Key Takeaways:
- Server downtime doesn't just stall operations, it leaves a wide range of significant negative impacts on a business.
- A single server outage can cascade into lost revenue, frustrated customers, and damaged reputation.
- Average cost of server downtime across all industries is reportedly $5,600 to $9,000 per minute.
- More organizations are scaling hybrid workloads and are adopting edge computing, which demands the need for intelligent, automated and secure server management products.
- As the workload demands evolve, Organizations are facing challenges to withstand disruptions and rapidly recover, balancing cost control and operational continuity.
- Software-defined resilience and deployments are improving.
- Automated observability and failover technologies are gaining more traction.
- Integration, delivery capabilities, compliance and governance requirements stand as a priority.
- Tailored, targeted approach works for high availability infrastructure.
Effective server management tools are the true saviors for uninterrupted business continuity.
This blog walks through what server management really entails, the types of servers powering modern businesses, its core objectives, the key functions delivered by best products, far-reaching business impacts, and how AI-powered server management tools are all set to reshape business continuity in 2026.
What is a Server? What are the Tasks of a Server?
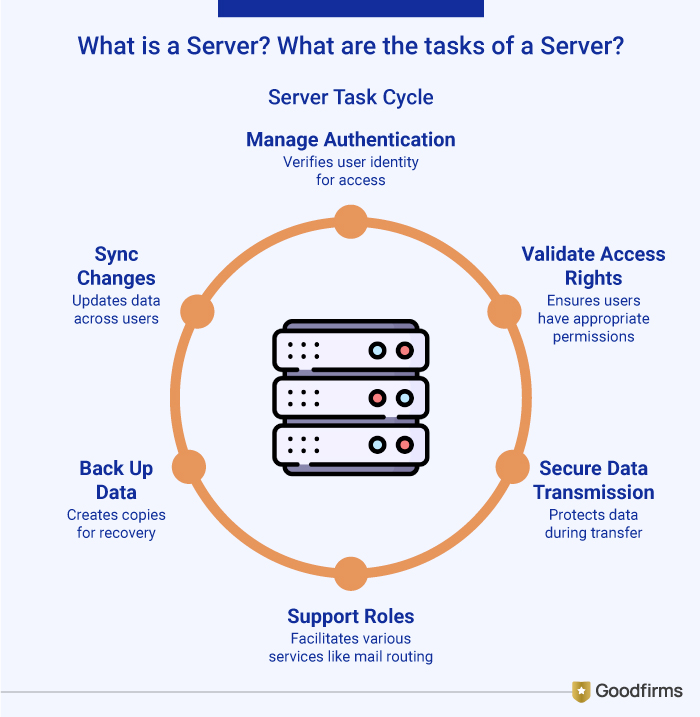
A server is a system programmed to store, process and deliver data or resources to other computers, known as clients, over a network. It provides a wide range of services from delivering web pages, email, storing, managing files to running applications.
The primary task of a server is data management, resource allocation, and managing client requests. Right from data authentication, validating access rights, ensuring secure data transmission, routing mails for smooth email delivery, DNS resolution for domain lookup or proxy filtering for secure browsing, to data backup and syncing changes across users, a server can take up multiple tasks.
Although the functions of a server are diverse, they can be narrowed down to perform specific functions.
What are the Types of Servers? What are their Roles?
