ABSTRACT:
The global waste recycling market is among the emerging sectors of vast market potential and numerous opportunities. The waste recycling market is playing a crucial role in protecting the environment from the different types of waste generated by humans, municipalities, and industries. The waste recycling market has witnessed rapid growth due to governmental policies and consumer awareness of using reusable and recyclable products. In addition, several legislations and regulators such as RCRA, EPA, etc. are also contributing to the development of the global waste recyclable market.
This research report by Goodfirms titled "Global Waste Recycling Market - Then, Now, and Future" aims to discover the different aspects of the Global waste recycling market, including drivers, key players, legislations, etc. In addition, this report explores and analyzes the concept of zero waste, waste recycling classification, waste recycling types, etc. The study also identifies the current market challenges and future opportunities in global waste recycling.
Table of Contents:
Introduction
Global Waste Recycling Market - Overview
Current Legislations and Regulators in Global Waste Recycling Market
- Legislations Governing Global Waste Recycling Market
- Regulatory Organizations for Waste Recycling
- Role of Different Stakeholders in Global Waste Recycling Market
Classification of Waste Recycling
Types of Waste Recycling and Management Procedures:
- Radioactive Waste Recycling
- Apparel Waste Recycling
- E-waste Recycling
- Biomedical Waste Recycling
- Plastic Waste Recycling
- Paper Waste Recycling
Drivers of Global Waste Recycling Market
- Increased Consumer Awareness About the Environmental Impacts of Waste
- Waste Trade is Going Global
- Growth in E-waste
- Waste Mismanagement
- Unhealthy Eating Habits
- Technological Advancements
- Governmental Programs and Policies
Trending Technologies in Global Waste Recycling Market
- Use of AI in e-waste recycling
- Real-time solid waste management using Solar Energy
- Waste recycling management through IoT
- Upgraded Pyrolysis for Plastic is Gaining Traction
Challenges in Global Waste Recycling Management:
- Incineration: Chemical Recycling is a Misnomer
- Surge in Biomedical Wastes Due to COVID19
- Environmental Contamination and Health Impacts due to E-waste Recycling
- Trade Restrictions placed by the Chinese government
Future of Global Waste Recycling Market
- Environmental Regulations are Becoming Increasingly Important
- Inclusive Behavior is Opening Opportunities
- 5G Will Take Waste Recycling to the Next Level
- Waste-to-Energy(WTE) Initiatives Will Boost Recycling
- Implications and Opportunities for CPG Companies
Zero Waste: A New Paradigm for Recycling in Circular Economies
Key Findings
Conclusion
References
Introduction
The surging amount of waste from different industries and households is a major concern for humans. Globally, around 2 billion tonnes of solid waste is generated by humans through industries, businesses, and households. On average, a person produces around 0.7 kg of waste on daily basis. There is a direct link between waste and income as the more a person earns, the more he will spend on buying which results in waste in the end. In addition, industries also hugely contribute to waste generation. Around 19% of global waste is recycled at the present time and more efforts are being made to recycle more waste which represents the huge scope of the market.(1) Recycling came into existence because of the need to reutilize the increasing waste instead of disposing of it in the environment.
The market share of recycling facilities has been rapidly growing, leading to global waste recycling market growth. In addition, increasing awareness among consumers and rising environmental issues are also contributing to the success of the waste recycling market. However, despite rapid growth, the global waste recycling market is also experiencing many challenges associated with incineration, an increase in e-waste, environmental contamination, etc. There is a dire need to address these challenges in a structured and proper manner.
This research titled: 'Global Waste Recycling Market - Then, Now, and Future' by Goodfirms attempts to explore the nuances of the global waste recycling market along with the significant drivers, key players, legislation, and regulatory organizations. The study further analyzes some crucial concepts of the waste recycling market, such as different types of waste recycling, classification of waste recycling, Zero waste concept, trending technologies, etc. This research also identifies the challenges and opportunities in the global waste recycling market.
Global Waste Recycling Market - Overview
The global waste recycling market is among the rapidly growing industry segments in 2022. Valued at $55.1 billion in 2020, the global waste recycling market may become a $90 billion industry by 2030.(2) Increasing awareness regarding the negative impact of waste on the environment and efforts from all stakeholders (Consumer, Industries, Governments, Regulators, etc.) will lead to this considerable growth.
However, an increase in waste generation will always be the prime driver. In addition, the Covid-19 pandemic is also leading to a new type of waste i.e., Pandemic waste that includes masks, PPE kits, gloves, etc.
The global waste recycling market is also experiencing various issues that can be addressed with the latest technologies, such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, machine learning, etc. Strict regulations are also being implemented and imposed upon businesses and consumers by the legal authorities for waste recycling and management.
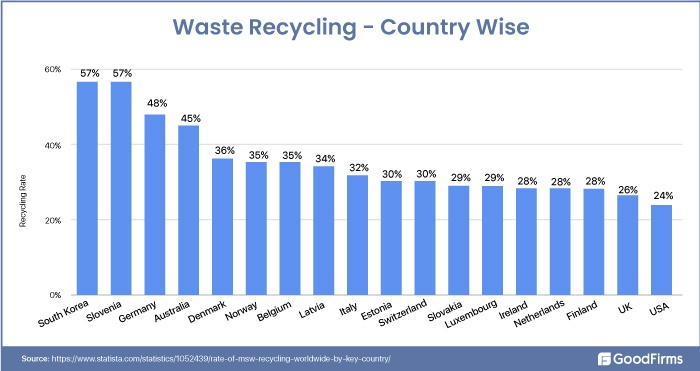
Global Waste Recycling Market - Country Wise
At present, humans are generating different types of waste such as municipal solid waste, hazardous waste, industrial non-hazardous waste, agricultural and animal waste, medical waste, radioactive waste, construction and demolition debris, extraction and mining waste, oil and gas production waste, fossil fuel combustion waste, etc. Each and every country generates different amounts of waste which are also recycled at different recycling rates. Waste management is one of the key UN sustainable development goals which almost every country on the planet is making efforts to accomplish. Some countries perform well in waste recycling and management, whereas others perform on average.
(source)
South Korea and Slovenia are among the top countries with high waste recycling rates.
