IT environments are often prone to challenges related to security, cost, and outages. Lack of visibility into assets and dependencies, inefficient incident and problem management, risk of service outages, compliance and audit challenges, increased costs and redundancy, and weaker security are some of the top challenges of any IT environment. With more businesses transforming their operations to digital models, automating the management of IT environments is critical.
Today, we are witnessing the increasing complexity in IT setups, with on-premises servers, cloud native apps, IoT devices, hybrid networks, etc.
This is where a configuration management database tool or CMDB software comes into play.
The modern AI-driven CMDB software solutions provide a real-time relational map of the IT ecosystem that IT teams use to get detailed information on all the existing assets, their dependencies, their configurations, and much more. Earlier, CMDB tools were treated as static databases. However, with the emergence of new technologies and innovations, modern CMDB tools come with the required machine learning capabilities, proactive and predictable features to automatically discover new assets, auto update configurations, identify anomalies, simulate what-if scenarios, etc., enabling enhanced visibility, informed decision making, and proactive risk management.
This blog tries to shed light on the major aspects of the CMDB tools, the difference between CMDB and ITAM tools, key components and features of CMDB tools, etc., while giving answers to questions like;
- How does ITAM and CMDB act in different situations?
- In the AI Era: Why does this distinction matter?
- How can CMDB and ITAM work together?
- What are the benefits of combined CMDB + ITAM use?
And much more.
What is CMDB software?
CMDB software solutions refer to the systems that help IT managers and teams manage, track, and visualize the configuration data of IT assets that is stored in CMDB databases. Serial number, asset tag, technical specifications, model and manufacturer, security configurations, licensing information, maintenance records, compliance status, change history, etc., are a few data types that CMDB tools manage and record.
CMDB software solutions help IT teams effortlessly establish relationships between different assets to understand, optimize, and control IT infrastructure. These software solutions provide a comprehensive view of IT infrastructure components and their relationships.
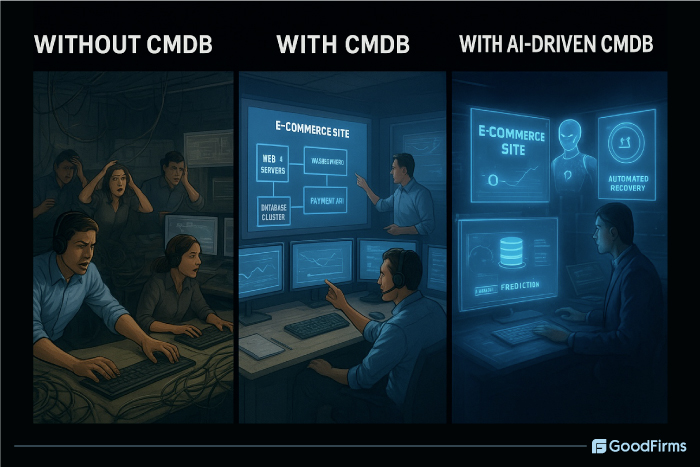
A Typical Scenario Without CMDB:
Consider a scenario where your company’s e-commerce site drops during peak sale hours. If the IT team is not aware of the servers hosting the payment gateway and if the documentation of device connections, including servers, databases, and APIs, is not clear, the team will waste time calling different key persons involved, checking the logs, and guessing the dependencies. The impact will be hours of downtime, loss of revenue, and frustrated customers.
With CMDB:
Consider the same outage when the CMDB tools are in place. The IT team will have to check the CMDB map, quickly identify the patched database server, and roll back within a few minutes or seconds. Downtime is less, and customers are not much affected. In this scenario, there is clear visibility, root cause analysis is quick, downtime is low, and there is clear accountability.
With AI-Driven CMDB
Much before the outage, the AI-powered CMDB detects the abnormal spikes and errors. The impact is analyzed quickly, and the root cause is predicted. An automated remedy is set to roll out, fixing all the issues instantly. The time taken to fight is less, and business continuity is maintained with minimal revenue loss.