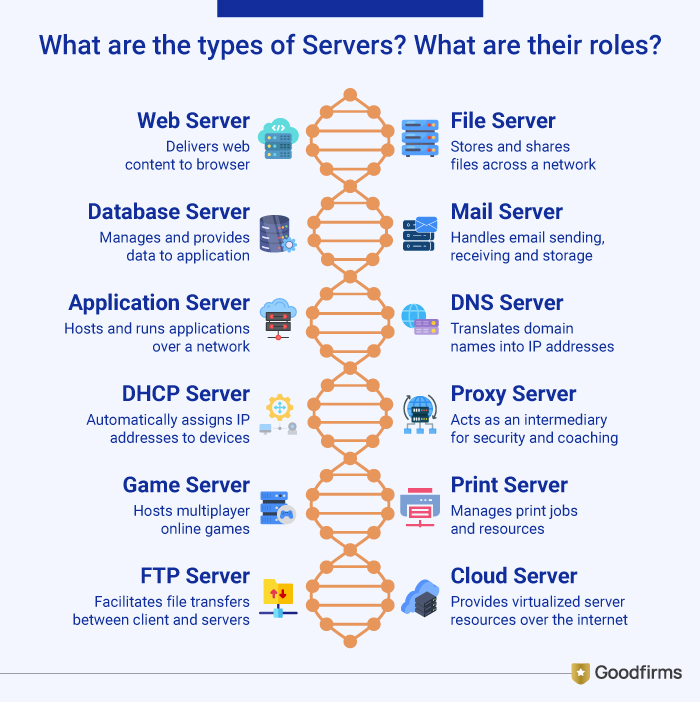
Servers come in various types categorized by various functions like information, data, services, and maintenance. Each server is designed for specific workloads from compact edge computing in hard conditions to high-density data center powering AI initiative.
Here are a few common types of servers with specifications about their roles;
- Web Server: Delivers web pages, images, and content to browsers using HTTP/HTTPS. (e.g., Apache, Nginx)
- File Server: Stores, organizes, and shares files across a network for users, ensuring backup and permissions control.
- Database Server: Manages large databases, processing queries and providing structured storage and retrieval of data for handling applications. (using DBMS)
- Mail Server: Handles sending, receiving, and storing emails supporting both internal and external communication across networks. (SMTP, IMAP, POP3)
- Application Server: Hosts and runs applications and business logic for users over a network.
- DNS Server (Domain Name System): Translates human-readable domain names (e.g., google.com) into IP addresses for internet functionality and performance.
- DHCP Server (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network.
- Proxy Server: Acts as an intermediary for requests, often for security, caching, managing traffic or filtering to enhance network performance and enforce access policies.
- Game Server: Hosts multiplayer online games, synchronizing player actions and data to manage real-time interactions ensuring low-latency connections.
- Print Server: Manages print jobs and resources for shared network printers centralizing control and improving efficiency.
- FTP Server (File Transfer Protocol): Facilitates file transfers between clients and servers.
- Cloud Server: Virtualized server resources delivered over the internet from a cloud provider support workloads ranging from web hosting to AI applications.
What is a High Availability (HA) Server?
A high availability (HA) server is a robust computing system designed to minimize downtime, withstand outages, including site-wide disasters and ensure continuous operation. Typically HA systems have two main factors to achieve 99.99% uptime or higher through redundancy and meet a certain set of predetermined user expectations.
HA servers operate in clusters, known as high availability clustering. In this, multiple nodes share workloads that work together as a single system. If one fails, another seamlessly takes over without data loss or service interruption. It incorporates automatic health monitoring, load balancing, and shared storage to eliminate single points of failure.
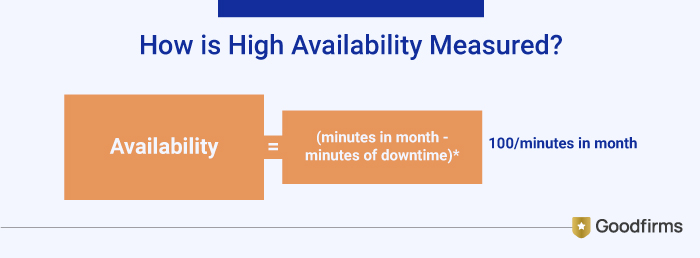
How is High Availability Measured?
High Availability can be measured relative to a system being 100% operational or never failing -- meaning it has no outages. For example, you can calculate the monthly availability rate based on the number of minutes in the month and the number of minutes of downtime during that month, as shown in the following formula:
What is Server Management?
Server management refers to the process of monitoring, maintaining, and optimizing servers to ensure they perform reliably, securely and at optimal performance levels. It encompasses a wide variety of tasks, including hardware and software management, system updates, performance tuning, security hardening, backup implementation, disaster recovery and round-the-clock support.