In South Korea, Waste recycling and management have been a critical priority for the last three decades. The country has one of the most robust waste management and recycling programs around the globe. These programs include legislation and initiatives such as a deposit-refund system, volume-based waste disposal system, extended producer responsibility, etc., to ensure minimum waste with rapid urbanization.(3) The country's waste is segmented into recycling, landfill, incineration, and composting for adequately managing the waste.
Similarly, Slovenia is also consistently making efforts to recycle its waste. Fifteen years ago, Slovenian waste went directly to landfills, but Slovenia is currently recycling around 75% of its waste.(4) From vast landfills in the past to clean cities at present, Slovenia has achieved a lot in the last few years. The Centre for waste management came into existence in 2015 to ensure zero waste. Less than 5% of waste is now going to landfills, and the remaining waste is sent to processing facilities for making solid fuel and recyclable materials.
Germany is also a leading country in recycling and waste management both at the European and global levels. Over the last few decades, the government has accomplished untamed progress in recycling and waste reduction. Germany is the leader in recycling because of the plans and policies such as the circular economy framework, waste hierarchy principles, Polluter pays schemes, subsidiary programs, etc.
Australia is another giant in the room in waste management and recycling. The Australian government invests heavily in waste management initiatives to promote recycling and waste reduction through its National Waste Policy. "Waste Less, Recycle More" is one such program by the Australian government with a budget of over $330 million.(5) The country is further aiming to move from this program to waste and sustainable materials strategy 2041 to reduce and eliminate waste going to landfills.
The UK is also slowly progressing in improving waste management through recycling. Despite producing millions of tons of plastic waste, the country gradually increases its plastic recycling rate through regulations and legislation. The deposit return scheme, packaging produce responsibility system reforms, and environmental act 2021 are some efforts by the UK parliament to ensure a high recycling rate consistently. The country is also experiencing more waste due to import restrictions placed by China on plastic waste. This is another reason behind the UK's adoption of more recycling strategies.
The USA also highly focuses on waste recycling to achieve a high recycling rate through proper regulations and initiatives. The country is working on several strategies like the National Recycling Strategy to achieve a 50% waste recycling rate by 2030.(6) Five objectives were determined by the US in 2021 for creating a cost-effective and more resilient recycling system. These are as follows:
- Improving the recyclable commodities market to promote development, increasing manufacturing of recyclable materials, etc.
- Enhancing the material collection and management infrastructure to increase awareness among people, continuing to fund research, improving trash collection, etc.
- Preventing the contamination in the recycling materials stream ensures the availability of resources and better quality of recycled material.
- Implementing proper programs and policies to assist the circular economy by strengthening federal coordination, conducting analysis of recycling challenges, etc.
- Developing new measurement standards and data collection methods for measuring targets, tracking performance indicators, creating recycling content measures, etc.
The USA and UK are among the most developed and technologically advanced countries of the 21st century. However, both countries do not have such an advanced level of waste recycling. Both USA and UK are among the worst countries when it comes to waste recycling. Their recycling rates are even lower than the recycling rates of smaller countries like Slovenia, South Korea, Latvia, etc. A strong focus on industrialization and production are among the prominent factors due to which these countries focused less on recycling in the past. These countries are slowly progressing towards waste recycling in terms of strategies, techniques, and investments.
Major Players in Global Waste Recycling Market
The global waste recycling market is growing, and so does the number of firms engaged in waste recycling and management activities. New organizations are regularly launching new procedures and technologies to recycle waste.
Some of the major players in the global waste recycling market are as follows:

Waste Management Inc.: A US-based firm with a turnover of around $4.66 billion in March 2022.(7) The company has been actively involved in waste disposal and recycling since 1968. With the help of its vast network of recycling plants, disposal sites, and vehicles, the company is providing its services to commercial, municipalities, and industries. In addition, Waste Management Inc is among the leading recycler and renewable energy providers in the US, providing trash collection, treatment, disposal, recycling, etc. services in multiple countries.
Novelis Inc.: Novelis Inc. is another global recycling giant with multiple recycling facilities worldwide. The company strives to provide high-quality recyclable products through its recycling footprint and international manufacturing units. With a revenue of over $1 billion in March 2022, Novelis Inc. serves several industries such as beverages, automotive, aerospace, and Specialty markets.(8) It is one of the largest aluminum can recyclers and rolled aluminum producers globally.
Republic Services: Republic services is another waste disposal giant that began its operations in 1981. Republic Services is an industry leader in e-recycling and waste disposal. With its 16,000 trucks in service, Republic Services is among the most prominent American fleet owners. The company has an efficient network of recycling facilities, landfills, and transfer stations for proper disposal and recycling activities. The revenue of Republic services at the end of 2021 was around $11.3 billion.(9) The company serves more than 14 million customers all over the globe through its sustainable and recyclable solutions.
Veolia: Veolia is a French corporation engaged in waste management, water control, and electricity resources. On 21 January 2022, Veolia recently acquired another French company named Suez to form the largest environmental company on Earth.(10) Veolia provides a wide range of services, including waste treatment, management, recycling, and disposal in more than 35 countries.
Covanta Holding Corporation: Covanta is a waste management firm headquartered in New Jersey, USA. The motto of the company is "no waste to be wasted." The organization actively serves consumers in energy recovery, solid waste management, garbage recycling, etc. The organization was recently merged with EQT infrastructure for $5.3 billion to improve its sustainable offerings.(11) With this merger, Covanta and EQT infrastructure aims to assist the circular economy by optimizing waste output.
Remondis: A leading German waste management business offering different services to commercial, industrial, business, and local authorities. Remondis handles over 30 million tonnes of waste materials each year, with over $ 8 billion in annual turnovers.(12) The organization aims to become a leader in metal and steel recycling by acquiring the TSR group. Remondis uses recycled products from the recovered waste as alternative energy sources.
Current Legislations and Regulators in Global Waste Recycling Market
Legislations Governing Global Waste Recycling Market
Different countries have different laws and regulations for waste management and recycling. There are no international rules that govern the global waste recycling market; instead, the governments control their respective waste recycling market through some laws and regulations.
The Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011: Introduced in 2011, the waste regulations set the requirements for businesses and stores to transport, collect, recover, and dispose of waste. Under this regulation, waste management options must include prevention, reuse, recycling, recovery, and disposal are considered a waste hierarchy. The waste regulations state that businesses should focus on the waste management hierarchy while handling or transporting the waste. The Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011 applies to all the businesses involved in waste production, transportation, waste disposal, storage, etc., and its the successor of The Hazardous Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2005 that came into effect in July 2005.