Key Components of CMDB Tools
For any CMDB tool to succeed, there are several components of CMDB tools that need to function properly. Without these components, CMDB tools lack the required capabilities for asset tracking, incident management, change management, automated data management and collection, planning, problem management, understanding service impact, ensuring compliance, etc., meaning more downtime, inefficiencies, and increased costs. Some of these key components of CMDB tools are as follows;
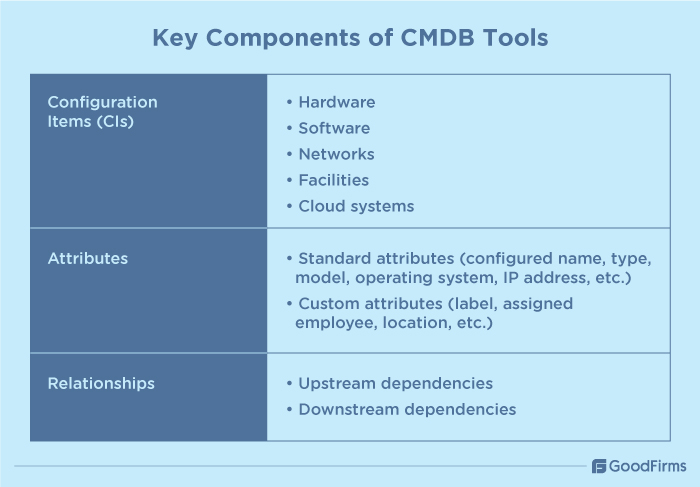
Configuration Items (CIs)
Configurable Items (CIs) refer to the building blocks, components, or assets that make up the IT infrastructure and whose data is stored and managed by CMDB tools. CIs primarily include hardware, software, networks, facilities, cloud systems, etc., that are maintained within the CMDB.
Attributes
In CMDB, attributes refer to the CI characteristics that are captured and entered in the records by the CMDB tools during asset discovery and are of two types. Standard attributes are hardcoded into the CIs, such as configured name, type, model, operating system, IP address, etc. Custom attributes are user defined and include label, assigned employee, location, etc.
Relationships
This refers to the interconnections between CIs which shows the way a CI or asset depends on other CIs and how they interact with each other. The purpose of relationships is to identify the upstream and downstream dependencies and how changes in one CI can affect other CIs.
Features of CMDB Software
Modern CMDB software solutions do not just act like normal databases that store configuration data of IT assets. Rather, they come with intuitive features and capabilities that transform them into intelligent platforms. These include automated CI discovery tools, relationship mapping, dependency and data visualization, seamless integration with existing tools, compliance and risk management, advanced reporting and dashboard, etc.
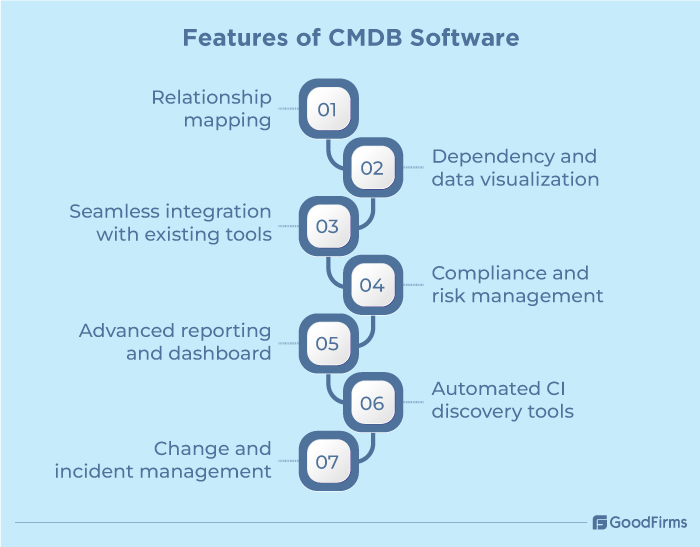
For instance, an ideal CMDB software comes with automated CI discovery tools to identify and record CIs on a regular basis, which helps IT teams in keeping the database updated and accurate, thereby reducing security risks. In fact, reducing security risks is a top priority for 25% decision makers in 2025, as per the 2025 IT Priorities Report.
The change and incident management capabilities help IT teams properly plan the changes and even assess the potential impact of those changes on other components. This is beneficial for IT teams in quickly troubleshooting and resolving issues. And, as per the 2025 Connectivity Benchmark Report, around 74% organizations have IT systems that are dependent upon others. The dependency mapping capabilities help IT teams determine which assets are dependent on other assets.