For many mid-sized businesses, internal IT teams are stretched thin. They often juggle server issues reactively, addressing problems only when something breaks. This approach leaves systems exposed to risks and costs the business valuable time. With the right server management tool or products it becomes effortless for businesses to automate routine tasks, manage hybrid environments that include both on-premises and cloud-based systems making it crucial for minimizing downtime, improving system performance and enhancing productivity.
What Servers are Used for Modern Businesses?
Modern businesses are heavily relying on redundant, high-availability servers to minimize downtime and ensure seamless operations during failures, outages, or surges. These systems often incorporate clustering, failed mechanisms, and virtualization for 99.99% uptime. The high availability server market grew to USD 14.84 billion in 2025, and is estimated to touch USD 22.66 billion by 2032.
What are the Form Factors of Servers?
Server form factors are basically that defines a server’s size, design, and other factors enabling it to fit into any device, operations, and business network requirements. The following is a detailed table of the form factors of a server;
|
Server |
Core Benefit |
Typical Use Case |
|
Rack Server |
Cost-efficiency & Space optimization |
Small to Medium-sized IT operations |
|
Blade Server |
High performance with centralized management |
Large enterprises with extensive IT needs |
|
Mainframe Server |
High throughout for data-intensive applications |
Finance, healthcare, government |
|
Cloud Server |
Scalability & remote accessibility |
Startups, tech companies |
|
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure |
Modular growth capacity |
Dynamic workloads requiring flexibility |
What are the Objectives of Server Management Tools?
The objective of server management software is to enable uninterrupted business continuity by minimizing the disruptions, running the servers efficiently while meeting the operation requirements of the businesses.
Key Objectives:
- 24/7 Monitoring and Support: The server management tools are designed to track resource pages, performance metrics and operational activities in real-time.
- Proactive Maintenance: Through routine checks and system tuning, these tools can provide regular updates and enable businesses to take preventative measures to avoid potential problems before they impact business.
- Enhanced Security: Constant vigilance and rapid response by cloning vulnerabilities through security hardening to protect valuable data from cyber attacks.
- Improved Performance: Ongoing optimization ensures servers are running at peak efficiency adjusting the infrastructure to meet performance demands.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup: It also ensures data integrity by providing daily backups and fast recovery protocols.
Business Impact: The Real Cost of Server Downtime
A reputed motor company recently reported a significant data breach stemming from unauthorized access to Red Hat servers.
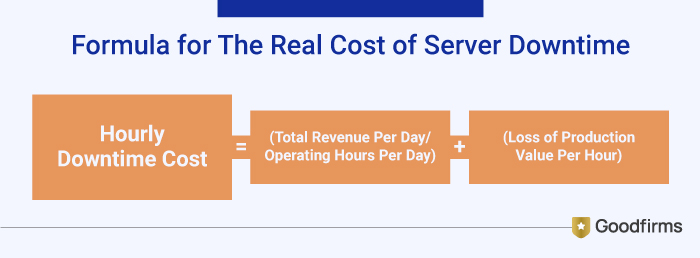
It is important to understand, business downtime can stem from various reasons, may be due to technical failure, maintenance, or human error. But it can severely disrupt business operations leading to damaged customer trust, reduced productivity, lost revenue, financial losses, company’s reputation in the marketplace etc. According to the recent ITIC’s 2024 Hourly Cost of Downtime Survey, indicates the cost of hourly downtime continues to spike. The average cost of a single hour of downtime now exceeds $300,000 for over 90% of mid-size and large enterprises. These costs are exclusive of litigation, civil or criminal penalties. To find the real cost per hour of downtime can be done using simple formula that is:
In order to minimize such risk and uninterrupted business continuity, it is important to prioritize IT security by investing in the best server management products to effectively manage business disruptions as the result of an adverse event.