Under the 2005 Order, any organization that produces more than 500kg of waste needs to notify the environmental agency regarding their waste production quantity, processes, chemical components, etc.(13) In addition, the organizations should also provide quarterly information and statistics to the environmental agency in Wales and England regarding waste recovery and disposal.
The Hazardous Waste (England and Wales) Regulations, also known as the successor of the Special Waste Regulations Act,1996, address the issue of landfills and increase the transport of waste to treatment and recycling facilities.
Covered Device Recycling Act: The covered device recycling act was enacted by the government of Pennsylvania on 23 November 2010. This act provides the framework for forming a recycling program for several types of devices, such as electronics. This act also set the duties on the businesses involved in the making or selling several covered devices such as TV, computer, peripherals, etc. Companies should ensure such waste should be collected, transported, and recycled correctly without compromising the environment.
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act: also known as RCRA, is a US law that gives authority to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to control and handle the entire hazardous waste stream of the US from generation to disposal. EPA, under this act, ensures the safe treatment of hazardous waste through strict guidelines, regulations, and policies. RCRA aims to encourage the reuse and elimination of waste in both non-hazardous and unsafe. RCRA also provides a framework for solid waste management in the USA through subtitles C and D.
Regulatory Organizations for Waste Recycling
ISWA, or International Solid Waste Association, is a nonprofit organization that aims to promote waste management and sustainable development worldwide. The organization is highly focused on information exchange across countries on solid and liquid waste management aspects. ISWA consistently works to increase reuse and reduce waste through recycling, collection, and proper treatment.(14) The vision of the International solid waste association is to dispose of the residual waste in safely engineered ways to accomplish a healthy and clean environment. The organization organizes events and campaigns at regular intervals to address the challenges of waste recycling. ISWA is also assisting several working groups involved in sustainable waste management.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency is another body focused on waste regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). EPA ensures that the goals of RCRA are fulfilled by properly disposing of the waste, conserving natural resources and energy through recovery and recycling, and waste elimination. EPA is working with several offices, such as the Office of Air and Radiation, the Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention, the Office of Land and Emergency Management, the Office of Research and Development, etc., to ensure people and institutions follow the waste management regulations.
Role of Different Stakeholders in Global Waste Recycling Market

In the global waste recycling market, several stakeholders play an essential role in ensuring that waste recycling occurs correctly. Each of these stakeholders is responsible for their activities and requires carrying out their activities together to eliminate the challenges and issues of waste recycling. Some of such stakeholders are as follows:
Government: The role of the government is to develop clear policies and plans to improve recycling conditions, waste collection sorting, and measure workability and public consensus building. In addition, the government also promotes general health and well-being by disposing of the waste away from society. The government, with the assistance of other agencies and pollution control boards, monitors the entire waste recycling and management stream to ensure proper recycling and disposal of waste.
Consumers and waste generators: These stakeholders also play a crucial role in the waste recycling market. Such stakeholders generally include households, industries, businesses, etc., that generate waste through their activities and processes. The part of such stakeholders is to ensure that they are generating minimum waste through their production and other procedures. In addition, they are also responsible for providing cooperation in waste collection sorting and developing environment-friendly products. Consumers, such as local people, are responsible for lowering the waste from their homes by using recycled and reusable products.
Waste management and recycling organizations: These organizations, such as recyclers, coprocessors, waste collectors, etc., are responsible for providing basic facilities to the waste recycling market, such as storage, collection, transportation, etc. These organizations have the role of ensuring that waste is properly collected, transported, and stored in the waste recycling centers without much impact on the environment.(15) Such organizations also provide one-stop solutions for societies and communities to recycle their waste from the trash.
Trade and Industry (End market): Trade and Industry stakeholders include manufacturers, sellers, and distributors of recycled products and materials. These stakeholders provide cooperation between different manufacturing industries and promote the technological development of the entire chain. The primary role of such stakeholders is to develop products that can serve the customer needs along with proposal disposal or recycling characteristics after use.
Classification of Waste Recycling
Waste recycling is a boon for societies at present that is addressing a variety of waste problems for the world and its inhabitants. Waste recycling is mainly classified into two types: based on sources and based on type. These two are discussed below in detail:
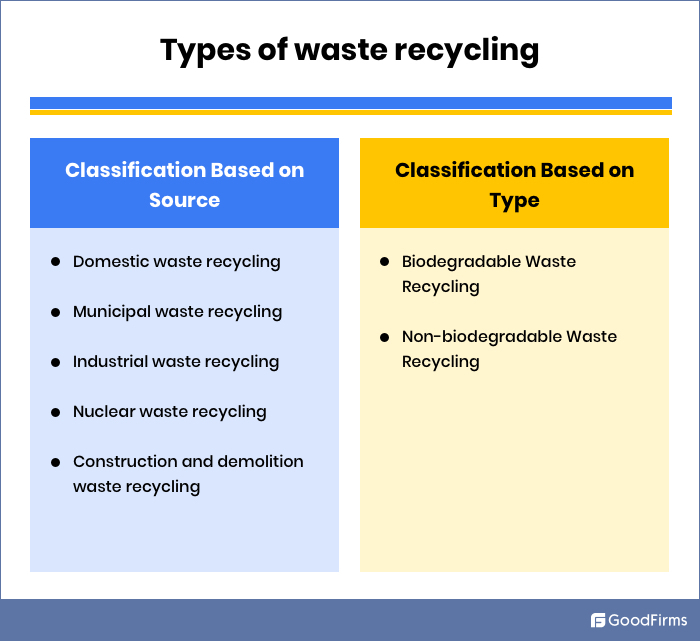
Classification Based on Source
These include different sources through which waste is generated in societies. Domestic waste recycling, industrial waste recycling, municipal waste recycling, Nuclear waste recycling, construction and demolition waste recycling, etc., are some types of classification based on the source.
Domestic waste recycling
Domestic waste recycling is considered the key to preventing municipal waste, as a considerable amount of waste is generated by households. In previous decades, domestic waste was disposed of using incineration or landfills, which led to rising in several issues ranging from environmental to human health.(16) Due to this, domestic waste recycling came into effect to address the rising domestic waste.