Moreover, features like relationship mapping and dependency visualization are useful in mapping all the relevant interdependencies between software, hardware, users, business processes, and services. Similarly, integration with existing business tools helps businesses establish better coordination across IT workflows.
As per the State of ITAM report, nearly 45% organizations are paying over $1 million in audit expenses. With compliance and risk management features of CMDB software, businesses can easily track unauthorized changes, software licenses, compliance with regulatory requirements, etc., which is helpful in preventing legal penalties and reducing the costs of software vendor audits.
Advanced reporting and dashboard features provide real-time insights into asset health, service dependencies, and compliance status to ensure optimal performance and productivity. A few CMDB tools even provide real-time insights into compliance and data security that is beneficial for the IT teams in keeping up with regulatory requirements. A recent report indicates that one third of businesses are failing to keep up with regulatory requirements which can be resolved using CMDB software solutions.
Difference Between CMDB and ITAM (With Situations and Examples)
Both configuration management database software and ITAM are integral components of any IT infrastructure but they serve different functions as per their capabilities. For instance, CMDB focuses on "What do we have, how is it configured, and how do things connect?". Whereas ITAM focuses on "What do we own, where is it, and how much is it worth?".
Here's a CMDB system setup with explanation as follows;
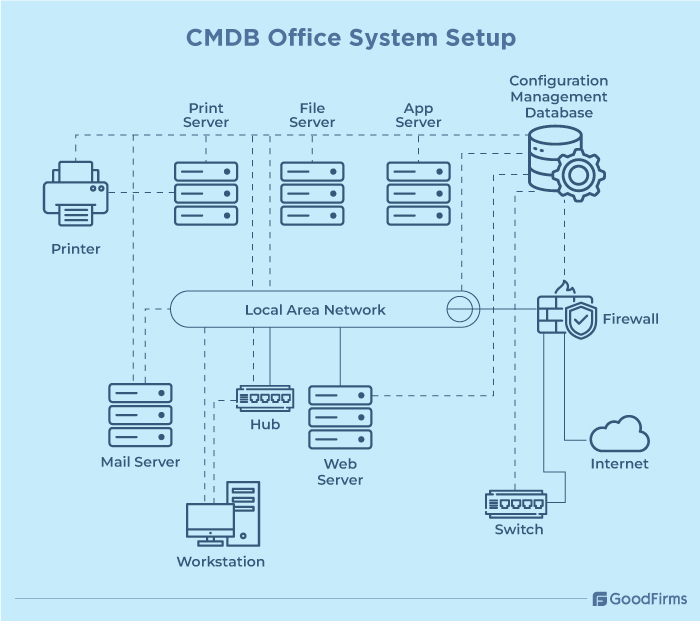
What do we have?
This above diagram shows all the IT assets or configurable items that has been identified and recorded by CMDB, including servers (print, file, web, mail, and App), network devices (switch, hub, and firewall), end-user devices (workstations and printers) and internet along with CMDB itself.
How is it configured?
CMDB tracks and records the following configuration details and operational metadata as follows;
For servers - OS type, patch level, storage capacity, assigned roles, user mailboxes, etc.
For end-user devices - assigned user details, installed apps, hardware specifications, model, drivers, etc.
For network devices- security rules, allowed protocols, access ports, IP address, VLAN setups, etc.
How do things connect?
Once the CIs are configured and recorded, CMDB maps out the relationship between them to show dependencies. For instance, workstations depend upon hub/switch, LAN, servers, etc., to work effectively. Printers depend on the print server and LAN. File sharing servers rely on LAN and internet. Mail services depend upon mail server, firewall, and internet, etc. CMDB links all these dependencies and flows, providing a complete visibility map.
In short, CMDB acts like a master map that can record and document every asset, its exact configurations, and how one asset or CI can connect with other CIs.
