep up with their release is essential to address the patching gap in any program.
"Unpatched systems are routinely exploited for vulnerabilities that are many months or years old.. Yes, patching some systems has the potential to break applications until the changes are incorporated, but there's room to test a patch prior to full deployment. Consider this: a patch or update explicitly addresses a vulnerability that is documented, at minimum, or potentially discussed in length publicly. Not deploying those updates offers attackers a blueprint into what systems are vulnerable," says Allan Buxton, Director of Forensics at Secure Data.
5) SQL Injections
A successful SQL injection attack might result in the unauthorized viewing of customer lists, the deletion of entire tables, and sometimes the attacker gaining administrative rights to a database.
"eCommerce websites have huge databases storing the information of the website. SQL injections are cyber security attacks intended to target these databases and extract information. With SQL injections scammers are able to tamper with the SQL queries applied on the databases and retrieve all the information from the website. After injecting a malicious code into the database, extracting or copying the complete databases, the hackers can even delete it all from your website. SQL injections can even be injected with simple user inputs on the website," says Jan Chapman, Co-founder & Managing Director at MSP Blueshift.
6) 3rd Party Technologies
Despite thorough tests, third-party apps and services can infiltrate any system without requiring permission from the website. This blind spot on a website's security infrastructure can severely compromise software platforms and data and disrupt the supply chain.
"The average eCommerce site has between 40-60 3rd party services, like live chat, personalization, and ratings & reviews. However, each of these 3rd parties presents a unique risk, as IT has little or no control over when 3rd party services are executed and on what pages they should be executed," says Bob Buffone, Chief Technology & Security Officer at YOTTAA.
He adds, "Hackers can use any 3rd party technologies running across your site, including your login and checkout pages, as an entryway to steal shopper data. For example, last year, Macy's made headlines after reaching a settlement of up to $192K for a data breach caused by a 3rd party gaining access to accounts on Macys.com and Bloomingdales.com. However, Macy's cybersecurity tools did not detect the breach until a month later, leaving customer account and payment information exposed for weeks."
However, Bob clarifies that the solution isn't to strip a site of 3rd party applications. Instead, he suggests that eCommerce brands must adapt their cybersecurity practices to gain insight into the 3rd party services on their site and control the execution of these services.
7) Account Takeover (ATO) Attacks
Because of ATO attacks, account holders have to endure identity theft, and online retailers lose their reputations. Even if the merchants are aware of these data breaches, many cannot usually identify and prevent them.
Ari Jacoby, CEO and co-founder of Deduce, believes that pretty much any company that registers or logs in users is a potential target for ATO fraud. He says, "Account takeover attacks increased by nearly 300 percent from 2019 to 2020.
The world's largest tech companies - Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, and Google - typically reduce instances of ATO by using advanced algorithms and the vast amounts of data collected from users to spot potentially fraudulent behavior and notify account holders via familiar email and mobile alerts.
But companies without access to FAAMG's Goliath resources are too often left to make do with less effective tools. Unfortunately, this leaves their account holders vulnerable because even the best predictive algorithms still need massive amounts of real-time data to work effectively."
What Are The Best eCommerce Security Solutions for SMBs?
Entrepreneurs need to understand how to stem the cyberattacks before they become hurdles on the road to success. Here are the eCommerce security solutions to help businesses prepare a solid incident response plan.
1) Strong Password and Two-factor Authentication
For most e-stores, consumers are responsible for creating their own passwords, often without guidance from system administrators. Many users refrain from generating strong passwords because they're afraid they might forget the complicated ones.
"To keep sensitive information safe, eCommerce sites should require two-factor authentication for users to sign into accounts. This means that along with entering their usernames and passwords, users will also get passcodes sent to their mobile devices. To access their accounts, they'll have to enter these passcodes, which prevents unauthorized access and account takeover (unless the hacker has access to the phone, which is unlikely). Also require strong passwords that are 12 to 16 characters long and include a combination of numbers, letters and symbols, with no repeated characters allowed," says Aliza Vigderman, Senior Editor, Industry Analyst at Security.org.
2) Up To Date Software
When an eCommerce website is not regularly updated for new software patches and as part of its routine maintenance, it could be at risk.
"To combat phishing, keep your software up to date at all times. Phishing attacks typically rely on outdated software because it is easier to exploit. Install updates for all software that you use to close any potential security gaps. In line with this, completely remove any software that you are no longer using because there is a high chance that it will be overlooked and become outdated, opening a door for hackers to enter," says Michael Knight.