The majority of solid waste from household include food waste, plastic, paper, etc., that are now trashed and collected separately. The domestic liquid waste is treated at sewage plants where toxic chemicals are removed from the water. Through this, recyclable materials are sent to recyclable plants, and harmful materials are sent to disposal facilities, leading to effective waste management.
Municipal waste recycling
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) - called as trash or garbage includes the recycling of waste generated through different municipal activities such as the construction of buildings, highways, street cleaning, household waste, etc. MSW is first aggregated based on the types and then sent to waste recycling facilities if qualified for recycling. Also, municipal waste recycling can drastically improve the economic viability of municipal solid waste-to-energy facilities through proper infrastructure and framework.
The liquid waste from municipal corporations is treated either in sewage facilities or chemical treatment facilities, where water is filtered out, and the remaining chemical, biological or physical composition is disposed of properly.
Industrial waste recycling
Industries, factories, food processing facilities, manufacturing plants, etc., are also contributing to a lot of waste produced on Earth. These sources generate a vast amount of solid and liquid waste through their different processes and activities. Such waste includes chemicals, scrap metals, building materials, tanneries, coal, etc., left after the product development. Most of this waste is sent to recycling facilities where waste scanning machines separate recyclable and non-recyclable waste. Recyclable waste is recycled, and the remaining waste is disposed of using incineration or pyrolysis.(17) Industrial waste includes hazardous and non-hazardous materials which are treated differently as per their characteristics.
Nuclear waste recycling
Nuclear waste is piling up at a rapid pace in nuclear power plants and bio-research facilities all across the globe. This highly radioactive waste usually comes from sources such as leftover fuel from nuclear power plants, byproducts of nuclear reactors, decommissioning nuclear facilities, etc. In addition, waste from hospitals and research facilities also contains radioactivity. Vitrification is one of the most commonly used Nuclear waste recycling methods aimed at reducing nuclear waste. Through nuclear waste recycling, new fuel, and nuclear byproducts are being developed by different countries.

Construction and demolition waste recycling
Construction and demolition waste usually include waste generated from renovations, construction, demolition, and repair of houses, buildings, bridges, roads, etc. It contains steel, wood, concrete, plaster, bricks, metal, etc. Some of this waste, such as bricks, plaster, etc., are reused in constructing new infrastructures such as buildings and roads. Other materials such as steel, wood, concrete, metals, etc., are recycled to develop recyclable products.
Human wars and conflicts also produce construction and demolition waste. The recent invasion of the Russian Federation on Ukraine resulted in a huge amount of this waste from damaged buildings and cities that will cost around £3.6bn to Ukraine.(18)
Classification Based on Type
Waste recycling is divided into two types based on the chemical, physical and biological characteristics of waste. These two types are biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste recycling.
Biodegradable Waste Recycling
Biodegradable waste includes remaining organic materials that can degrade from complex simple compounds such as textiles, paper, food waste, peels of fruits and vegetables, etc. Most biodegradable materials are not fit for recycling as they can pose risks to the recycling process. Such materials are composted instead of recycling, whereas other materials like paper are sent to recycling facilities.
Non-biodegradable Waste Recycling
Also known as recyclable waste, non-biodegradable waste includes inorganic materials such as plastic, metals, glass, cans, etc. Most of the non-biodegradable waste is recycled into new products. Some waste that does not qualify for recycling is sent to landfills and factories for disposal and incineration.
Types of Waste Recycling and Management Procedures:
Human societies have used waste recycling for centuries. Throughout these centuries, they have kept inventing new methods to recycle different types of waste. Some of the waste recycling types evident in present-day societies include e-waste, bio-waste, plastic, fashion apparel, radioactive waste, paper recycling, etc. It positively influences human societies to reduce their carbon footprint and regulate waste effectively.
Radioactive Waste Recycling
Radioactive waste comes from nuclear centers, hospitals, industries, research centers, etc. Some radioactive waste is recyclable such as uranium, plutonium, and thorium can be reused for powering other conventional reactors. In addition, some of this waste is also recycled to produce electricity which is served to nearby areas.
Through radioactive waste recycling, different countries are effectively reducing their carbon footprint to preserve the environment.
Apparel Waste Recycling
Fabric waste recycling is one of the critical steps in achieving a full-fledged circular economy. The organizations are using open-loop and closed-loop tactics in recycling apparel waste. The open-loop strategy allows the development of new material from old waste, whereas the closed-loop approach enables the development of the same product from the trash.
Apparel waste recycling is generally categorized in three approaches, i.e. chemical, mechanical, and biochemical. These approaches use different mechanisms, such as melt extrusion, shredding, carding, depolymerization, dissolution, etc., to recycle the waste generated by fashion and other types of apparel.(19) The Apparel waste recycling market is also experiencing several challenges associated with material complexity, quality issues, reverse logistics processes, etc. These should be addressed as soon as possible.
E-waste Recycling
Since the internet discovery, countless units of electronic equipment such as mobile phones, televisions, computers, etc. have been purchased by consumers. E-waste is growing alarmingly as the devices become obsolete in a few years, leaving behind massive waste in plastic, metals, electronic parts, mechanical parts, etc. This waste is treated through recycling, incineration, or disposal to landfills.(20) In addition, batteries from devices, cars, machines, etc. also contribute to the e-waste recycled into facilities. However, e-waste recycling is considered non-environment friendly due to which new eco-friendly recycling e-waste methods are needed.
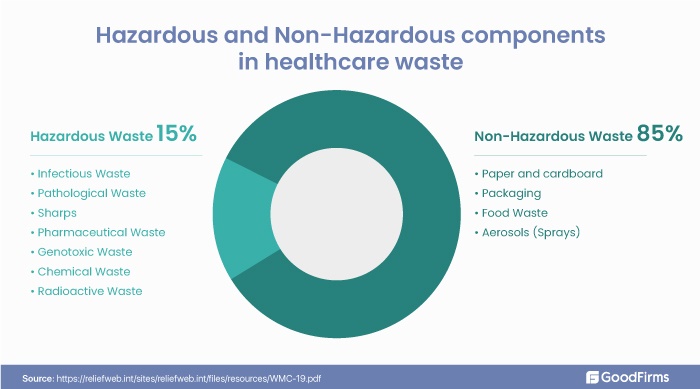
Biomedical Waste Recycling
Bio-medical waste includes all the hazardous and non-hazardous waste produced by healthcare institutions and processes. This waste contains infectious waste, pathological waste, chemical waste, pharmaceutical waste, etc. The surge in biomedical waste due to covid-19 pandemic is also stressing the need to recycle biomedical waste. Some bio-medical trash, such as plastic syringes, packaging, food trays, etc., can be easily recycled compared to chemical or pathological waste. Due to this, biomedical waste is now separately collected and managed.