Now, let's come to the ITAM system setup with explanation as follows;
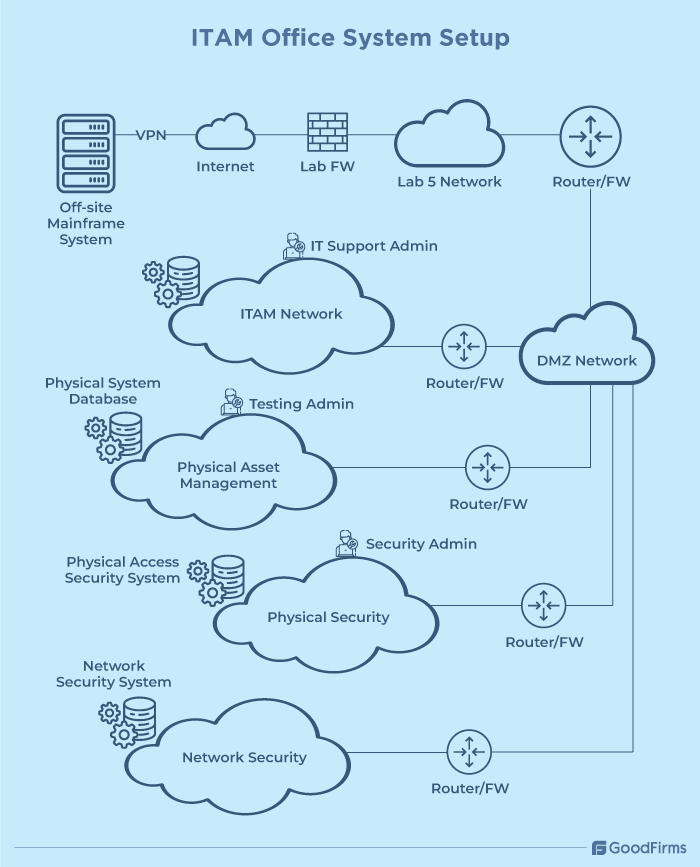
What do we own?
ITAM is majorly focused on asset ownership details, such as who manages which asset, where it is located, and how much value it holds. For instance, the above image shows which teams are managing which systems. The IT support admin is responsible for managing the IT system databases. Physical assets are tracked by the receiving team, and security admins are responsible for tracking physical and network security. ITAM ensures that every server, firewall, router, workstation, etc., is accurately recorded as an asset.
Where is it located?
The image also highlights the multiple zones and networks where assets are deployed, such as the off-site mainframe system, which is located externally and connects to the IT infrastructure through a VPN. The ITAM tags and registers each asset with relevant information, such as location, responsible person, purchase date, etc. For example, ITAM can show that a router X, located between the DMZ network and Lab 5 network, is managed by the IT support team along with the purchase date and year.
How much is it worth?
Once every asset is tagged and registered, ITAM then tracks their financial and operational value by analyzing their purchase costs, depreciation schedules, replacement timelines, licensing costs, warranties, service contracts, etc., to identify highly strategic assets, underutilized assets, redundant licences, contract renegotiation opportunities, and do much more.
How ITAM and CMDB Act in Different Situations?
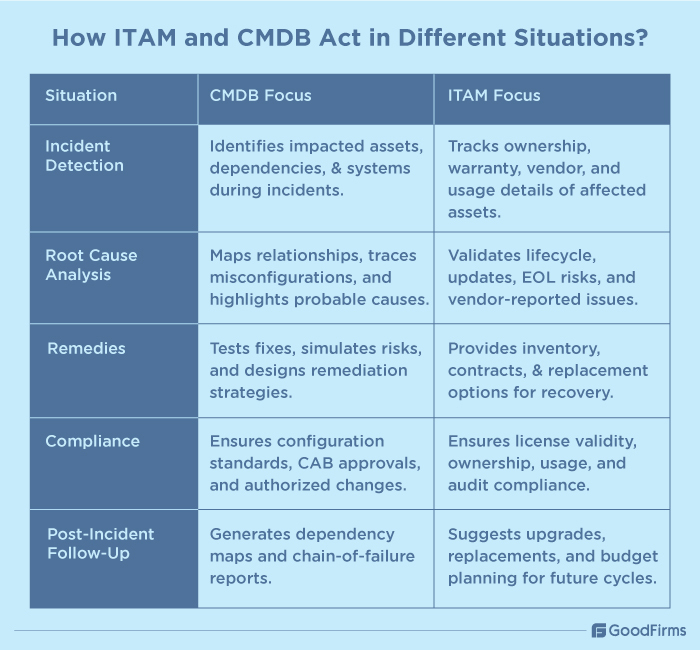
Incident detection
Whenever any incident took place within the IT infrastructure, modern CMDB software helps IT teams in identifying the assets which are impacted by the incident. Whereas, ITAM tools are more focused on asset inventory and ownership.