3) A Test System
An eCommerce website needs to have a testing process for login capability, system integration, penetration and access control, insecure information transmission, performance bottlenecks, shopping cart functionality, order tracking, payment processing.
"Invest in a test system, and test updates and patches for full deployment. The financial barrier has never been lower. Virtual infrastructure is robust and if you're already using cloud infrastructure, cloning it into an isolated test area is pretty feasible. Devote some staff time into building an update cycle that works for your business. Consider it an investment in prevention that can be budgeted more effectively and predictably than mitigation," says Allan Buxton.
4) Real-time Identity Network
With the implementation of a real-time identity network, eCommerce businesses can provide end-to-end security regarding authentication, user identification, and entitlements.
"The most effective way to keep information safe is to keep crooks out of user accounts by using massive amounts of real-time data to spot and stop suspicious behavior before fraud is committed," says Ari Jacoby.
He adds, "The most common approach to trying to secure user accounts is reactionary and relies on detecting anomalies from a customer's own data, and scraping the dark web for compromised credentials - basically telling you to be careful because your house ALREADY burnt down.
A much more powerful way is to employ a real-time identity network that draws from a billion online interactions per day from hundreds of thousands of websites. That allows businesses to detect and see threats across the consumer web before those crooks even try to target an account - like pointing out smoke so you can prevent the fire in the first place."
5) Industry Recognized Cyber Risk Management Framework
Implementing a cybersecurity framework is a fundamental way of meeting an eCommerce store's legal obligations under data privacy laws, like The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), etc.
"Every technology dependent company, especially eCommerce-based organizations, must follow an industry recognized cyber risk management framework. There are many frameworks, such as NIST CSF, CIS Controls, ISO, and others," says Zach Fuller, Founding Partner of Silent Sector.
He adds, "They all have overlapping controls and contain 90% of the same recommendations. The best approach is to choose one that you feel makes sense for your organization, perform a gap analysis against that framework (or have a security company support it), and begin working toward alignment with the controls. You can look at the NIST CSF and CIS Controls spreadsheets available through a simple Google search."
6) Safe Development Framework
Backend frameworks allow web developers to address various website concerns such as scalability, turnaround time, security, etc. Jan Chapman believes that at the time of development, programmers have great responsibility and power to code it in a way that can prevent cyberattacks.
He says, "Developers programming the website can choose a stable and safe framework, like Laravel or Django. These frameworks have well documented practices following that provides prevention against SQL Injection attacks. Moreover, at the time of deployment they must deploy some advanced firewall like AWS Shield or CloudFlare."
7) Trained Employees and the Clients
With a comprehensive cyber awareness program, employees can recognize attack vectors, prevent security violations and respond to a potential threat.
"Detection of possible phishing threats is necessary to avoid further financial damage. Companies should be giving training or seminars that will keep them informed on the proper detection of possible threats from emails or any forms of media that contains these malicious messages. It is imperative for the management to create a reporting platform that connects to the IT team/department for proper checking when in doubt once a malicious message is received," says Julian Goldie, CEO of Goldie Agency.
8) Minimum Data Storage Locations
Deciding where to house corporate data requires a detailed risk analysis. Information transmission often involves passing through various countries. Any of these countries can claim jurisdiction, including countries where hackers may have intercepted traffic paths.
"If hackers find their way to your eCommerce's sensitive data from one way or another, there's nothing much you can do, so all you can do is to get prepared before it actually happens," says Jesse David Thé, CEO of Tauria.
He advises, "One great way to do this is by minimizing your data storage locations. Storing all sensitive data at a unique location that has strong access controls and frequent monitoring is much more efficient than having several, low-protected storage locations."
9) Zero Trust Security System
Zero Trust is a strategic initiative rooted in the principle of 'never trust, always verify.' By combining multi-factor authentication, identity protection, identity and access management (IAM), and next-generation endpoint security technology, this framework simplifies granular user-access control, leverages network segmentation, and prevents lateral movement.
"In a Zero Trust Security System, permission to access information would be granted on an as-needed basis. That way, there will be nothing on its trust list. This might seem like a tedious task but this is definitely a solution that works. Moreover, this security model guarantees that each permission is only going to be granted for each specific piece of data. This means that in cases where breaches still managed to happen, the risk of compromise is minimized and limited," says Andrew Raso, CEO & Co-Founder of Online Marketing Gurus.