Plastic Waste Recycling
Plastic is one of the most used materials globally that is hugely polluting almost all ecosystems ranging from land to water. In addition, plastic is a non-degradable material, due to which recycling becomes much more essential. The plastic content is rapidly increasing in the municipal waste stream due to consumer goods, automotive, construction, packaging, etc. Even in the UK, plastic is used in multiple industries such as agriculture, furniture, electronics, building construction, medical, footwear, etc., generating vast amounts of trash in the European region.(21) Global institutions like OECD are suggesting several practices to tackle the growing plastic waste as follows.
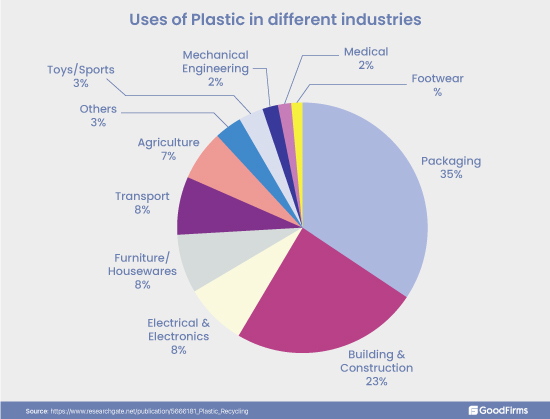
- Making changes in the design of products such as technological implementations, using alternatives of plastics in packaging, etc.
- Developing improved waste management systems for boosting recycling rates, improving trash collection, etc.
- Organizing remediation and clean-up activities to collect trash from oceans, rivers, beaches, etc. to remove plastic from natural habitats.
Microplastics are plastics that hugely impact human lives and the environment. From the arctic to Antarctica, microplastics damage natural ecosystems, and the worst part is that they cannot be easily quantified or recycled. Plastic waste management is usually done through incineration, recycling, landfills, etc., excluding microplastics.
Paper Waste Recycling
The paper industry also contributes to the total municipal waste generated by institutions and households. Over the last few decades, paper waste has increased significantly posing a severe threat to the environment and the sustainable development goal of waste management. Most of the paper waste collected through industries, organizations, and households is sent to recycling. Remaining paper waste, such as paper towels, paper cups, laminated paper, etc., are sent to landfills and incinerated as per the material types. Through recycling, new products such as cardboard, notebooks, etc. are developed from paper waste, which can again be recycled upto seven times. Investments in water, electricity, funds, etc., are needed to ensure paper recycling without any issues.
Drivers of Global Waste Recycling Market
The global waste recycling market is growing at a rapid pace. This growth is driven by some drivers which are contributing to the success of this market. Increasing consumer awareness, growth in e-waste, and waste mismanagement are some of the drivers that are shaping the global waste recycling market.
Increased Consumer Awareness About the Environmental Impacts of Waste
At present, humans have access to a different medium of mass communication, due to which information spreads rapidly and quickly. This has resulted in increased consumer awareness regarding the waste they produce through their consumption. This changing perception leads to the rise of a new consumer movement toward waste management. Recycling rates and the use of recycled products are increasing worldwide, leading to the growth of the global waste recycling market.(22) In addition, consumers are increasingly avoiding the use of plastic in packaging and other activities to support the environment. Consumers are even demanding eco-friendly products and packaging to ensure lower waste.
Waste Trade is Going Global
All around the world, there is a growing demand for sustainable, low-impact ways to deal with waste. As a result, waste trading among countries and businesses around the world is becoming an increasingly important industry. The waste trade is the business of buying and selling waste. For example, companies can buy recyclables from households, process them, and then sell them to manufacturers to make new products. Waste traders are involved in all parts of the process, from collecting waste to disposing of it and everything in between. Businesses are turning to waste traders to help them dispose of their waste in a responsible and efficient way.
Growth in E-waste
E-waste is one of the most common forms of waste evident in present-day societies. Around 57 million metric tons of e-waste was generated in 2021 due to the improving spending power of consumers.(23) This is another major driver behind the growth of the global waste recycling market as e-waste contains materials like plastic, aluminum, copper, etc. that can be recycled back into new products. Electronic devices are being used in both households and businesses for different purposes, contributing to E-waste growth.
Waste Mismanagement
Most countries are trying to manage their waste effectively, but the majority still lack the proper waste management frameworks and systems. Especially in developing countries, open dumping and open burning are still considered the final disposal systems.(24) This is also resulting in the growth of the global waste recycling market as open dumping and open burning result in the rise of various health and environmental issues among the people.
Unhealthy Eating Habits
People in the present time have access to a massive variety of food items that are available at stores, restaurants, and online platforms. Due to this, they tend to avoid eating at home and prefer to eat fast food, beverages, etc., outside, which is considered an unhealthy eating habit. These food items also leave trash in packaging, food wastage, etc., which is a significant part of municipal solid waste.
Technological Advancements
Humans have been focusing on waste recycling for the last few centuries, but their success rate has increased with the new technological developments. New recycling methods and frameworks kept on developing with new technologies. Manual labor work of the past is now automatically carried out through machines. In addition, technologies such as infrared and Artificial intelligence are currently used for waste sorting and management. More new developments in waste recycling are expected in the upcoming time through combining AI/ML, IoT, etc., together. Several waste management and recycling software are already available in the market for streamlining the administrative and production processes of recycling facilities. Some software like Waste Atlas is useful in comparing and benchmarking the global solid waste management and recycling.
Governmental Programs and Policies
The policies and programs of several countries aim to reduce waste and increase the adoption of recyclable products and also contribute to the growth of the global waste recycling market. The US government is providing funding to businesses working in the waste management market.(25) The UK government is also funding $23.5 million for waste management activities and campaigns.(26) Some governments are also providing incentives and subsidies to businesses involved in waste management and recycling, opening new opportunities for organizations.