For example, if an ERP system goes offline, CMDB tools can help IT teams trace the dependencies to determine which dependent system, i.e., database server, middleware, or cloud hosting can be impacted due to the offline ERP.
Whereas ITAM tools help IT teams determine who uses the ERP system, its warranty status, vendor support details, maintenance scope, etc.
Root cause analysis
Once incidents are detected, the role of CMDB is to trace the cause and effect. CMDB helps businesses in identifying the downstream impact of misconfigured assets on the other systems. Whereas, ITAM focuses on validating the hardware/software status, its lifecycle details, anticipated updates, replacement schedule, etc.
Considering the ERP outage case, suppose the outage was caused due to a patch update. In such conditions, CMDB tools can reveal the change in firewall configurations caused due to the patch update process. With logs and relationships, CMDB can highlight the patch update as the probable cause.
While ITAM can suggest the estimated time for ERP server updates, was it properly updated, is it past its end-of-life cycle, etc. ITAM can also highlight vendor reported frequently encountered issues. This does not directly give information on the exact cause but provides historical context regarding software reliability.
Remedies
Through CMDB, IT teams can test what can go wrong if a fix is applied. Through this, they can determine which exact components need fixing and what are the associated risks, thus helping design remediation strategies without any collateral damage. Whereas ITAM won't directly help design a remediation strategy, it provides the resources to remedy the issue.
In the case of offline ERP, CMDB can help IT teams restore the ERP system by testing the roll back of the update. Additionally, CMDB can also highlight that restarting the ERP alone won't work unless other dependent services are aligned.
ITAM helps IT teams analyze inventory and vendor replacement policies to confirm availability of spare servers for ERP. If the ERP system needs replacement, then ITAM tools can provide warranty contracts and procurement details.
Compliance
Once the remediation process starts, it is vital for IT teams to conduct compliance checks post incident. CMDB tools offer compliance-related insights on configuration standards whereas ITAM ensures compliance with licensing, ownership, and usage.
For example, CMDB can confirm whether the firewall configurations in patch update were authorized by the CAB or not. If not, then it can raise a compliance violation ticket. Whereas, ITAM can confirm if the license of the ERP is valid, software isn't running beyond its capacity, audit requirements are met, etc.
In compliance, CMDB focuses on CAB approval, while ITAM focuses on confirming compliance with other aspects of the ERP system.
Post-incident follow up
Once the incident is resolved, CMDB can provide a post-incident report with dependency maps that highlight the exact chain of failure. Whereas ITAM suggests lifecycle upgrades that can be done in the next fiscal cycle.
For instance, CMDB can report that ERP failure was caused by change in firewall configurations that was a result of patch update. However, ITAM could suggest that the ERP server is nearing end of life and recommends a budget plan to invest in new software.
In the AI Era: Why Does The Distinction Between ITAM and CMDB Matter?
At present, one of the core focuses of modern businesses is to leverage AI and automation to streamline business functions. In such a scenario, there is a dire need for businesses to effectively differentiate between their ITAM and CMDB roles. Both of these systems deal with IT assets, but their focus and scope differs in AI-powered environments.
By understanding the distinction between the two, businesses can effectively carry out their ITAM and CMDB tasks without any misunderstanding and improper merging, allowing them to unlock the full potential of the IT infrastructure.