Top 4 Server Management Products for Efficient and Uninterrupted Business Continuity:
.jpg)
The top server management products from these specified vendors excel in delivering high availability, automated monitoring, and failover capabilities for uninterrupted business continuity:
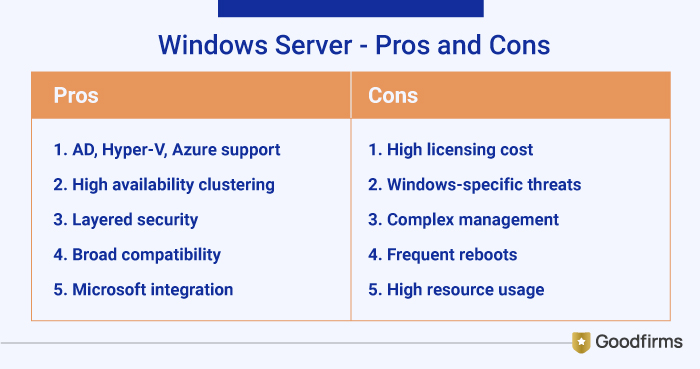
1. Windows Server
Windows Server provides comprehensive management through tools like Server Manager and Windows Admin Center, enabling centralized monitoring, failed clustering, and Hyper-V virtualization for resilient operations. It caters to various requirements of small businesses to large enterprises with virtualized/cloud environments, featuring core-based licensing and Azure integrations.
Key Features & Enhancements
- Hybrid Cloud: It has better integration with Azure for cloud-ready operations.
- Security: It has enhanced identity protection, Active Directory, and SMB security.
- Performance: It provides faster I/O with DirectStorage, enabling support for more CPU cores (up to 256) and RAM (up to 64TB).
- Storage: It supports hotpatching for faster updates without restarts, improved Storage Spaces Direct.
It includes several editions:
- Standard: It is suitable for SMBs for physical or lightly virtualized environments.
- Datacenter: It offers unlimited virtualization rights for highly virtualized, large-scale data centers.
- Datacenter: Azure Edition: This is an optimized edition for Azure Stack HCI and running in Azure, integrating deeply with cloud services.
- Essentials: This is a limited version for small businesses (up to 25 users/50 devices), sold via OEM only.
Pros:
- Provides extensive Active Directory, Hyper-V Line Migration and Azure for hybrid continuity.
- Built-in high availability clustering that reduces downtime to minutes.
- Offers layered security, authentication and encryption
- Works with hardware and software ecosystems, having broad compatibility
- Seamlessly integrate with Microsoft products (SQL, .Net, Exchange) and mainstream software.
Cons:
- High licensing costs for enterprises.
- Vulnerable to Windows-specific threats without constant patching.
- Time consuming and require specialized skills advanced setups and troubleshooting
- Often requires disruptive reboots and frequent updates
- Demands for significant RAM, CPU especially with the GUI.
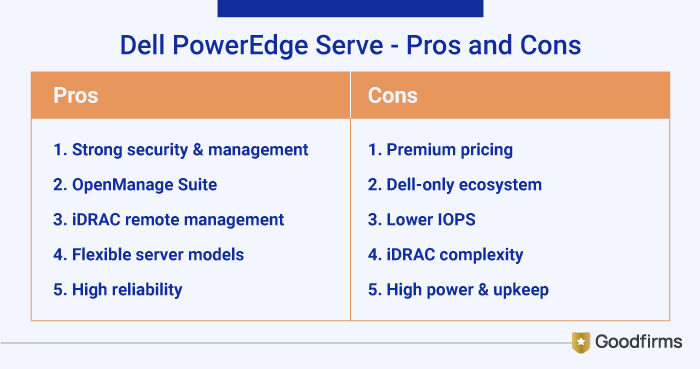
2. Dell PowerEdge server:
It offers advanced automation, cyber-resilient security and scalable designs to support a wide range of workloads. It is ideal for companies that have data center structure and want to expand it, boost productivity, enhance security and performance. The different Dell PowerEdge models are more or less likely to meet your business needs. Here are some several popular server models of the Dell PowerEdge line, they are PowerEdge R740, PowerEdge R640 and PowerEdge T40.
Key Features and Enhancements:
- Advanced Processing Power: It offers significant performance improvements for demanding workloads, like AI, virtualization, database management.