Trending Technologies in Global Waste Recycling Market
Use of AI in e-waste recycling
In the past few decades, immense technological growth has contributed much to the increase in e-waste. This increase in e-waste is also a driving force for the e-waste recycling market, which is expected to be valued at over 90 billion by 2030.(27)
Artificial Intelligence is offering robust opportunities to recycle this vast amount of e-waste. From waste collection to recycling operations, AI assists multiple e-waste recycling functions and processes using its deep learning algorithms. Some of such procedures and processes are as follows:
- Real-time monitoring and tracking of waste recycling bins, trucks, and trash places.
- E-waste robotic recycling systems collect, identify, and recycle waste from households and industrial spaces.
- Managing toxic and harmful waste with less human intervention.
- Segregating distinct materials from solid e-waste using sensors, cameras, etc.
Artificial Intelligence significantly impacts the cost and recycling operations, making them more innovative and more efficient. AI is assisting humans in determining significant patterns of waste recycling evaluation to drastically improve the time and the costs of the recycling process.
Real-time solid waste management using Solar Energy
In solid waste recycling management, solar technology also plays a pivotal role in supporting various functions. Solar energy is useful in powering trash bins and containers to work, irrespective of electricity availability and issues. In addition, solar energy is also helpful in preventing downtime and connectivity issues between servers and waste management personnel. Solar energy is working as an autonomous power supply method so that sustainable energy can be utilized for waste recycling and management.
Waste recycling management through IoT
The Internet of Things also efficiently contributes to smarter waste recycling using IoT technology. A waste recycling system has several elements associated with storage, generation, transportation, collection, and recycling that can be integrated with IoT tools such as sensors, IoT platforms, gateways, etc. IoT rapidly optimizes the waste collection, management, and recycling processes in several areas. Two such areas are as follows:
Smart Bins: IoT technologies such as sensors, RFID, and image recognition in smart bins allow the authorities to determine the trash level in dustbins. In addition, sensors in these bins help classify and recognize the different types of waste trashed in containers.
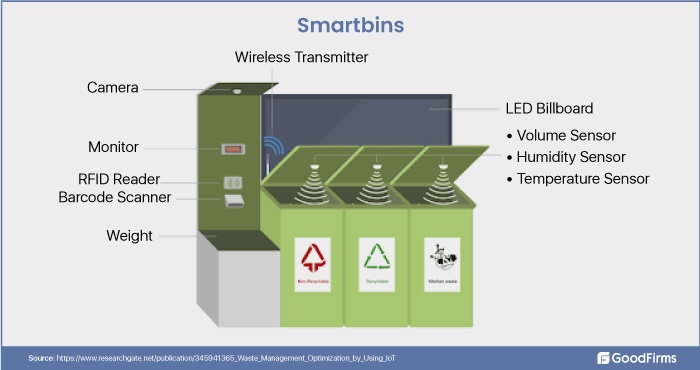
(source)
Smart Trucks: IoT-based smart trucks are also crucial in waste recycling and management as they provide real-time reporting and alerts associated with route status, load weight, service completion, etc. In addition, smart trucks are also fruitful in serving a safe working environment for people.
IoT integration in waste recycling leads to several benefits, such as reducing CO2 emissions, enhanced waste recycling analysis, reduced costs, etc.
Upgraded Pyrolysis for Plastic is Gaining Traction
The incineration of plastic products for power generation was an old practice. The primary issue of this practice is that it leads to the excretion of undesirable pollutants such as furans and dioxins in the environment. Due to this, tackling the growing plastic waste has become a significant issue for institutions around the globe.
Technologies such as pyrolysis contribute to the development of new forms of recyclable plastic. Plastic products developed through pyrolysis are also helpful in replacing the chemically produced products.
In previous times, pyrolysis also contributed to the release of undesirable pollutants into the environment and other issues such as the development of improper products and additional processing. Upgraded bitumen, i.e., Hydrochemolytic Plastics Upcycling (HPU) is used by some organizations in converting their liquid hydrocarbons to plastics under controlled and milder conditions.(28)
The organizations are also doing upgradation in other forms of plastic such as Polypropylene and Polystyrene to make them recyclable.
However, as good as it sounds, pyrolysis comes with several challenges, such as the formation of toxic chemicals, dioxins release into the environment, etc.
Challenges in Global Waste Recycling Management:
Incineration: Chemical Recycling is a Misnomer
World administrations that adopt modern technologies for converting waste into energy, especially plastics into fuel(29), are misreading recycling processes. Converting plastic to fuel by burning or waste incineration leads to the production of toxic chemicals, air particulate matter, and dioxins that are harmful to humans. Plastic chemical recycling is not a credible way to mitigate plastic waste issues. In the end, the final product is again plastic, and the byproducts are toxic greenhouse gases.
Surge in Biomedical Wastes Due to COVID19
The pandemic has caused an unanticipated surge in the biomedical waste category, with tons of discarded masks, aprons, plastic/latex gloves, bottles of sanitizers, face shields, cleaning agents, etc., added to the environment every day. The pandemic also affected the global waste disposal system causing more stress to the terrestrial environment. As the disruption was sudden, the medical industry and the governments around the world were not prepared with reusable bio-medicals such as reusable non-plastic PPE kits. Governments seek effective management of medical waste to prevent further health risks to humans and marine life.
Environmental Contamination and Health Impacts due to E-waste Recycling
The tsunami of e-waste in both developed and developing countries leads to various health and environmental problems. The recycling of e-waste adversely influences environmental contamination in terms of heavy metals, organic pollutants, etc. In addition, this environmental contamination impacts the health of engaged workers, site inhabitants, nearby residents, etc.(30) Some of these environmental contaminations and health impacts of e-waste recycling are as follows:
- Fishes living in water bodies near recycling facilities consume water pollutants and metals that pose health risks for non-veg people.
- Detection of metals in the soil around e-waste recycling facilities leads to soil pollution and increased carcinogenic risk.
- Exposure to inorganic arsenic substances also contributes to rising health issues among children and harms the environment.
- Dioxin-like compounds and microplastics also create health issues for the people living in and around e-waste recycling facilities.
Trade Restrictions placed by the Chinese government
Recently, the People's Republic of China placed a ban on solid waste imports by issuing a notification to the World Trade Organization. Around 35 types of waste materials, including plastics, have been denied entry to China to protect the natural environment and human health. This poses a threat to global waste recycling as the ban impacts the entire waste management trade chain.