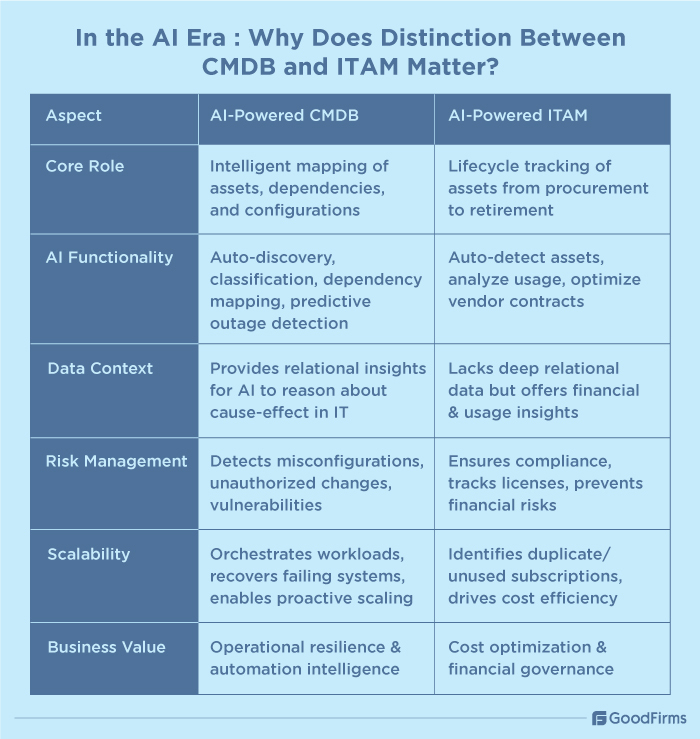
In the AI era, CMDB is expected to act like an intelligent layer of IT infrastructure that can automatically discover, classify and update the CIs, quickly map dependencies between various CIs, predict potential service outages, automatically detect misconfigurations and policy violations, dynamically scale assets up and down, etc., to ensure proactive intelligence for IT operations.
Similarly, in the AI era, businesses are expecting ITAM to become more strategic than reactive. AI-powered ITAM can automatically detect all the connected assets, accurately analyze asset usage patterns and vendor contracts, and provide sustainability reporting to reduce risks and optimize costs.
Here are some of the reasons why this distinction matters in the AI era as follows;
Data context
CMDB can deliver the required deep relational insights and data sets that AI needs to effectively reason about the cause and effect in IT infrastructure.
Risk management
Through CMDB data, businesses can drive operational automation, and with ITAM help, businesses can use AI for financial governance, reducing the risks significantly.
Scalability in Hybrid and Cloud Environments
In hybrid and multi-cloud setups, AI can help IT teams use CMDB’s relationship mapping to recover failing systems, automatically orchestrate workloads, and rebalance resources, which are crucial for scaling the IT infrastructure without any human intervention.
AI-powered ITAM can automatically detect unused or duplicate cloud subscriptions and recommend consolidations to reduce resource and cost wastage while scaling the system up or down.
How can CMDB and ITAM work together?
Earlier, businesses relied on on-premises data centers for whose management CMDB was a perfect option. However, with the advent of cloud virtualization, SaaS explosion, and hybrid infrastructure, CMDB tools are finding it hard to quickly meet the business needs. To combat such a problem, businesses can collectively use both CMDB and ITAM to ensure potential savings and maximum ROI.
Here is a real-life scenario that explains how ITAM and CMDB can work hand-in-hand as follows;
Situation
An IT company with a huge number of servers finds out that one of the critical servers is experiencing a failure during peak business hours.
Role of ITAM in such a scenario
In such a situation, ITAM primarily focuses on the contractual, financial, and lifecycle side of the failed component, i.e., the server in our case. ITAM helps IT teams gain a clear idea of server details, such as purchase date and license, ownership information, such as who owns the server, and support coverage, such as warranty and replacement. Through this, businesses can easily determine the lifecycle status of the asset.
Role of CMDB in such a scenario
The role of CMDB in such a scenario is to provide information on the operational and service dependency side of the failed server. CMDB provides relationship maps, business service impact analysis, and links to historical records, allowing IT teams to effectively evaluate the impact of server failure on other components of the IT infrastructure.
Role of ITAM and CMDB combined in such a scenario
By combining the two in this situation, IT teams can quickly identify and resolve the server failure. For instance, ITAM helps businesses verify the server details, ownership information, and support coverage, whereas CMDB is useful in establishing the dependencies between the failed server and other assets. ITAM offers asset context, whereas CMDB offers service impact visibility. Through this coordinated action, IT teams can instantly trigger warranty/vendor escalations, prioritize business critical services, communicate impact to end users, and initiate mitigation steps to replace or repair the impacted server before any other critical asset takes a hit.