- Intelligent Automation: The iDRAC (Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller) with lifecycle controller, provides monitoring, remote system management, automated deployment, reducing administration time etc.
- Enhanced Security: It has different cyber resilient architecture built-in such as silicon-based root of trust, secure boot, secure component verification.
- Scalable storage and I/O: It provides flexible and high performance storage options with integrations like boot optimized storage solution for the OSand support, enhanced performance and scalability.
Pros:
- Supports superior security, sustainability tracking, and one-to-many console management.
- OpenManage Suite centralized for deploying, monitoring with automatic updates in seconds.
- Integrated remote management (iDRAC) allows monitoring and controlling from anywhere.
- Models cater to various needs (rack, tower, modular) for high density, performance and config options.
- Offers exceptional reliability, stability, reducing unplanned downtime significantly.
Cons:
- Premium pricing compared to open alternatives.
- Best suited for only Dell hardware ecosystems.
- Lower IOPS and disk speeds hinder scaling for high-user environments
- iDRAC interface needs improvements, as it has limited scalability and intricate set process
- Higher power usage, and configuration challenges for upgrades and maintenance
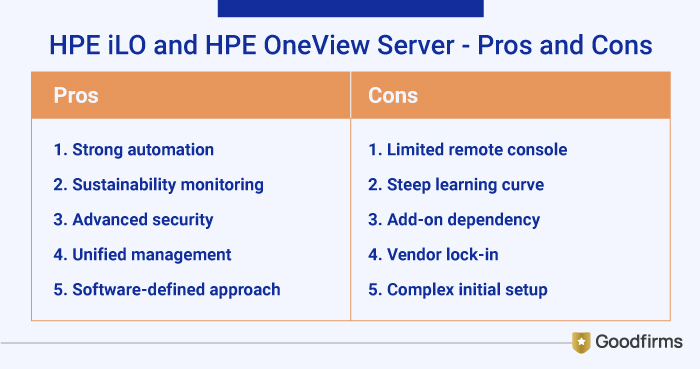
3. HPE iLO and HPE OneView
HPE's iLO 6 delivers embedded management for ProLiant servers and other HPE products. It allows administrators to proactively monitor, manage remotely, enhance security, resolve issues quickly, automate common tasks, and improve operational efficiency. While HPE One View is a software-defined infrastructure management solution delivered as a virtual appliance that runs on a hypervisor. It helps in simplifying IT operations by transforming servers, storage and networking into a single defined infrastructure through a unified API.
HPE iLO Editions, it includes different editions, typically determined by licensing:
- iLO Standard: It offers baseline functionality embedded in the server, which includes essential features like basic monitoring and remote power control.
- iLO Advanced: This provides more advanced features, such as the full graphical remote console, multi-user collaboration, remote security logs, and advanced power management capabilities.
- iLO Advanced Premium Security Edition: In this version it comes with enhanced security features and is a good fit for leveraging some advanced predictive analytics within the HPE InfoSight ecosystem.
Key Features Includes:
- Remote Console: It provides graphical remote access to the server's console, essential for OS installation and troubleshooting.
- Virtual Media: It allows remote mounting of ISO files or local drives as if they were physically connected to the server.
- Health Monitoring: It monitors system health, power, and thermal control, providing alerts for potential issues.
- Security: It offers hardened security features, including role-based access control and secure data transmission.
HPE OneView Editions: It is available in two main editions:
- HPE OneView Standard: In this edition, it provides foundational monitoring, health status updates, and inventory management for managed devices at no additional cost. It is agentless and out-of-band, leveraging the embedded iLO for communication.
- HPE OneView Advanced: This one is a fully-featured, licensed edition that unlocks the active management, automation, and software-defined capabilities. It also includes server profile templates, automated provisioning, and comprehensive lifecycle management across compute, storage, and networking. An HPE OneView Advanced license often includes an HPE iLO Advanced license to enable the full feature set.
Key Features Includes:
- Software-Defined Automation: It uses various templates and profiles to automate the provisioning and configuration of infrastructure resources consistently and at scale.