Future of Global Waste Recycling Market
Waste recycling has been an integral part of waste management for several centuries. Throughout these centuries, the methods and activities of waste recycling kept on changing with technological advancements. In the future, the recycling market is expected to see several opportunities to reduce waste and preserve the environment.
Environmental Regulations are Becoming Increasingly Important
With the growing focus on waste recycling, environmental awareness is also increasing. This is contributing to the development of new regulations which never existed before. In addition, some such regulations also aim to address the challenges of climate change and recycling. Environmental regulations will play a major role in the future growth of the global waste recycling market.
Inclusive Behavior is Opening Opportunities
With the different available mediums of mass media, consumers are becoming more aware of their carbon footprint. More people are now using reusable and recyclable products, leading to growth in the global waste recycling market. The rate at which consumers are shifting to eco-friendly and recyclable products will continue to increase in the near future. This will result in massive demand for products that promote environmental well-being instead of damaging nature. In addition, not only people but various institutions and governments are also closely working together to ensure proper waste management and recycling.
5G Will Take Waste Recycling to the Next Level
The deployment of 5G infrastructure is making the concept of smart cities a reality. In addition, IoT is also boosting the implementation of Smart cities in which the majority of things work without human intervention. From garbage collection trucks to automatic recycling after waste segregation, 5G rapidly transforms the industrial landscape through automation and robotics. Strategies such as underground waste management, resident recycling network, waste collection optimization, etc. are being tested and implemented by different countries for automatic waste management and recycling. More new recycling tactics and technologies can occur in the upcoming time after 5G becomes normal.
Waste-to-Energy(WTE) Initiatives Will Boost Recycling
The waste-to-energy market is rapidly growing and is expected to cross $50 billion by 2027.(31) In waste to energy, waste is burned to produce energy such as electricity and steam. Waste to the energy market is rapidly becoming an integral part of the circular economy, due to which governments are highly focused on this. In addition, this concept also addresses future resource scarcity issues. Governments are also introducing new initiatives so that businesses and people can quickly work on waste recycling and reduction.
Implications and Opportunities for CPG Companies
Consumer packaged goods are the ones that people frequently use in their daily lives. Such products include cosmetics, food, cleaning accessories, beverages, etc. CPG companies generate vast amounts of plastic waste throughout their production and supply chains. Now organizations are coming up with new policies and strategies to reduce their carbon footprint and eliminate plastic waste, to move towards a more sustainable environment. Some organizations have already started adopting the latest technologies to enhance the customer experience while reducing plastic waste. Some CPG companies are even experimenting with their products in terms of refillable containers, reusable packaging, and fully compostable packages.

Coca-Cola, a world-known beverage company, uses 100% recycled plastic to manufacture its bottles. This will reduce plastic use in the organizational processes by 20%. Through this commitment, Coca-Cola aims to improve its environmental footprint by recycling more plastic material.(32)
Another example is Burger King, which is a US-based organization. The company gave an eco-friendly makeover to its utensils, wrappers, straws, fry pods, etc. In addition, Burger King is also testing reusable packaging for its products to reduce plastic use. Similarly, one of the major competitors of Burger King i.e. McDonald is also testing plastic-free concept stores to prevent plastic usage. In these stores, the focus will be on using eco-friendly products such as wooden spoons, edible cups, paper straws, etc. in the McDonald's stores.
CPG companies are now adopting sustainability practices to preserve our planet while serving customers. They are making their packaging and processes more sustainable by ensuring compostability and recyclability.(33) In addition, modern consumers are also environmentally conscious, due to which they are ready to pay more prices for plastic-free packaging and products.
Companies are saving millions of dollars by using plastic and waste recycling. CPG companies drastically reduce the costs of building new products through plastic and waste recycling. CPG companies are also utilizing the latest technologies to create hype among customers and other companies also do the same. Companies like Unilever and PepsiCo are also leveraging waste and plastic recycling to focus on the aim of zero waste.(34) Some waste of these companies is recycled, some are reused on-site, and the remaining is traded to other industrial suppliers.
Companies that want to enhance their brand image, create a loyal customer base, and champion ethical practices can deploy sustainable and environment-friendly practices.
Zero Waste: A New Paradigm for Recycling in Circular Economies
Zero waste is a subset of circular economies. The Zero Waste concept is all about reusing, recycling, and composting everything we can to prevent the environmental impacts of litter, waste, and consumption. It is a system of interconnected strategies that work towards the ultimate goal of producing and consuming goods in a way that regenerates rather than depletes resources. It considers the entire lifecycle of a product, from extraction to disposal.
The Centralized Management and Use of Resources (CMUR) is the fundamental principle of the Zero Waste Concept. It emphasizes source segregation, reuse, and reducing the use of resources considered to be of low value or excess.
In the United States, the first Zero Waste community was established in 1993 in North Carolina. There are now over 500 communities that have adopted the Zero Waste concept, with many more planning to convert their towns. King County, Washington, adopted a Zero Waste policy to end all garbage dumps and landfills by 2030.(35) Even the United Kingdom has its version of the Zero Waste system and has set a target of diverting half of all municipal waste from landfills by 2025.
The Zero Waste Movement strives to eliminate the ever-growing and never-ending stream of single-use plastic waste that pollutes our land, water, and air and threatens our ecosystem. Implementing the Zero Waste Concept can end the menace of plastic and save our environment.
Zero Waste Strategies include:
- Introducing public awareness and education campaigns to change humans' mindsets, social systems, and actions to form zero waste communities.
- Collecting the trash from separate bins for paper, metals, plastics, e-waste, etc.
- Enforcing community recycling and curbside collection system instead of incineration.
- Introducing zero plastic waste programs to accomplish sustainable practices and packaging.
- Implementing proper centralized and decentralized waste infrastructure.
- Empowering regulatory policies and social technologies for waste monitoring and assessment.(36)
- Including all stakeholders of society in the waste management process for proper recycling and disposal.
Key Findings
- The global waste recycling market is a rapidly growing market segment with vast market potential for innovations.
- South Korea and Slovenia are among the top waste recycling countries globally.
- Waste Management Inc. is the leading waste recycling company in the waste recycling market.
- The concept of zero waste is rapidly gaining popularity for recycling in circular economies.
- Acts like waste regulations 2011, Hazardous waste regulations 2005, RCRA, etc. govern the global waste recycling market.