Benefits of Combined CMDB + ITAM Use:
Many organizations in modern times often treat CMDB and ITAM as separate initiatives. When used separately, their functions are different, but when combined together, they can quickly help IT teams in bridging the gap between asset financial management and configuration relationship management. Here are some of the benefits of combining the CMDB and ITAM as follows;
Unified Visibility and Control
Through ITAM, IT teams can acquire important information associated with tracking of existing assets, their lifecycle stages, who owns them, etc. However, to capture deep configuration details and dependencies, CMDB is required that can map assets to services, applications, and infrastructure dependencies. According to a recent ITAM Confidence Gap 2025 survey, businesses are losing over 25% on ghost assets and millions in unused licenses. With unified visibility and control, such losses can be significantly eliminated as IT teams would have an idea on which licences are unused and which ghost assets are not required.
For instance, if a company owns a huge number of assets, laptops, servers, and cloud instances, then ITAM can record the purchase details, license, and warranty for the available assets. However when it is combined with CMDB, IT teams can also view how these different assets are tied to each other, allowing them to proactively monitor asset utilization, identify redundant purchases, and spot shadow IT assets from a single place.
Optimized Lifecycle management
While ITAM deals with financial and contractual aspects of the asset lifecycle, CMDB deals with operational and technical details. When combined, they form a powerful set of tools through which IT teams can significantly optimize the end-to-end asset lifecycle. For instance, consider the lifecycle of a server. In this, ITAM only focuses on recording the warranty, renewal contracts, or purchase data of the assets. Whereas CMDB focuses on maintaining the data on installed software, applications, and network relationships. Whenever the server lifecycle ends, ITAM will send alerts to replace it. But, CMDB can show how the replacement will affect the dependent systems, making the transition seamless.
Improved security
While ITAM tools help businesses track ownership, license, and software entitlements, CMDB systems provide information on how different assets are configured and connected. Together, they build a comprehensive security posture to better assess the risks and manage vulnerabilities. In fact, a significant number of businesses, i.e., 39% are focusing on increasing data security and reducing the risks through their IT management practices, as per IT asset management research. For instance, when the antivirus license of certain laptops and systems becomes outdated, ITAM provides limited value and can only identify the devices. But when CMDB is used, IT teams can also immediately assess which business-critical services those laptops access.
Smart financial planning and cost optimization
ITAM solutions are one of the most powerful tools to track asset costs, license utilization, and depreciation for effective financial planning. But, it lacks the operational context which can lead to missed opportunities. By combining ITAM tools with CMDB software solutions, businesses can align their financial strategy with technical reality, bringing better results and efficiency.
For example, businesses having a huge number of software and tools often experience challenges in managing them. In such a scenario, ITAM solutions only help IT teams determine which tools are used very rarely or not at all. Whereas, CMDB tools can reveal which licenses can be required for future expansions and which licenses can be ignored to save the costs.
Additionally, as per the ITAD benchmark report 2025, around 30% respondents are expecting to spend more on IT infrastructure in the next year. By combining ITAM and CMDB, businesses can exponentially save huge costs as they can better understand which services, tools, and systems need to be continued and which ones need to be discarded.
Faster root cause analysis
Whenever an IT issue occurs, the first reaction of IT teams is to pinpoint the root cause. In such situations, ITAM tools only state about the assets that are active and under warranty but it does not provide the required context to understand how inactiveness in one system can affect other systems. This is possible with the dependency mapping capabilities of CMDB tools.
Through these capabilities, IT teams can determine how an asset or configuration interconnects with other networks, applications, and services.
Additionally, a few AI-powered CMDB solutions can even analyze patterns from past incidents to suggest the likely issue and its resolution, enabling proactive and data-driven IT management. In fact, 43% respondents of the 2024 EMA Research Report focus on proactive response to incidents before they impact end users.
Conclusion
The global CMDB software solutions market is anticipated to cross $1.68 billion in 2025 with a CAGR of 10.5%, reaching $2.5 billion by 2033. This immense growth is a sign that the CMDB use will grow rapidly in the upcoming years, marking a bright future for the CMDB tools. As the growing complexities in the IT ecosystems is forcing businesses to move beyond traditional approaches to IT management, the CMDB tools help IT teams dive deeper into the technical and operational layers of IT infrastructure, offering a window of opportunity to IT teams. Not only CMDB, but ITAM is also a vital component of IT management. When CMDB and ITAM are used together, businesses can easily acquire a 360 view of their IT environments with enhanced visibility and control. Businesses can also use free and open source IT asset management software as they can seamlessly integrate with modern CMDB solutions to better optimize IT costs, reduce risks, and ensure streamlined digital operations.




.jpg)