- Unified Interface: It offers a single, consolidated dashboard to view the health and inventory of all managed resources across the data center.
- Lifecycle Management: It helps in automating firmware and driver updates across the infrastructure using baselines ensuring compliance and reducing configuration drift.
- Integration: It integrates with a wide ecosystem of partner tools, including virtualization (VMware, Microsoft System Center) and cloud management platforms.
Pros:
- Robust automation methods for large-scale firmware and compliance.
- Built-in server for managing sustainability and performance monitoring.
- Advanced security features including firmware validation
- Manages server, storage and networking from a single pane
- Enables software-defined infrastructure, simplifies firmware updates and lifecycle operations across data center
Cons:
- Lags in remote console features and security depth.
- Needs a steeper learning curve for multi-vendor setups.
- Requires add-ons to manage a larger number of servers.
- Primarily manages HPE hardware, limiting multi-vendor environments.
- More comprehensive, but may be complex to set up initially.
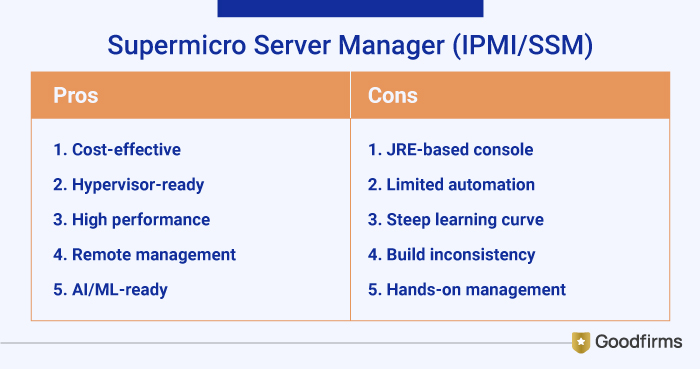
4. Supermicro Server Manager (IPMI/SSM)
Supermicro's IPMI-based Server Manager and SSM handle SuperServer fleets with basic remote access, focusing on customizable, cost-effective management for high-density continuity.
Core Features
- Centralized Console: It has a single pane of glass for many servers, reducing deployment and maintenance time.
- Health & Monitoring: It helps in tracking CPU, memory, storage, power usage, and alerts via Email/SNMP.
- Firmware Management: It supports in automating BIOS/BMC and updating it across numerous servers.
- Power Management: It provides remote power control (On/Off/Reset) and power policy management.
- Remote Presence (KVM): HTML5/VNC-based console redirection for remote access.
- OS Deployment: It consists of tools for OS installation (Linux/Windows) and kickstart file management.
- API & Integration: RESTful APIs, CLI, and plugins (e.g., VMware) for custom integration.
Editions & Licensing (Key Differences)
Supermicro's management software ecosystem includes SSM, Supermicro Update Manager (SUM), SuperDoctor 5 (SD5), and others.
- Base SSM: It provides core monitoring, management, and basic firmware/OS deployment.
- Service Calls (SFT-DCMS-SVC-KEY): This is a licensed feature requiring keys per target node, enabling automated ticket creation and multi-level alerts with the Supermicro Global Service Team for critical hardware failures, linking to paid support agreements.
- SuperCloud Composer (Newer): It is an advanced orchestration platform that integrates SSM and other tools for hybrid cloud management, newer systems (X14+) use this.
Pros:
- Lower initial costs and flexible open architecture.
- Best option for custom hypervisors and NoSQL workloads.
- Delivers high performance server capabilities with competitive prices.
- IPMI & SSM provides robust remote management and boot control.
- Highly customizable hardware and strong support for AI/ML workloads.
Cons:
- Lacks HTML5 consoles (uses outdated JRE) and advanced analytics.
- Supports fewer security and automation features than Dell/HPE.
- Require more learning curve, and necessitate more manual configuration.
- Few users report occasional inconsistencies in build quality or component level compared to other brands.
- Needs more active management and familiarity with underlying hardware and software for optimal results.