10) Secured Payment Gateway
A payment gateway enables a secured online transaction between the merchant and a customer by encrypting data such as card and bank details.
Daniel Foley, SEO Manager at Litta, asks to avoid storing clients' credit card details on a company's database. Instead, he says, "Allow a third party, such as PayPal or Stripe, to handle payment transactions on your behalf. This improves the security of your client's personal and financial information. Also, know that keeping credit card data is a requirement for PCI-DSS compliance as well."
11) Restricted Access to Production Servers
A production server creates value for the companies by hosting live applications/websites and executing daily business processes.
"The production servers, most likely in the cloud, should be on an isolated network separate from all other IT systems. Network access should be restricted to specific whitelisted IP's and use two factor authentication for access," says Mark Herschberg, who's Fractional CTO & Cybersecurity Consultant.
What Are The Best eCommerce Security Tools?
eCommerce security tools can help entrepreneurs employ serious measures to stop the infiltration of web applications and their networks. 73.90% of eCommerce businesses use firewalls to secure their digital assets.
Below are the essential security tools.
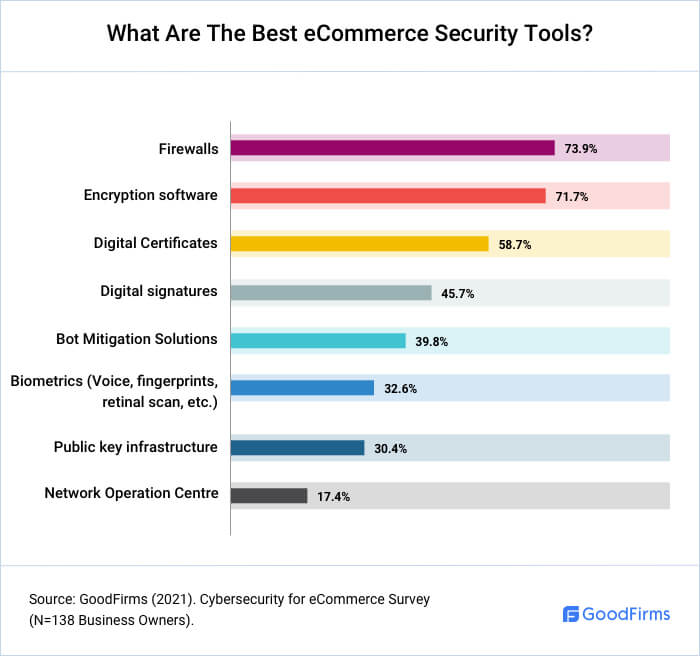
- Firewall comprises an array of features for funneling and authorization of data, in turn, ensuring the safety of large-scale data and servers.
- Encryption Software is a security program that uses one or more encryption algorithms to encrypt the content of a file, data object, network packet, or application to make it secure and unviewable by unauthorized users.
- Digital Certificates such as an SSL certificate ensure that the user's web browser is connected to a legitimate website. This prevents MitM (man-in-the-middle) attacks, where attackers insert themselves into the middle of the link to get access to encrypted data.
- Strong Antivirus Software automatically scans incoming letters and attachments, detects and blocks phishing/ransomware/DDoS attacks, and helps decrypt the encrypted data upon reaching the desired receiver.
- Bot Mitigation Solutions are essential to thwarting unwanted activities such as credential stuffing, credential cracking, content and price scraping, resource hoarding, etc. These solutions leverage several bot detection techniques to identify and block malicious bots, allow good bots to operate, and prevent the network from being overwhelmed by unwanted bot traffic.
Do Businesses Outsource Cyber Security Or Keep It In-house?
Entrepreneurs often struggle in deciding whether to rely on in-house teams or outsourced cybersecurity solutions to help protect their businesses. There are certain basic differences in both cost and efficiency between these options.
In-house teams -
- Require investment in security automation software, security tools, office space, experts, training, etc.
- Needs time commitment
- Demands heavy involvement of management
- Have better knowledge of the organization
- Blend perfectly with existing security
Outsourced solutions -
- Are comparatively more affordable, particularly for SMBs
- Can be deployed within weeks after policies review and requirement identification
- Don't require a significant management investment
- Have lack of organization-specific knowledge
58.7% of the surveyed business owners have an internal IT department to manage cybersecurity, while 21.7% outsource the service.