- Regulatory organizations such as EPA and ISWA are also regulating the global waste recycling industry.
- Different stakeholders, such as government, institutions, and consumers, should collectively make efforts to improve waste recycling and management.
- The waste recycling market is classified into several types based on source and based on type.
- Increasing consumer awareness, growth in e-waste, and waste mismanagement are some of the drivers shaping the global waste recycling market.
- Different types of waste recycling include radioactive waste recycling, Apparel waste recycling, E-waste recycling, Plastic waste recycling, etc.
- Several organizations and governments are using Artificial intelligence for waste collection, sorting, and recycling.
- Solar technologies are being used to determine the real-time status of the waste stream and supply chain.
- IoT is also assisting the waste recycling market in terms of smart bins, Smart trucks, etc., to enhance waste recycling and reduce costs.
- Upgraded pyrolysis is also gaining traction due to the enormous amount of plastic waste generated.
- Incineration is a significant challenge faced by the global waste recycling industry in terms of chemical recycling.
- The surge in bio-medical waste due to covid is another challenge for the global waste recycling market.
- China's trade restrictions on waste imports are also posing a threat to the worldwide waste recycling market.
- Inclusive behavior of people and institutions regarding waste recycling can lead to this market's success in the upcoming time.
- 5G implementation and waste-to-energy initiatives will also open up new global waste recycling market opportunities.
- CPG companies can also acquire rapid growth with assistance from the recycling market in providing eco-friendly packaging and products.
Conclusion
Global waste recycling market offers tremendous opportunities to businesses and governments at the present time. From household waste to nuclear waste, recycling is functional in almost all segments of this market which is a major reason behind the estimated growth. Enormous e-waste, changing perceptions of consumers, unhealthy eating habits, etc. will drive huge growth in the global waste recycling market. In addition, the legislation and regulations from the regulators are also assisting waste recycling companies in acquiring more support socially, legally, and economically.
However, several challenges poses threat to the growth of the global waste recycling market. Some organizations are addressing these challenges through technologies such as IoT, AI, ML, 5G, etc. These technologies are not only addressing the challenges but also laying the foundation for the future course of the global waste recycling market.
References
- https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/239662/size-of-the-global-recycling-market/#:~:text=The%20global%20waste%20recycling%20services,environmental%20impacts%20of%20waste%20increases.
- https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/waste/ten-zero-waste-cities-how-seoul-came-to-be-among-the-best-in-recycling-68585#:~:text=In%20South%20Korea%2C%20the%20disposal,very%20little%20waste%20was%20recycled.
- https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2019/may/23/zero-recycling-to-zero-waste-how-ljubljana-rethought-its-rubbish
- https://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/your-environment/recycling-and-reuse/waste-less-recycle-more
- https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-11/final-national-recycling-strategy.pdf
- https://www.macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/WM/waste-management/revenue
- https://investors.novelis.com/2022-05-11-Novelis-Reports-Fourth-Quarter-and-Fiscal-Year-2022-Results
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/493387/revenue-of-republic-services/#:~:text=Republic%20Services%20reported%20a%20revenue,drop%20in%20revenue%20since%202012.
- https://www.veolianorthamerica.com/suez-na
- https://www.covanta.com/news/press-releases/covanta-and-eqt-infrastructure-to-create-the-leading-sustainable-waste-solutions-provider
- https://www.remondis-industrie-service.de/en/about-us/facts-figures/
- https://www.wastecare.co.uk/regulations/hazardous-waste-england-and-wales-regulations-2005/#:~:text=The%20Hazardous%20Waste%20Regulations%2C%20which,movement%20of%20waste%20was%20introduced.
- https://www.iswa.org/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7392467_Solid_waste_collection_and_recycling_in_Nibong_Tebal_Penang_Malaysia_A_case_study
- https://www.oecd.org/environment/waste/policy-highlights-improving-plastics-management.pdf
- http://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-0215/ijsrp-p3843.pdf
- https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/may/03/russias-war-in-ukraine-causing-36bn-of-building-damage-a-week
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355480420_Fabric_Waste_Recycling_a_Systematic_Review_of_Methods_Applications_and_Challenges
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260268009_A_REVIEW_OF_ELECTRONIC_WASTE_E-WASTE_RECYCLING_TECHNOLOGIES_IS_E-WASTE_AN_OPPORTUNITY_OR_TREAT
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5666181_Plastic_Recycling
- https://newsroom.tomra.com/consumer-awareness-is-the-driving-force-is-businesses-becoming-more-sustainable/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1067081/generation-electronic-waste-globally-forecast/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6466021/pdf/ijerph-16-01060.pdf
- https://www.reusables.org/u-s-ends-2021-on-a-high-note-in-federal-recycling-policy-with-a-step-forward-on-reuse/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/news/225-million-funding-to-turn-industry-waste-into-environmental-wins
- https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2022/04/21/2426699/0/en/E-Waste-Recycling-Market-will-Touch-USD-99-67-Billion-at-a-Whopping-16-2-CAGR-by-2030-Report-by-Market-Research-Future-MRFR.html
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/rrapier/2021/10/10/a-novel-solution-to-plastic-pollution/?sh=a436c2d183c0
- https://www.gao.gov/blog/can-chemical-recycling-reduce-plastic-pollution
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0269749115301871
- https://hub.birmingham.ac.uk/resources/article/llm-future-of-waste-to-energy/
- https://www.fooddive.com/news/coca-cola-transitions-to-bottles-made-from-100-recycled-plastic/594709/
- https://consumerbrandsassociation.org/press-releases/cpg-industry-calls-for-standardized-recycling-system/
- https://www.greenbiz.com/article/pepsi-unilever-5-circular-economy-strategies-consumer-goods
- https://www.epa.gov/transforming-waste-tool/how-communities-have-defined-zero-waste
- https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-030-23176-7_46-1.pdf
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Global Waste Recycling Market - Overview
- Current Legislations and Regulators in Global Waste Recycling Market
- Classification of Waste Recycling
- Types of Waste Recycling and Management Procedures:
- Drivers of Global Waste Recycling Market
- Trending Technologies in Global Waste Recycling Market
- Challenges in Global Waste Recycling Management:
- Future of Global Waste Recycling Market
- Zero Waste: A New Paradigm for Recycling in Circular Economies
- Key Findings