How AI is Reshaping Server Monitoring to Build Smarter, More Reliable Systems in 2026 and Beyond?
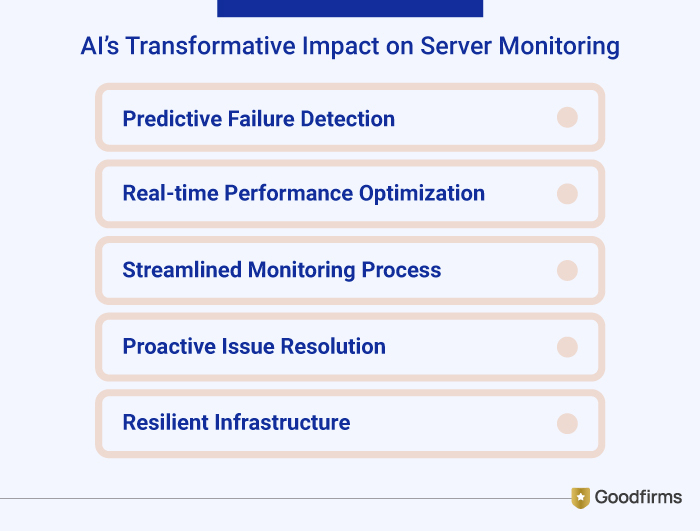
As organizations are progressing towards the predictive era, AI-powered server management is helping in delivering insights that can anticipate problems, automate fixes, streamline monitoring processes, real-time performance optimization, predict failure detection, proactive issues resolution, resilient infrastructure and assist IT leaders to shift from firefighting to forward planning for uninterrupted business continuity. Incidentally, 60% of organizations are already using artificial intelligence (AI) in their IT infrastructure and 30% are considering implementing AI.
Artificial intelligence for IT operations (AIOps) are already helping maintain IT infrastructure, automating various operations using ML and NLP and other advanced AI technologies, providing real-time insights, improving business service delivery and reducing costs.
AIOps are self-healing systems, as it has potential to assist organizations achieve excellence in monitoring, security and compliance, offering deeper insights, advanced automation, reducing risks, lower costs and helping make and faster decisions.
AI and IoT can come together to reduce downtime by 50%, reduce breakdowns by 70% and reduce overall maintenance cost by 25%.
The implementation of AIOps can reduce system downtime and reduce MTTR by more than half. For example, IBM Watson AIOps can detect up to 95% of anomalies before they lead to critical failures.
This shows that AIOps technologies are gradually becoming an integral part of modern IT infrastructure for automated observability and failover technologies. Over time in 2026 and beyond, AI technology will create a hype for uninterrupted business continuity and demand for smarter server management will only increase for better performance, lower costs, stronger security and stay ahead in the digital race.
Top Server Management Tools for Better Server Management:
Server management tools are software solutions that help businesses to automate, and simplify the management of servers including hardware, software and the server environment. The server tools also assist in monitoring performance, server activity, detect troubleshoot problems, automate server provisioning, patching and backup. At Goodfirms, businesses can select the reliable and verified server management tools for better server management depending on the business needs and preferences. Site24x7, ManageEngine OpManager, V2 Cloud, Atera, Lansweeper, Kaseya VSA, Splunk, LETSCMS MLM, New Relic, Datadog are a few top server management tools.
What to Consider When Choosing a Server?
- Purpose - As per the business performance requirements, traffic, and workloads.
- Performance - Applications, memory,
- Security & Scalability - Encryption, user-authentication, and physical security.
Conclusion:
With the growing role of automation, edge computing and sustainability, it is an essential step for every business to build a strong foundation for resilient, efficient and secure business operations, as the future of servers looks more dynamic than ever. The bottom line is to avoid downtime, security breaches and server performance inefficiencies. By embracing the best server products, and the best server management tools, businesses of any type and size can avoid disruption and have an uninterrupted business continuity. Organizations can opt for AI-powered server management tools to proactively evaluate server setups, and optimize resources to ensure the infrastructure remains robust, secure and scalable.