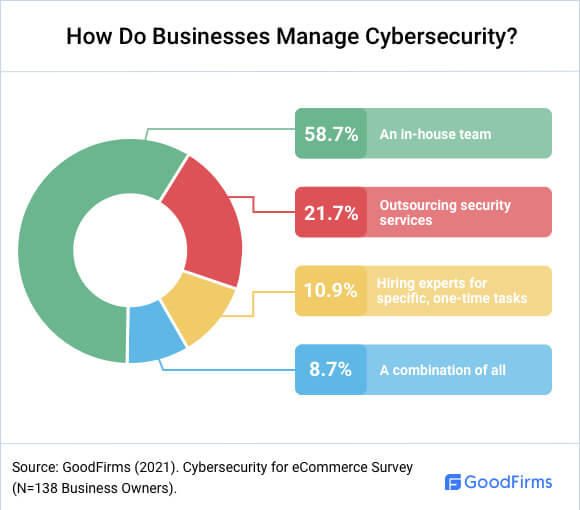
"It's best to hire the services of a third party IT company that can provide premium cybersecurity assistance. When you use the services of a reputable company, you can discover effective and fast solutions to manage and prevent all types of threats at one time. Many third party IT companies provide custom cyber-defense plans. These plans can meet the unique needs of each individual eCommerce company," says Phil Crippen from John Adams IT.
Conclusion
In the technology-dominated world, eCommerce security has become truly essential. More than ever, because many digital retail stores battle CyberWar without knowing what they are fighting for, who they're fighting against, and what weapons the fraudsters are using.
Also, 69.6% of the SMBs have moved their workloads to the cloud, creating more digital touchpoints and introducing more threat vectors. Businesses need to implement various fraud prevention measures to fend off various security threats such as malware, phishing, SQL injections, account takeovers, etc. For instance, they need to use bot mitigation solutions, antivirus and anti-malware software, firewalls, SSL certificates. In addition, they must keep software up-to-date, have a real-time identity network, industry-recognized cyber risk management framework, minimum data storage locations, and adopt other security strategies. By implementing quality cybersecurity in your workplace, you can have smooth, productive operations, reduce IT downtime, save the organization money and succeed in increasing customers' trust in your brand.
About Cybersecurity in eCommerce Survey
Goodfirms surveyed 138 business owners to learn how to set up a robust cybersecurity framework.
We sincerely thank our Research Partners for giving us insights into the prevalence of cyberthreats in the eCommerce industry.
A mix of senior-level executives and business process managers participated in this survey. These included CTOs (23.91%), CEOs (21.74%), Founders/Co-Founders (19.57%), Managers (8.70%), Security Experts (6.52%), Presidents (4.35%), MD (4.35%), and other executives (10.87%).
These respondents belonged to various sizes of companies - 97.8% of Small Companies (1-249 employees) and 2.2% of Large Companies (500+ employees).
* For any queries, drop an email to [email protected]
- Baby Items
- Born for Pets
- Claims UK
- CocoFinder
- Cosier
- DataDome
- Deduce
- Elluminati Inc
- EXPERTE
- Goldie Agency
- GSDLovers
- IDStrong
- Inboard Skate
- Incorporation Insight
- Incrementors
- InfoTracer
- John Adams IT
- Getlua
- Kasada
- Kasera
- Litta
- MSP Blueshift
- OA Design Services
- Online Marketing Gurus
- Optimising IT
- Pandio
- PowerBank Expert
- Restore Privacy
- Secure Data
- Security.org
- Silent Sector
- Strupek
- Surfky
- Tauria
- TautUSA
- The Charming Bench Company
- The Critter Depot
- The Smith Investigation Agency
- Twiz LLC
- Virtina
- Wethrift
- Wincope
- YOTTAA
Table of contents
- How Many Organizations Have Experienced Cyber Threats?
- What is eCommerce Security?
- What Are The Top Security Threats To eCommerce Websites?
- What Are The Best eCommerce Security Solutions for SMBs?
- What Are The Best eCommerce Security Tools?
- Do Businesses Outsource Cyber Security Or Keep It In-house?
- Conclusion
- About Cybersecurity in eCommerce Survey









